Abstract
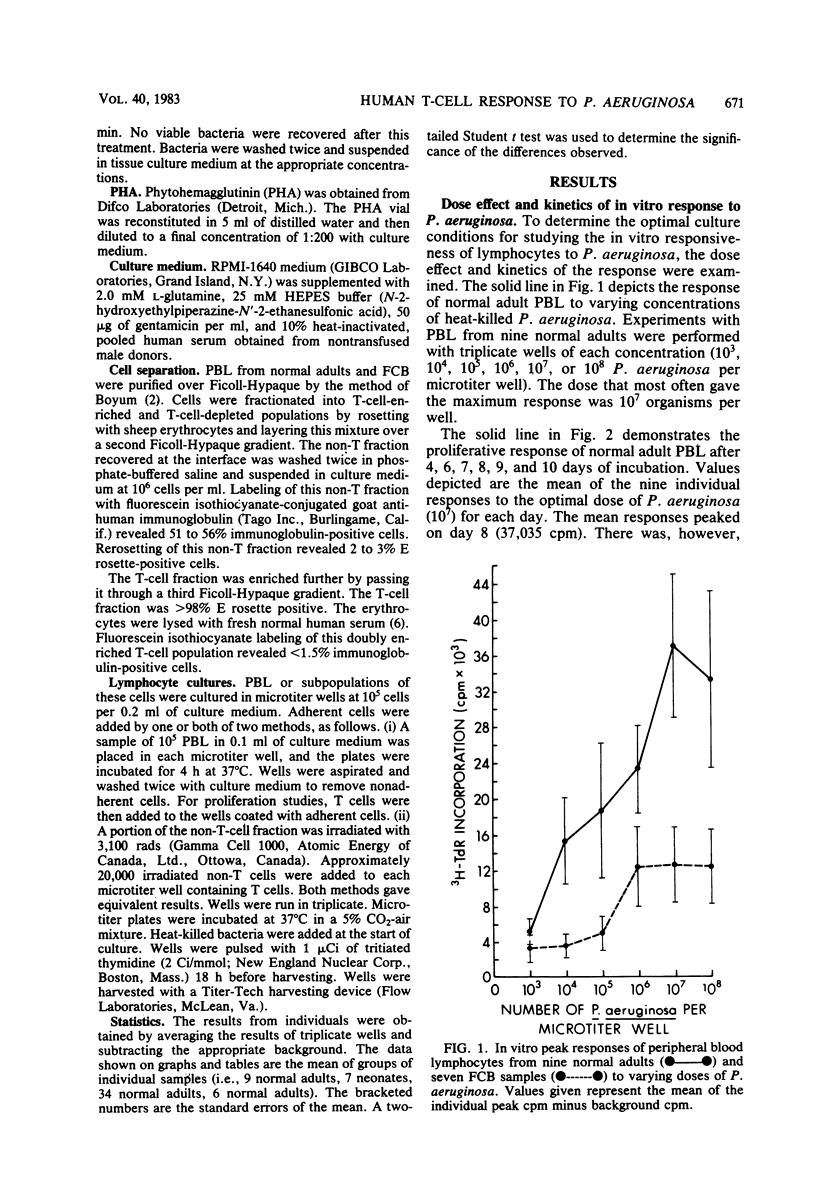
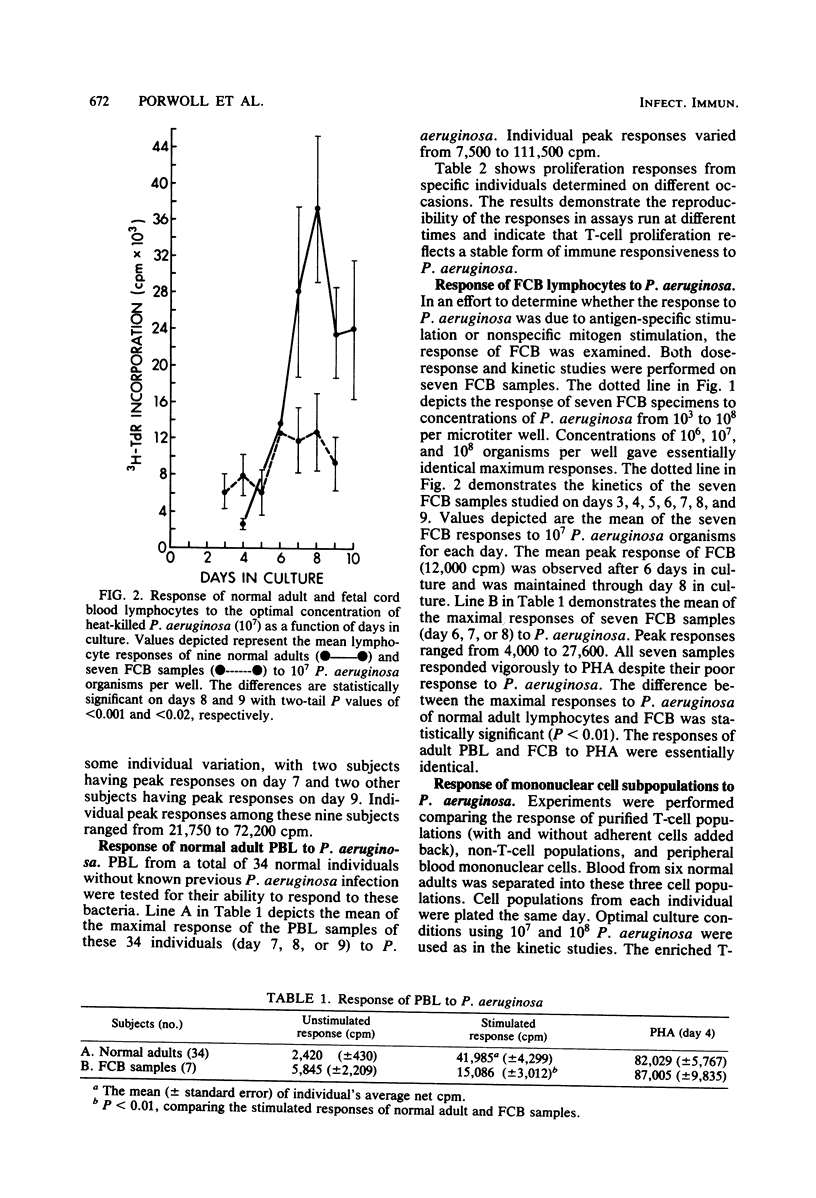
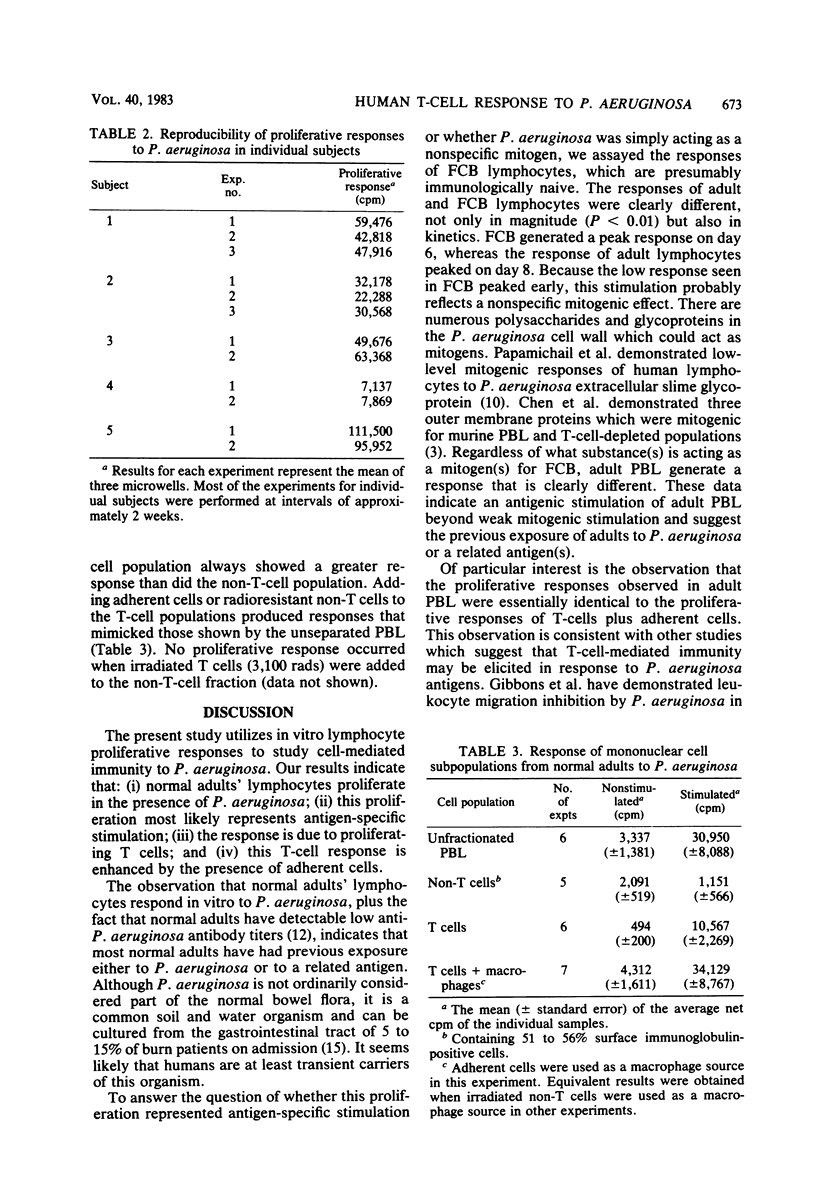
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative bacillus that is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in immunosuppressed patients, burn patients, and patients with cystic fibrosis. Although immunity to these bacteria has been associated with serum antibody, more recent evidence suggests that T-cell-mediated immunity may also be important. To evaluate human T-cell responsiveness to these bacteria, the optimal conditions were determined for in vitro proliferation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes to Fisher-Devlin immunotype 1 P. aeruginosa. The proliferative response of normal adult peripheral blood lymphocytes to heat-killed P. aeruginosa was studied in 34 subjects (range, 7,600 to 111,500 net cpm). Analysis of cell subpopulations indicated that T-lymphocytes are the major proliferating cells and that this response is enhanced by the presence of adherent cells. Data from fetal cord lymphocyte responses suggest that the proliferation seen in normal adult lymphocytes is induced by antigenic and not mitogenic stimulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTEN K. F., COHN Z. A. Contribution of serum and cellular factors in host defense reactions. I. Serumfactors in host resistanc. N Engl J Med. 1963 Apr 25;268:933–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196304252681707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Hancock R. E., Mishell R. I. Mitogenic effects of purified outer membrane proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):178–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.178-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz