Abstract
Isolation of a Rochalimaea-like organism from a febrile patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus was confirmed. Analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences, together with polymerase chain reaction and restriction endonuclease length polymorphism analysis of a portion of the citrate synthase gene, demonstrated that the agent is closely related to members of the genus Rochalimaea and that the isolate is genotypically identical to the presumptive etiologic agent of bacillary angiomatosis. However, the same genotypic analyses readily differentiated the new isolate from isolates of other recognized Rochalimaea species as well as other genera of bacteria previously suggested as putative etiologic agents of bacillary angiomatosis and related syndromes. We propose that the novel species be referred to as Rochalimaea henselae sp. now.
Full text
PDF




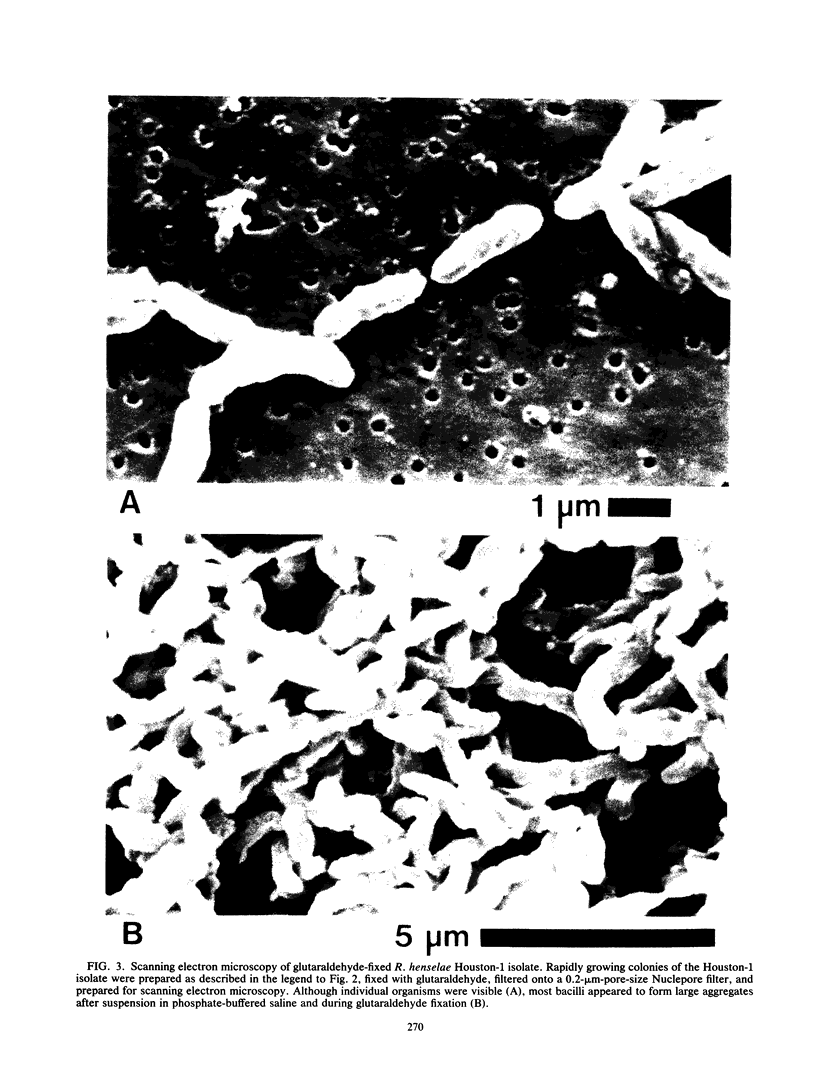




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angritt P., Tuur S. M., Macher A. M., Smith K. J., Park C. S., Hobin F. P., Myrie-Williams C. Epithelioid angiomatosis in HIV infection: neoplasm or cat-scratch disease? Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):996–996. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91813-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Walsh G. P. Conservation of genomic sequences among isolates of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4844–4851. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4844-4851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper C. A., Lombard C. M., Deresinski S. C., Tompkins L. S. Visceral bacillary epithelioid angiomatosis: possible manifestations of disseminated cat scratch disease in the immunocompromised host: a report of two cases. Am J Med. 1990 Aug;89(2):216–222. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90301-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoit P. E., Berger T. G., Egbert B. M., Yen T. S., Stoler M. H., Bonfiglio T. A., Strauchen J. A., English C. K., Wear D. J. Epithelioid haemangioma-like vascular proliferation in AIDS: manifestation of cat scratch disease bacillus infection? Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):960–963. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91779-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. Crohn's disease-isolated mycobacteria are identical to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as determined by DNA probes that distinguish between mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.796-801.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. P., Dorsch M., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J., Stackebrandt E. 16S rRNA sequences of Bartonella bacilliformis and cat scratch disease bacillus reveal phylogenetic relationships with the alpha-2 subgroup of the class Proteobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2144–2150. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2144-2150.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkocha L. A., Geaghan S. M., Yen T. S., Nishimura S. L., Chan S. P., Garcia-Kennedy R., Honda G., Stoloff A. C., Klein H. Z., Goldman R. L. Clinical and pathological features of bacillary peliosis hepatis in association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1581–1586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Spruill C. L., Plikaytis B. D. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1576–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1576-1589.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Falkow S., LeBoit P. E., Perkocha L. A., Min K. W., Welch D. F., Slater L. N. The organism causing bacillary angiomatosis, peliosis hepatis, and fever and bacteremia in immunocompromised patients. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 23;324(21):1514–1514. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105233242117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Loutit J. S., Schmidt T. M., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. The agent of bacillary angiomatosis. An approach to the identification of uncultured pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1573–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shawar R., Sepulveda J., Clarridge J. E. Use of the RapID-ANA system and sodium polyanetholesulfonate disk susceptibility testing in identifying Haemophilus ducreyi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):108–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.108-111.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater L. N., Welch D. F., Hensel D., Coody D. W. A newly recognized fastidious gram-negative pathogen as a cause of fever and bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1587–1593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Anderson B. E., McDade J. E. Detection of Rickettsia rickettsii DNA in clinical specimens by using polymerase chain reaction technology. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2866–2868. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2866-2868.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B. Estimation of DNA sequence divergence from comparison of restriction endonuclease digests. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1257–1265. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela G., Vinson J. W., Molina-Pasquel C. Trench fever. II. Propagation of Rickettsia quintana on cell-free medium from the blood of two patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Sep;18(5):708–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson J. W. In vitro cultivation of the rickettsial agent of trench fever. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(2):155–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Dobson M. E., Samuel J. E., Dasch G. A., Mallavia L. P., Baca O., Mandelco L., Sechrest J. E., Weiss E., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic diversity of the Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4202–4206. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4202-4206.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Dobson M. E., Weiss E. A common origin of rickettsiae and certain plant pathogens. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):556–558. doi: 10.1126/science.3931222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Pickett D. A., Slater L. N., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Rochalimaea henselae sp. nov., a cause of septicemia, bacillary angiomatosis, and parenchymal bacillary peliosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):275–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.275-280.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Blitchington R. B., Greene R. C. Amplification of bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA with polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1942–1946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1942-1946.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]