Abstract
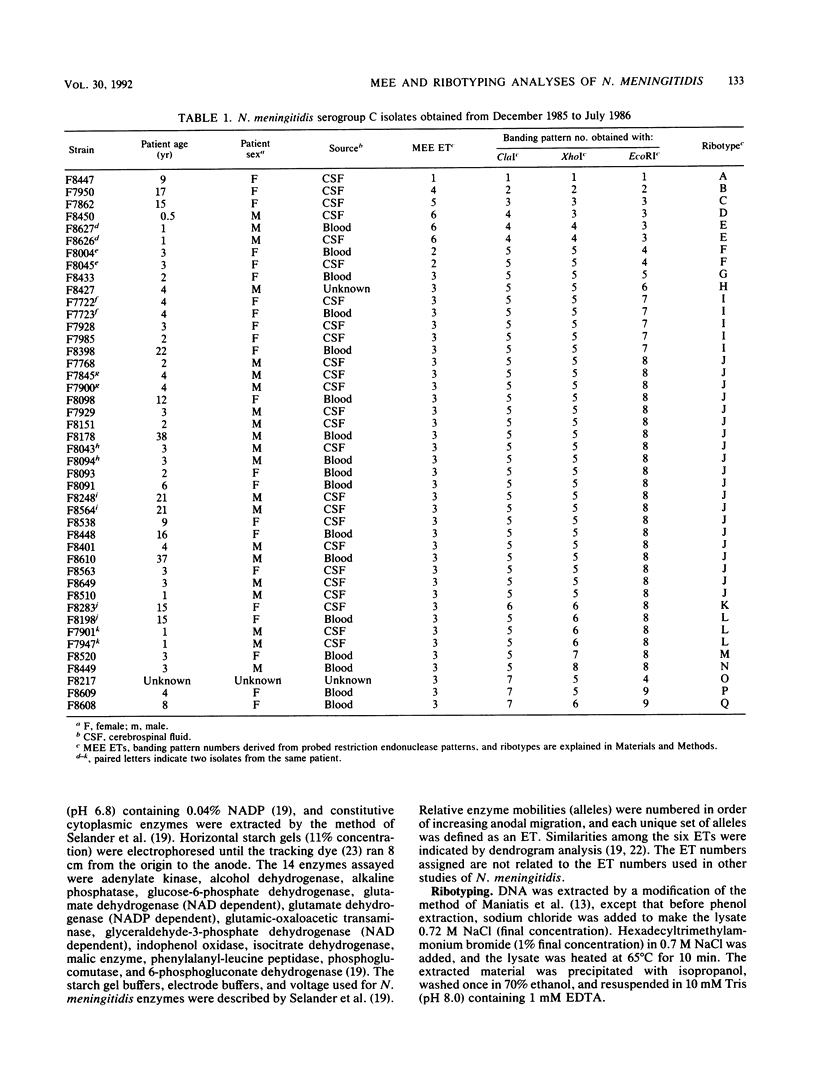
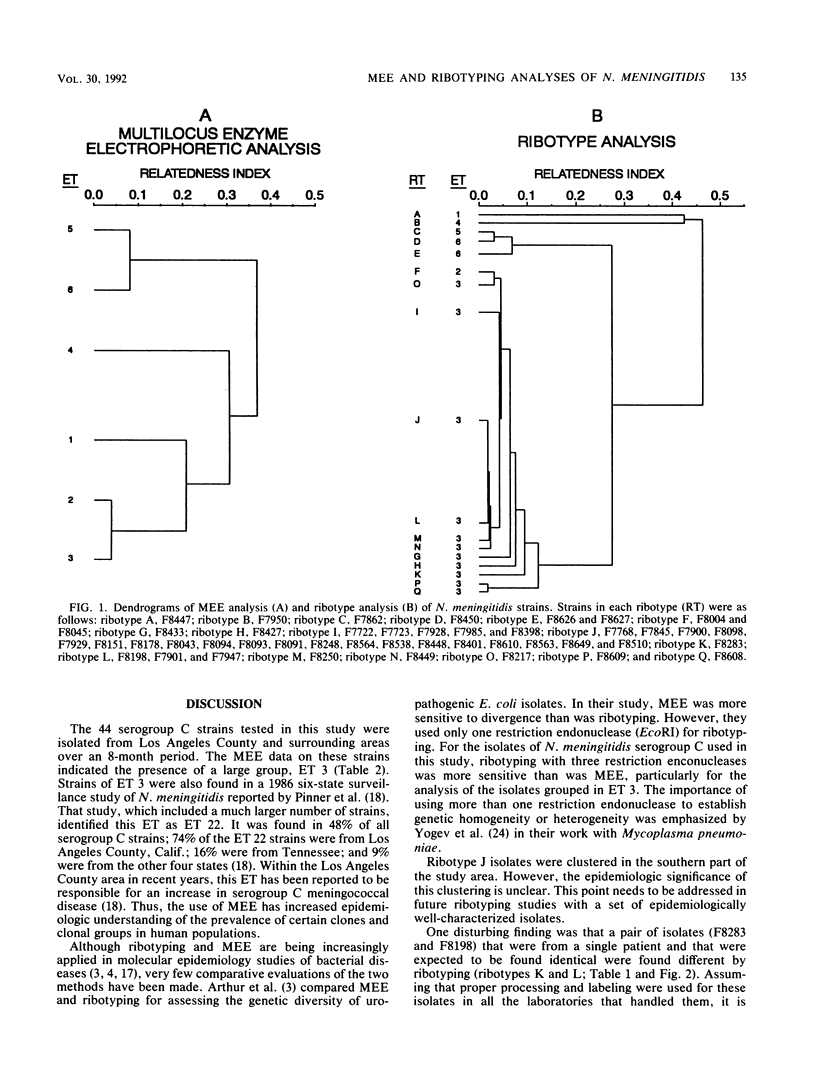
We compared multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE) and ribosomal DNA fingerprinting (ribotyping) for subtyping 44 strains of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C that were isolated in Los Angeles County, California, between December 1985 and July 1986. The isolates were divided into six enzyme types (ETs) by MEE, but 36 of the isolates were clustered in one ET, 3. The same isolates were divided into 17 ribotypes by use of restriction endonucleases ClaI, EcoRI, and XhoI. Twenty of the 36 ET 3 isolates were divided into 17 ribotypes by use of restriction endonucleases ClaI, EcoRI, and XhoI. Twenty of the 36 ET 3 isolates were grouped in a single ribotype, J. The rate of infection with ribotype J strains was higher in the southern part of the study area than in the northern part. Isolates from each of eight pairs (each isolate pair was cultured from the same patient from the same or different sites) were found identical by MEE, but ribotyping revealed a difference in one pair. In this study, ribotyping showed a greater discriminating capacity than MEE for subtyping N. meningitidis serogroup C, but the epidemiologic relevance of this increased sensitivity needs further assessment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altwegg M., Altwegg-Bissig R., Demarta A., Peduzzi R., Reeves M. W., Swaminathan B. Comparison of four typing methods for Aeromonas species. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1988 Jun;6(2):88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Arbeit R. D., Kim C., Beltran P., Crowe H., Steinbach S., Campanelli C., Wilson R. A., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms among uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates: pap-related sequences compared with rrn operons. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):471–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.471-479.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Bøvre K., Gaustad P., Bryn K., Holten E., Høiby E. A., Frøholm L. O. Multilocus genotypes determined by enzyme electrophoresis of Neisseria meningitidis isolated from patients with systemic disease and from healthy carriers. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Mar;132(3):641–652. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-3-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Frøholm L. O., Bøvre K., Holten E., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., Zollinger W. D., Selander R. K. Intercontinental spread of Neisseria meningitidis clones of the ET-5 complex. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(6):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00415492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Frøholm L. O., Bøvre K., Holten E., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., Zollinger W. D., Selander R. K. Intercontinental spread of a genetically distinctive complex of clones of Neisseria meningitidis causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E., Frøholm L. O., Zollinger W. D., Selander R. K. Genetic structure of Neisseria meningitidis populations in relation to serogroup, serotype, and outer membrane protein pattern. