Abstract
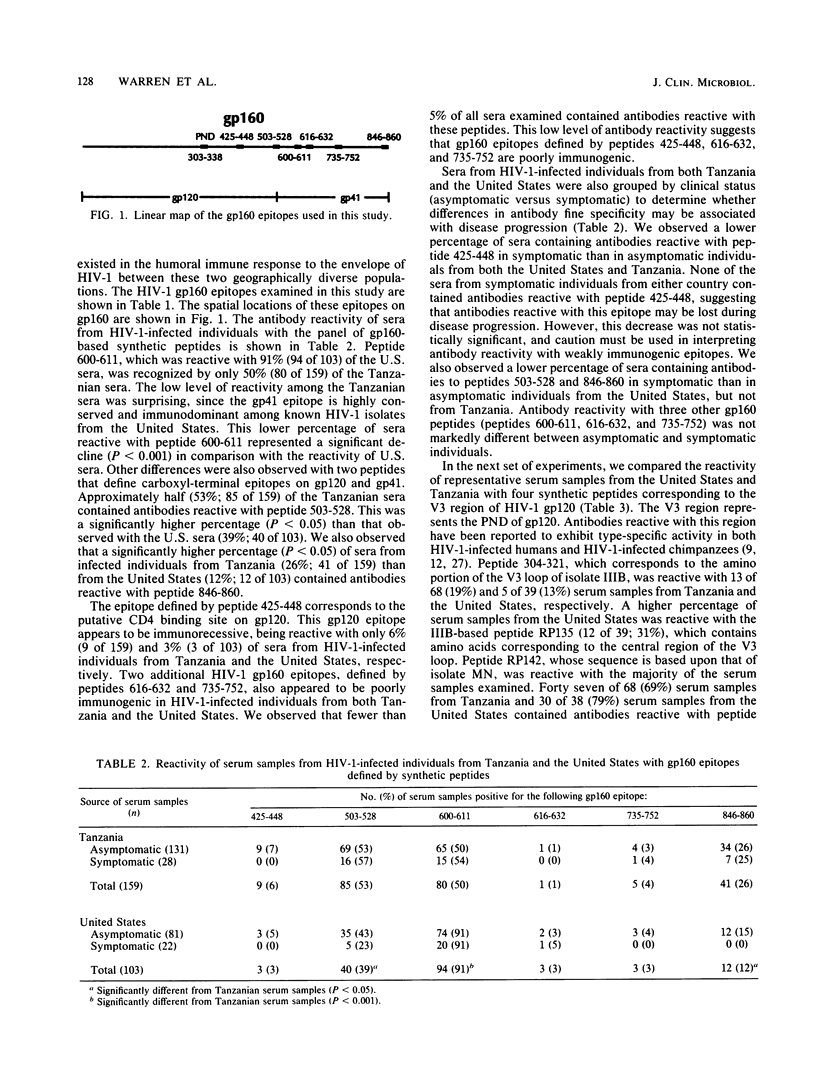
In this study, we compared sera from 159 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected individuals from Tanzania and 103 infected individuals from the United States for antibodies reactive with 10 HIV-1 gp160 epitopes defined by synthetic peptides. Our data indicate that the anti-gp160 antibody fine specificity differs between infected individuals from these two geographically diverse populations. For example, 50% of the Tanzanian sera contained antibodies reactive with an immunodominant HIV-1 gp41 epitope defined by peptide 600-611, whereas 91% of the sera from the United States were reactive. Differences in serologic reactivity between HIV-1-infected individuals from Tanzania and the United States were also observed with gp160 epitopes defined by peptides 503-528 and 846-860. Included among the peptides examined were four which corresponded to the V3 region of gp120. The majority of sera from either country contained antibodies reactive with peptide RP142, whose V3 sequence is based upon that of HIV-1 isolate MN. Further characterization of serologic reactivity suggested that sera from Tanzania were more likely to neutralize HIV-1 isolate IIIB or MN in vitro than were sera from the United States. These differences in antibody fine specificity between HIV-1-infected individuals from Tanzania and the United States suggest that regional isolates of HIV-1 may exist.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Update: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome--Europe. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1986 Jan 24;35(3):35-8, 43-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanh T. C., Dreesman G. R., Kanda P., Linette G. P., Sparrow J. T., Ho D. D., Kennedy R. C. Induction of anti-HIV neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3065–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. W., Morgan W. M., Hardy A. M., Jaffe H. W., Darrow W. W., Dowdle W. R. The epidemiology of AIDS: current status and future prospects. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1352–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.2994217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. W. The epidemiology and prevention of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):657–662. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, McCormick J. B., Mitchell S., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Synthetic peptide immunoassay distinguishes HIV type 1 and HIV type 2 infections. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2888192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Fine mapping of an immunodominant domain in the transmembrane glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2639–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2639-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Schwimmbeck P. L., Nelson J. A., Truax A. B., Oldstone M. B. Diagnosis of AIDS by using a 12-amino acid peptide representing an immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):261–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Henkel R. D., Pauletti D., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Essex M., Dreesman G. R. Antiserum to a synthetic peptide recognizes the HTLV-III envelope glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1556–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.3006246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- N'Galy B., Ryder R. W. Epidemiology of HIV infection in Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(6):551–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Taylor P., Rubinstein P., Stevens C. E. Search for epitope-specific antibody responses to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) envelope glycoproteins signifying resistance to disease development. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Oct;6(10):1183–1192. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norley S. G., Kurth R. Neutralizing antibodies and antigens in AIDS. Infection. 1991;19 (Suppl 2):S83–S88. doi: 10.1007/BF01644473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Närvänen A., Korkolainen M., Suni J., Korpela J., Kontio S., Partanen P., Vaheri A., Huhtala M. L. Synthetic env gp41 peptide as a sensitive and specific diagnostic reagent in different stages of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Med Virol. 