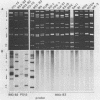
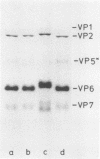
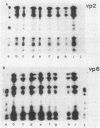
Abstract
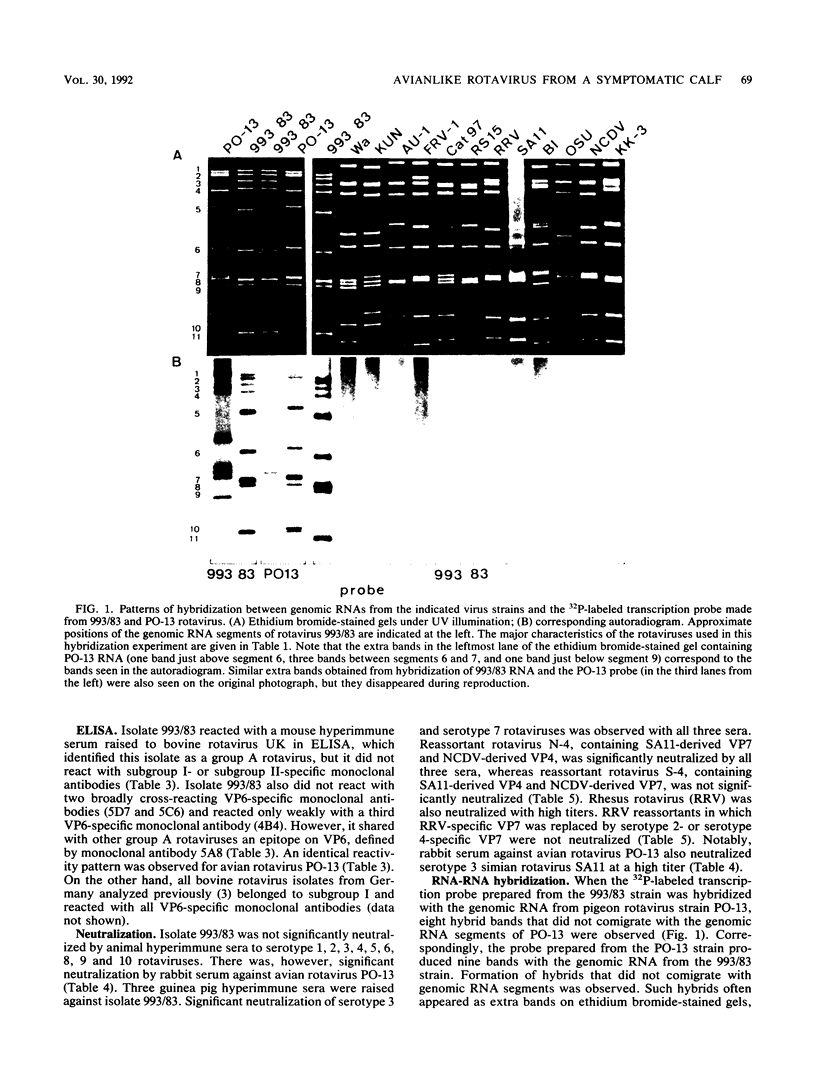
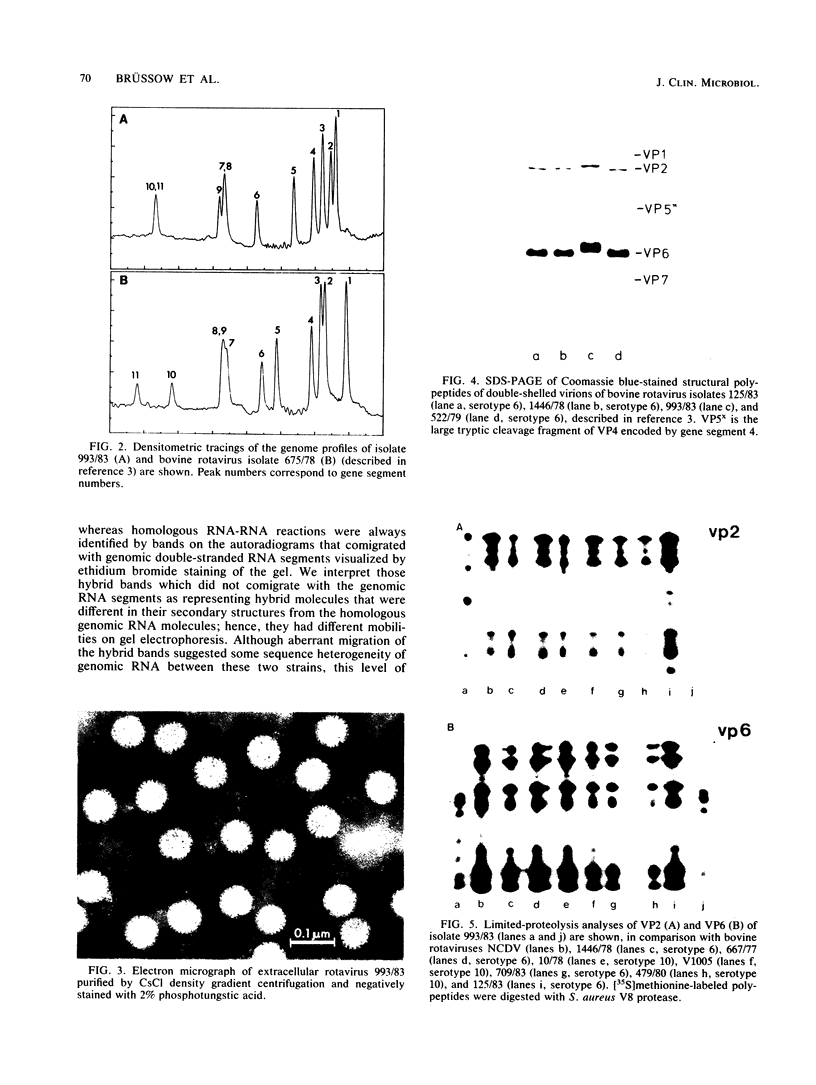
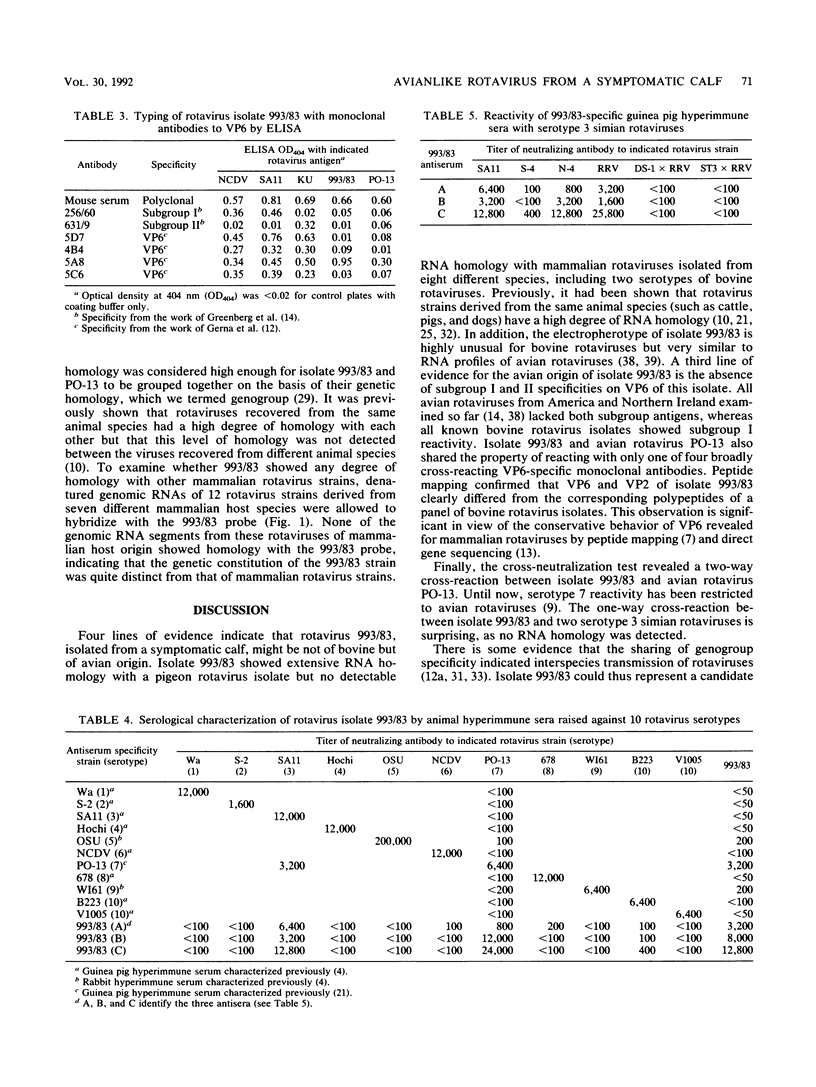
An atypical group A rotavirus (993/83) was isolated from a 3-day-old German calf with diarrhea. It differed from 35 conventional German bovine rotavirus isolates analyzed previously with respect to subgroup (strain 993/83 was non-subgroup I and non-subgroup II), serotype (strain 993/83 showed a two-way cross-reaction with serotype 7 and a one-way cross-reaction with serotype 3), and electropherotype (strain 993/83 showed comigrating gene segments 10 and 11). Isolate 993/83 reacted with only one of four monoclonal antibodies that recognized a common VP6 epitope(s). In addition, VP6 and VP2 of isolate 993/83 showed one-dimensional peptide maps that differed substantially from the peptide maps of VP6 and VP2 from all bovine rotavirus isolates. By RNA-RNA hybridization, the 993/83 probe failed to react with a panel of mammalian rotavirus strains, including bovine rotaviruses. It hybridized, however, to genomic RNA of an avian rotavirus strain. Isolate 993/83 could thus represent a candidate for a natural interspecies transmission of rotavirus between different classes of vertebrates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann P. A., Hess R. G. Routine isolation and cultivation of bovine rotaviruses in cell culture. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2149–2150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch C. J., Heath R. L., Marshall J. A., Liu S., Gust I. D. Isolation of feline rotaviruses and their relationship to human and simian isolates by electropherotype and serotype. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2731–2735. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüssow H., Eichhorn W., Rohwedder A., Snodgrass D., Sidoti J. Cattle develop neutralizing antibodies to rotavirus serotypes which could not be isolated from faeces of symptomatic calves. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1559–1567. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüssow H., Snodgrass D., Fitzgerald T., Eichhorn W., Gerhards R., Bruttin A. Antigenic and biochemical characterization of bovine rotavirus V1005, a new member of rotavirus serotype 10. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2625–2630. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyall-Smith M. L., Holmes I. H. Comparisons of rotavirus polypeptides by limited proteolysis: close similarity of certain polypeptides of different strains. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):720–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.720-728.