Abstract
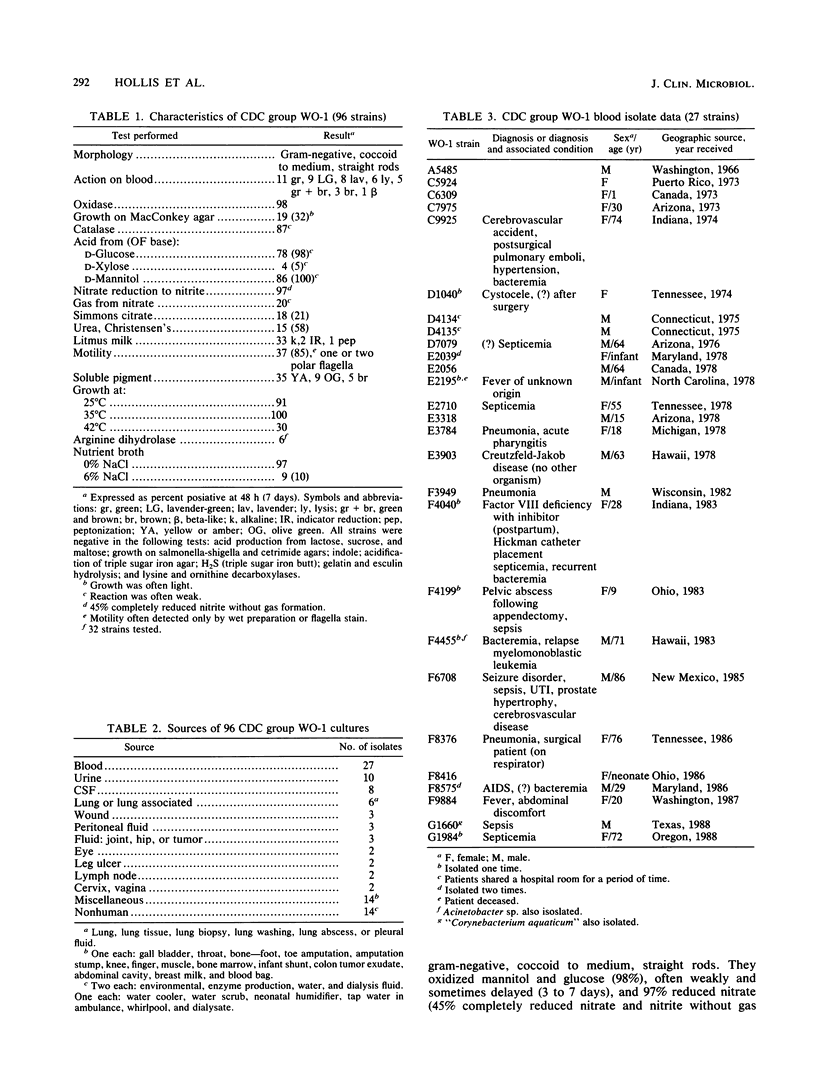
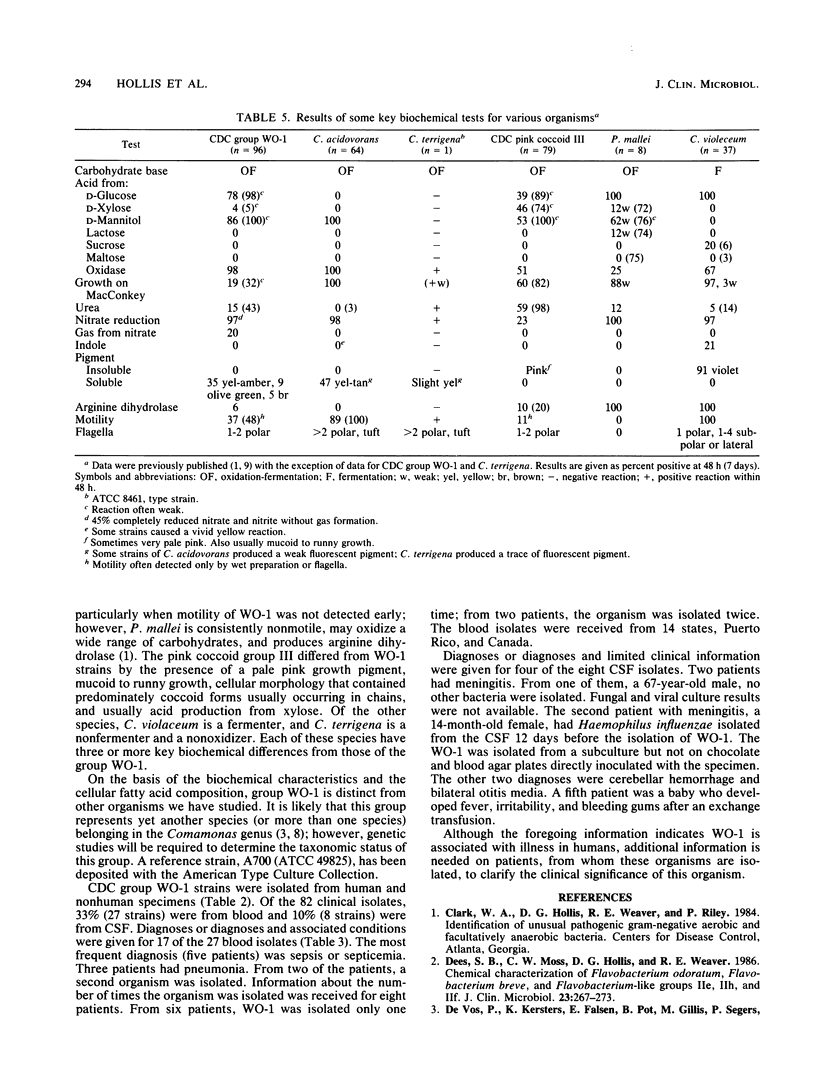
Ninety-six strains of weakly oxidative gram-negative rods isolated primarily from clinical specimens form a distinct group that has been designated Centers for Disease Control (CDC) group WO-1 (WO stands for weak oxidizer). The phenotypic characteristics of CDC group WO-1 were most similar to those of Comamonas acidovorans, Pseudomonas mallei, and CDC pink coccoid group III. The WO-1 group can be differentiated from C. acidovorans by the oxidation of glucose (often weak and sometimes delayed), motility by means of one or two polar flagella, and, when positive, the complete reduction of nitrate and nitrite. Motility and usually the failure to produce arginine dihydrolase distinguish this group from P. mallei. The WO-1 strains differ from the pink coccoid group III by the absence of pink growth pigment, the lack of predominantly coccoid cellular morphology, and usually the inability to produce acid from xylose. The cellular fatty acid compositions of 29 group WO-1 strains were characterized by large amounts of C16:0 and C16:1w7c; smaller amounts of C18:1w7c, C14:0, C12:0, and 3-OH-C10:0; and trace to small amounts of C15:1w6 and C17:0 acids. The fatty acid profile of WO-1, compared with the profiles of other bacteria we have tested previously, was most similar to the profiles of two phenotypically different organisms, Comamonas terrigena (a nonoxidative, multipolar gram-negative rod) and Chromobacterium violaceum (a fermentative gram-negative rod). Ubiquinone-8 was the major quinone in the five WO-1 strains examined. Eighty-five percent of the WO-1 strains were isolated from human specimens. Thirty-three percent were from blood, and 10% were from cerebrospinal fluid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dees S. B., Moss C. W., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Chemical characterization of Flavobacterium odoratum, Flavobacterium breve, and Flavobacterium-like groups IIe, IIh, and IIf. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):267–273. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.267-273.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B. Cellular fatty acids and metabolic products of Pseudomonas species obtained from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Dec;4(6):492–502. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.6.492-502.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Wallace P. L., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Cultural and chemical characterization of CDC groups EO-2, M-5, and M-6, Moraxella (Moraxella) species, Oligella urethralis, Acinetobacter species, and Psychrobacter immobilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):484–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.484-492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace P. L., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Moss C. W. Biochemical and chemical characterization of pink-pigmented oxidative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):689–693. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.689-693.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