1988 Oct;26(2):111–118. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C., Nielsen C. M., Vestergaard B. F., Gerstoft J., Krogsgaard K., Nielsen J. O. Temporal relation of antigenaemia and loss of antibodies to core antigens to development of clinical disease in HIV infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Sep 5;295(6598):567–569. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6598.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Laga M., Ryder R., Perriëns J., Temmerman M., Heyward W., Curran J. W. The global epidemiology of HIV infection: continuity, heterogeneity, and change. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(4):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Plummer F. A., Mhalu F. S., Lamboray J. L., Chin J., Mann J. M. AIDS: an international perspective. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):573–579. doi: 10.1126/science.3277271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Profy A. T., Salinas P. A., Eckler L. I., Dunlop N. M., Nara P. L., Putney S. D. Epitopes recognized by the neutralizing antibodies of an HIV-1-infected individual. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4641–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. A., Kostek B. M., Schleif W. A., Lewis J. A., Emini E. A. A microtiter cell-culture assay for the determination of anti-human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody activity. J Virol Methods. 1988 Jul;20(3):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Moschese V., Broliden P. A., Fundaró C., Quinti I., Plebani A., Giaquinto C., Tovo P. A., Ljunggren K., Rosen J. Presence of maternal antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus 1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 epitopes correlates with the uninfected status of children born to seropositive mothers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8055–8058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmutzhard E., Fuchs D., Hengster P., Hausen A., Hofbauer J., Pohl P., Rainer J., Reibnegger G., Tibyampansha D., Werner E. R. Retroviral infections (HIV-1, HIV-2, and HTLV-I) in rural northwestern Tanzania. Clinical findings, epidemiology, and association with infections common in Africa. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Aug;130(2):309–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Jr, Silver S., Profy A. T., Putney S. D., Langlois A., Weinhold K., Robinson J. E. Human monoclonal antibody that recognizes the V3 region of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 and neutralizes the human T-lymphotropic virus type IIIMN strain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8597–8601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Langlois A. J., McDanal C. B., McDougal J. S., Bolognesi D. P., Matthews T. J. Neutralizing antibodies to an immunodominant envelope sequence do not prevent gp120 binding to CD4. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4195–4200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4195-4200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. Q., Wolf H., Shuler K. R., Eichberg J. W., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Synthetic peptides define the fine specificity of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gp160 humoral immune response in HIV type 1-infected chimpanzees. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):486–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.486-492.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. Q., Wolf H., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Patterns of antibody reactivity to selected human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp160 epitopes infected individuals grouped according to CD4+ cell levels. J Clin Immunol. 1991 Jan;11(1):13–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00918790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. N., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Parker D., Roberts C., Duncan J., Weller I., Carne C., Tedder R. S., Pinching A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in two cohorts of homosexual men: neutralising sera and association of anti-gag antibody with prognosis. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