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Cohen J. Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):410–449. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.410-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Hoshino Y., Boeggeman E., Purcell R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic relatedness among animal rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1986;87(3-4):273–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01315305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Battaglia M., Milenesi G., Passarani N., Percivalle E., Cattaneo E. Serotyping of cell culture-adapted subgroup 2 human rotavirus strains by neutralization. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):722–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.722-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Di Matteo A., Parea M., Torsellini M., Battaglia M. Rapid detection of human rotavirus strains in stools by single-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol Methods. 1989 Apr-May;24(1-2):43–56. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Parea M., Arista S., Miranda P., Brüssow H., Hoshino Y., Flores J. Isolation and characterization of two distinct human rotavirus strains with G6 specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.9-16.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Nishikawa K., Maloy W. L., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Comparative sequence analysis of the genomic segment 6 of four rotaviruses each with a different subgroup specificity. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1659–1669. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa H., Wada R., Hirasawa K., Akiyama Y., Oda T. Isolation of equine rotavirus in cell cultures from foals with diarrhea. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Feb;46(1):1–9. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Flores J., Hoshino Y., Glass R. I., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Chanock R. M. Rotavirus: the major etiologic agent of severe infantile diarrhea may be controllable by a "Jennerian" approach to vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):815–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsuzawa T., Konno T., Suzuki H., Kapikian A. Z., Ebina T., Ishida N. Isolation of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):727–730. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.727-730.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Nakagomi O., Offit P. A. Presence of three P types (VP4 serotypes) and two G types (VP7 serotypes) among bovine rotavirus strains. Arch Virol. 