Abstract
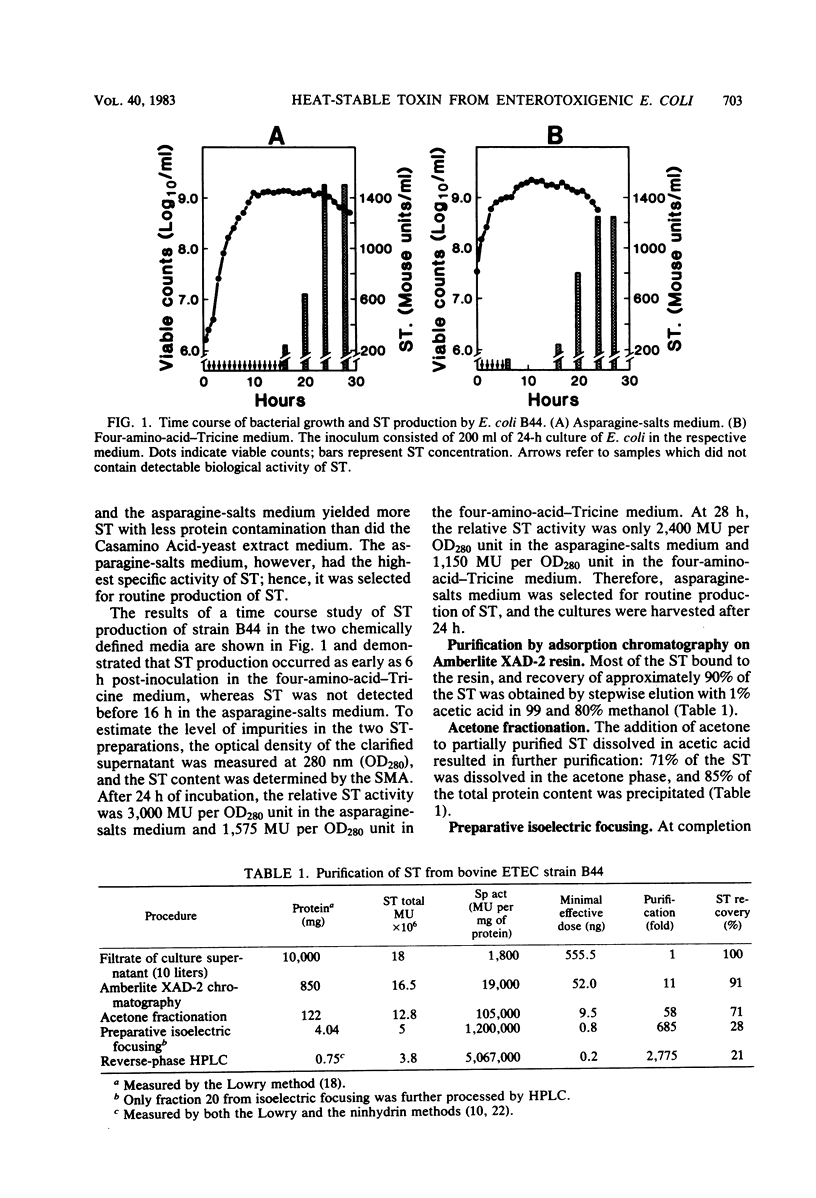
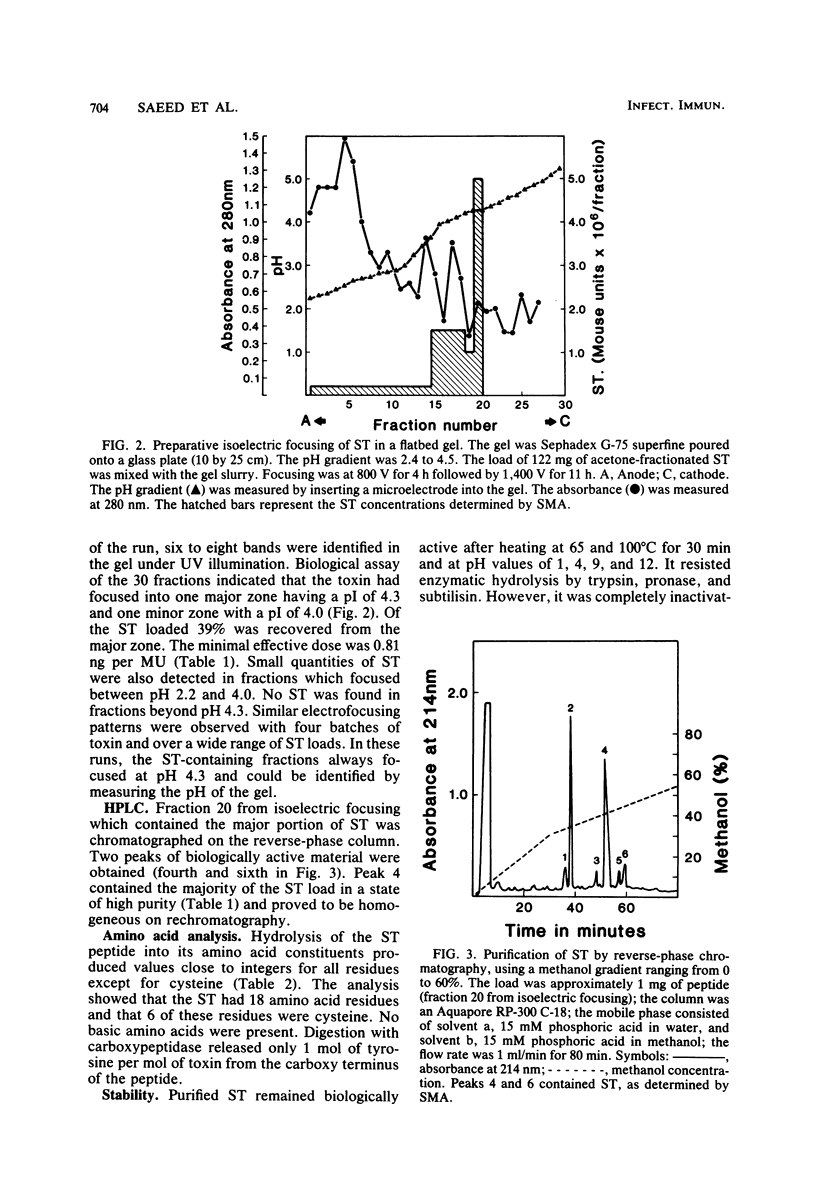
Heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) from Escherichia coli pathogenic for cattle was mass produced in a chemically defined medium. The toxin was concentrated and purified by sequentially applying batch adsorption chromatography on Amberlite XAD-2 resin, acetone fractionation, and preparative isoelectric focusing in a flatbed granulated gel. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography was used to purify the toxin further and to eliminate contaminating ampholytes. The toxin was purified more than 2,000-fold and had a minimal effective dose of less than 0.5 ng. It was biologically active after heating to 100 degrees C for 30 min and was not hydrolyzed by trypsin, pronase, and subtilisin, but it was inactivated by treatment with 0.1 M 2-mercaptoethanol or 4 X 10(-5) M dithiothreitol, suggesting that disulfide bonds are essential for retaining its biological activity. The amino acid analysis revealed 18 amino acid residues per molecule, which is in agreement with the composition of ST from a human strain of enterotoxigenic E. coli. The amino acid composition of our ST matched the published coding sequence of the last 18 codons of Tn1618, a transposon isolated from the bovine enterotoxigenic E. coli strain B41 and shown to be present also in some strains of porcine enterotoxigenic E. coli. These findings further support the existence of a form of ST common to bovine, porcine, and human strains of enterotoxigenic E. coli.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta-Martinez F., Gyles C. L., Butler D. G. Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin in feces and intestines of calves with diarrhea. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jul;41(7):1143–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Nutrition and enterotoxin synthesis by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli: defined medium for production of heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Heat-stable enterotoxins from Escherichia coli P16. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1038–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1038-1040.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Giannella R. A. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7744–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Clements J. D., Robertson D. C., Finkelstein R. A. Subunit number and arrangement in Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):677–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.677-682.