E., Mosovich L. L., Neter E. Serogroups of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the immune response of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):269–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: immune status in patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):628–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.628-635.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebel H. M., Radaj P. A., Holmes D., Schwartz B. D., Rodey G. E. Functional characteristics of TG and TnonG cells in a three party MLR. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):118–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons A., Allan J. D., Holzel A., McFarlane H. Cell-mediated immunity in patients with cystic fibrosis. Br Med J. 1976 Jan 17;1(6002):120–122. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6002.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munster A. M., Winchurch R. A., Birmingham W. J., Keeling P. Longitudinal assay of lymphocyte responsiveness in patients with major burns. Ann Surg. 1980 Dec;192(6):772–775. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198012000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Dimitracopoulos G., Tsokos G., Papavassiliou J. A human lymphocyte mitogen extracted from the extracellular slime layer of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):686–688. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Markham R. B. Induction in mice of cell-mediated immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa by high molecular weight polysaccharide and vinblastine. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2121–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Safety and immunogenicity of high molecular weight polysaccharide vaccine from immunotype 1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):303–308. doi: 10.1172/JCI110453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Pulmonary host defenses in rabbits after immunization with Pseudomonas antigens: the interaction of bacteria, antibodies, macrophages, and lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S134–S142. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter R. A., Walker K. A., Williams V. R., Horgan G. M., Parker M. T., Asheshov E. H., Bullimore J. F. Faecal carriage of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospital patients. Possible spread from patient to patient. Lancet. 1966 Dec 17;2(7477):1331–1334. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Chase P. A., Polmar S. H. Changes in lymphocyte reactivity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospitalized patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):37–41. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Chase P., Polmar S. H. Defective cellular immunity to gram-negative bacteria in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):398–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.398-402.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Polmar S. H. Cellular immunity to bacteria: impairment of in vitro lymphocyte responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.735-740.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Polmar S. H. Lymphocyte responsiveness to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: Relationship to status of pulmonary disease in sibling pairs. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