1990;115(3-4):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF01310530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Wyatt R. G., Sharpee R. L., Sereno M. M., Kalica A. R., Kapikian A. Z., Twiehaus M. J. Diarrhea in gnotobiotic calves caused by the reovirus-like agent of human infantile gastroenteritis. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):471–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.471-474.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Greenberg H. B., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M. Reassortant rotaviruses as potential live rotavirus vaccine candidates. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.949-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Single gene substitution rotavirus reassortants containing the major neutralization protein (VP7) of human rotavirus serotype 4. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):822–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.822-826.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Valdesuso J., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Analysis by RNA-RNA hybridization assay of intertypic rotaviruses suggests that gene reassortment occurs in vivo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):295–300. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.295-300.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamoto N., Oki K., Tomita M., Kinjo T., Suzuki Y. Isolation and characterization of rotavirus from feral pigeon in mammalian cell cultures. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Jun;100(3):481–492. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki M., Sameshima R., Ata M., Minami K., Okabayashi K., Harasawa R. Characterization of canine rotavirus RS 15 strain and comparison with other rotaviruses. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Aug;47(4):531–538. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Nishioka N., Hashiguchi Y., Kuniyasu C. Serotypes of bovine rotaviruses distinguished by serum neutralization. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):851–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.851-855.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N. Identification of rotavirus genogroups by RNA-RNA hybridization. Mol Cell Probes. 1989 Sep;3(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(89)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1159–1164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1159-1164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Ohshima A., Aboudy Y., Shif I., Mochizuki M., Nakagomi T., Gotlieb-Stematsky T. Molecular identification by RNA-RNA hybridization of a human rotavirus that is closely related to rotaviruses of feline and canine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1198-1203.