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W., Schneider R. A. Distribution and virulence of Escherichia coli in the small intestines of calves with and without diarrhea. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Nov;39(11):1750–1755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Scoot A., Forsyth G. W., McKenzie S. L., Worthington R. W. Evidence for two heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):965–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.965-966.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological relationship of different preparations of coliform enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):771–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.771-778.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Hirth P., DeWilde M., Harford N., Lecocq J. P. Cell-free synthesis of enterotoxin of E. coli from a cloned gene. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):473–474. doi: 10.1038/284473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Nagy B., Isaacson R. E., Orskov I. Occurrence of K99 antigen on Escherichia coli isolated from pigs and colonization of pig ileum by K99+ enterotoxigenic E. coli from calves and pigs. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):614–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.614-620.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Skartvedt S. M. Etiologic diagnosis of diarrheal disease of calves: frequency and methods for detecting enterotoxin and K99 antigen production by Escherichia cola. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Sep;37(9):1025–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. Amino acid analysis: aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent for the ninhydrin reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6281–6283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radola B. J. Isoelectric focusing in layers of granulated gels. II. Preparative isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;386(1):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Kavanaugh W. M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S., Konigsberg W. H., Schafer D. E. Sequence homologies between A subunits of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):50–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Argenzio R. A. Comparison of enterotoxic activities of heat-stable enterotoxins from class 1 and class 2 Escherichia coli of swine origin. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.245-251.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


