Abstract
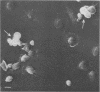
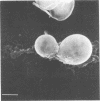
Cell-mediated immunity plays the dominant role in the immune response of mice to Blastomyces dermatitidis infections. Since macrophages play an important role in cell-mediated immunity, the interactions between sensitized murine peritoneal macrophages and the yeast phase of B. dermatitidis were investigated. Scanning electron microscopy showed that the sensitized macrophages readily phagocytized B. dermatitidis yeast cells. In addition, there appeared to be activation of metabolic pathways within the sensitized macrophages, as indicated by increased chemiluminescence activity during phagocytosis. Sensitized macrophages were significantly better at controlling intracellular proliferation of the yeast cells when compared to nonsensitized cells. This was determined by disruption of macrophages and plating for viable yeasts. Scanning electron microscope observations offered further substantiation. Experiments with Candida albicans indicated that B. dermatitidis non-specifically activated macrophages. At 2 h postphagocytosis, 30% fewer C. albicans in B. dermatitidis-activated macrophages were able to form germ tubes. These studies demonstrated the multiple potential of activated macrophages with regard to their functional activity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Morozumi P. A., Philpott D. E., Stevens D. A. Virulence of fungi: correlation of virulence of Blastomyces dermatitidis in vivo with escape from macrophage inhibition of replication in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):864–871. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.864-871.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Pagram F. Macrophage activation during experimental murine brucellosis: a basis for chronic infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):197–205. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.197-205.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Mills L. R., Best G. K., Denton J. F. Histologic reactions to cell walls of an avirulent and a virulent strain of Blastomyces dermatitidis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):179–186. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozad G. C., Chang C. T. Cell-mediated immunoprotection in blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):398–403. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.398-403.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R. E., Lehrer R. I. Fungicidal properties of a chymotrypsin-like cationic protein from human neutrophils: adsorption to Candida parapsilosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):382–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.382-388.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. H. Further studies on the inhibition of Histoplasma capsulatum within macrophages from immunized animals. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):577–581. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.577-581.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D., AUZINS I. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. I. THE CARRIER STATE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:215–228. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. H., Ottenson E. A., Smith T. K., Wells S. A., Burdick J. F. Reconstitution of defective cellular immunity with foetal thymus and dialysable transfer factor. Long-term studies in a patient with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):414–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiti P. K., Kumar R., Mohapatra L. N. Candidacidal activity of mouse macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):477–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.477-482.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Halpern J. W., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility differences of inbred strains of mice to blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.160-168.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabarra B., Cavelier J. F., Dry M., Dimitriu A. Scanning electron microscopic studies of activated macrophages in the mouse. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):489–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Mills E. L., Simmons R. L., Quie P. G. Chemiluminescence response of phagocytizing human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):129–134. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.129-134.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo-Moreno A., Schneidau J. D., Jr Nature of the skin-reactive principle in culture filtrates prepared from Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1741–1748. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1741-1748.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scillian J. J., Cozad G. C., Spencer H. D. Passive transfer of delayed hypersensitivity to Blastomyces dermatitidis between mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):705–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.705-711.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer H. D., Cozad G. C. Role of delayed hypersensitivity in blastomycosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):329–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.329-334.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 28;290(13):717–723. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403282901306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. Allergenicity of mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic acid preparations in mice and guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):134–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.134-139.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]