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2781–2792. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2781-2792.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zollinger W. D., Poolman J. T. Serotype antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and a proposed scheme for designation of serotypes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):504–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Harnish B. W. Inversions between ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7069–7072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irino K., Grimont F., Casin I., Grimont P. A. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius strains associated with Brazilian purpuric fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1535–1538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1535-1538.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. S., Reeves M. W., Schwartz B., Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Intercontinental spread of an epidemic group A Neisseria meningitidis strain. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):260–263. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olyhoek T., Crowe B. A., Achtman M. Clonal population structure of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A isolated from epidemics and pandemics between 1915 and 1983. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9(4):665–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Beck A., Dayal P. A., Dawson C. Detection of genomic variation in Providencia stuartii clinical isolates by analysis of DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms containing rRNA cistrons. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2161–2166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2161-2166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard-Pasquier N., Picard B., Heeralal S., Krishnamoorthy R., Goullet P. Correlation between ribosomal DNA polymorphism and electrophoretic enzyme polymorphism in Yersinia. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Aug;136(8):1655–1666. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-8-1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Measurement of DNA length by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Dec;100(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods T. C., McKinney R. M., Plikaytis B. D., Steigerwalt A. G., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J. Multilocus enzyme analysis of Legionella dumoffii. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):799–803. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.799-803.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogev D., Halachmi D., Kenny G. E., Razin S. Distinction of species and strains of mycoplasmas (mollicutes) by genomic DNA fingerprints with an rRNA gene probe. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1198–1201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1198-1201.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogev D., Levisohn S., Kleven S. H., Halachmi D., Razin S. Ribosomal RNA gene probes to detect intraspecies heterogeneity in Mycoplasma gallisepticum and M. synoviae. Avian Dis. 1988 Apr-Jun;32(2):220–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



