Abstract
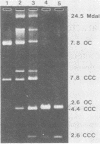
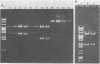
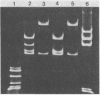
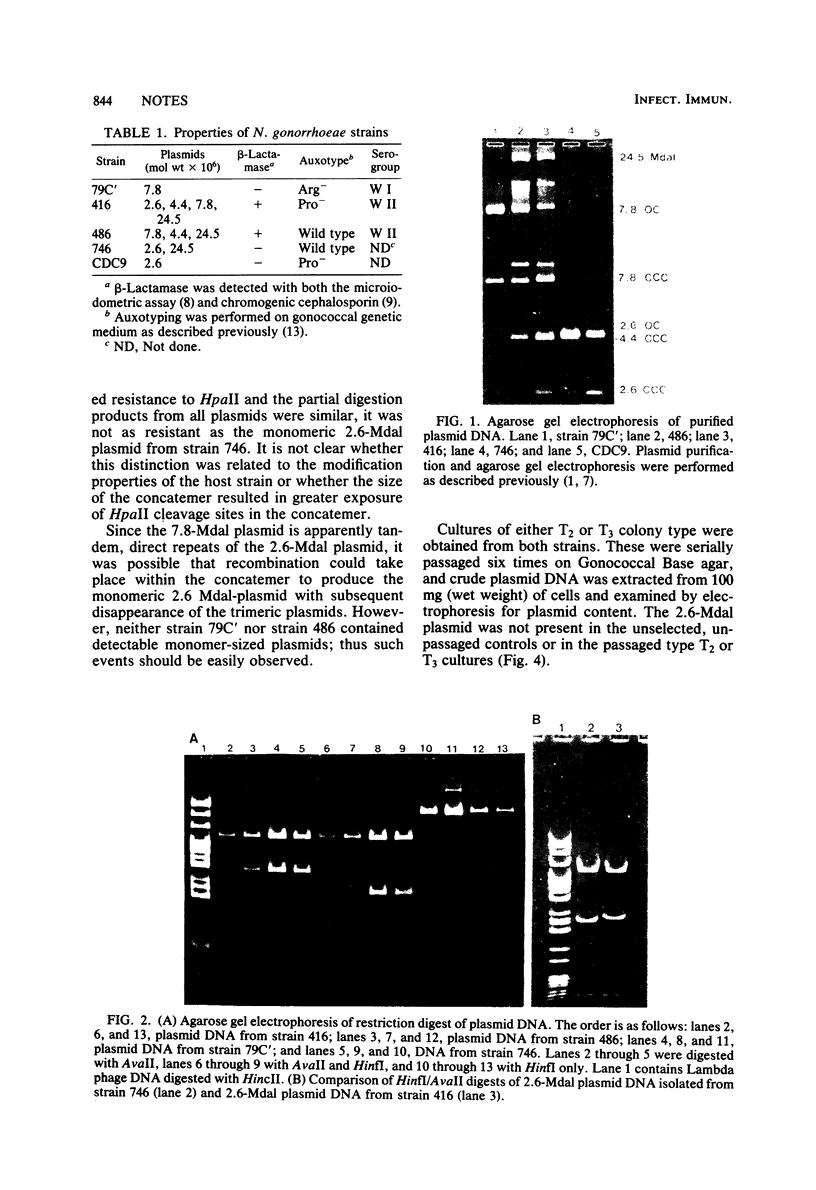
Three strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae carried novel plasmids of 7.8 megadaltons (mdal) molecular mass in addition to plasmids previously observed in this organism. The presence of the 7.8-mdal plasmids was not accompanied by any distinguishable phenotype in the strain possessing them. Analysis of plasmid DNA with restriction endonucleases showed that these plasmids were composed of three directly repeated copies of a 2.6-mdal cryptic plasmid frequently found in N. gonorrhoeae. In addition, the 7.8-mdal plasmids exhibited characteristics common to the 2.6-mdal plasmid, structural lability and sites resistant to cleavage with HpaII. The concatemeric forms of the cryptic plasmid appear to be stable in these strains and do not undergo internal recombination to produce the 2.6-mdal monomer, nor were higher concatemers detected.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Normark S. A relationship between plasmid structure, structural lability, and sensitivity to site-specific endonucleases in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):251–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00267436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. R., Pauzé M. Appearance in Canada of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with a 3.2 megadalton penicillinase-producing plasmid and a 24.5 megadalton transfer plasmid. Lancet. 1981 Sep 26;2(8248):700–700. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. R., Pauzé M. Relationship between plasmid content and auxotype in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):625–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.625-628.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. S., Foster G. C. Electrophoretic comparison of endonuclease-digested plasmids from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1297–1304. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1297-1304.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Holmes K. K., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.712-717.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of two beta-lactamase-specifying plasmids isolated from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):557–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.557-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Piot P., Falkow S. The ecology of gonococcal plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):491–494. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom E. G., Knapp J. S., Buchanan T. B. Serology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: W-antigen serogrouping by coagglutination and protein I serotyping by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay both detect protein I antigens. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):229–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.229-239.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Ploscowe V. B., Weiss J. A., Young F. E. Rapid method for auxotyping multiple strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.244-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Blackman E., Biswas G., Sparling P. F. Conjugative plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.278-286.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Klingeren B., Dessens-Kroon M., van Wijngaarden L. J. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the Netherlands: epidemiology and genetic and molecular characterization of their plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):789–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]