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Matsuda Y., Ohshima A., Mochizuki M., Nakagomi O. Characterization of a canine rotavirus strain by neutralization and molecular hybridization assays. Arch Virol. 1989;106(1-2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01311046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Nakagomi O. RNA-RNA hybridization identifies a human rotavirus that is genetically related to feline rotavirus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1431–1434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1431-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Pothier P., Cohen J., Lourenco M. H., Thompson R., Guimbaud P., Chenon A., Dauvergne M., Bricout F. Survey of human rotavirus propagation as studied by electrophoresis of genomic RNA. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):688–693. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F., Blavat G., Greenberg H. B. Reassortant rotaviruses containing structural proteins vp3 and vp7 from different parents induce antibodies protective against each parental serotype. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.491-496.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Fitzgerald T., Campbell I., Scott F. M., Browning G. F., Miller D. L., Herring A. J., Greenberg H. B. Rotavirus serotypes 6 and 10 predominate in cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.504-507.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M. Nonreactivity of American avian group A rotaviruses with subgroup-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2846–2848. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2846-2848.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., McNulty M. S., Allan G. M. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of avian rotavirus RNA. Arch Virol. 1980;63(2):87–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01320765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James H. D., Jr, Pittman A. L., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Direct isolation in cell culture of human rotaviruses and their characterization into four serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.310-317.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Sly D. L., London W. T., Palmer A. E., Kalica A. R., Van Kirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Induction of diarrhea in colostrum-deprived newborn rhesus monkeys with the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Arch Virol. 1976;50(1-2):17–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01317997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]