Abstract
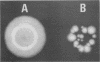
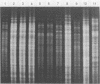
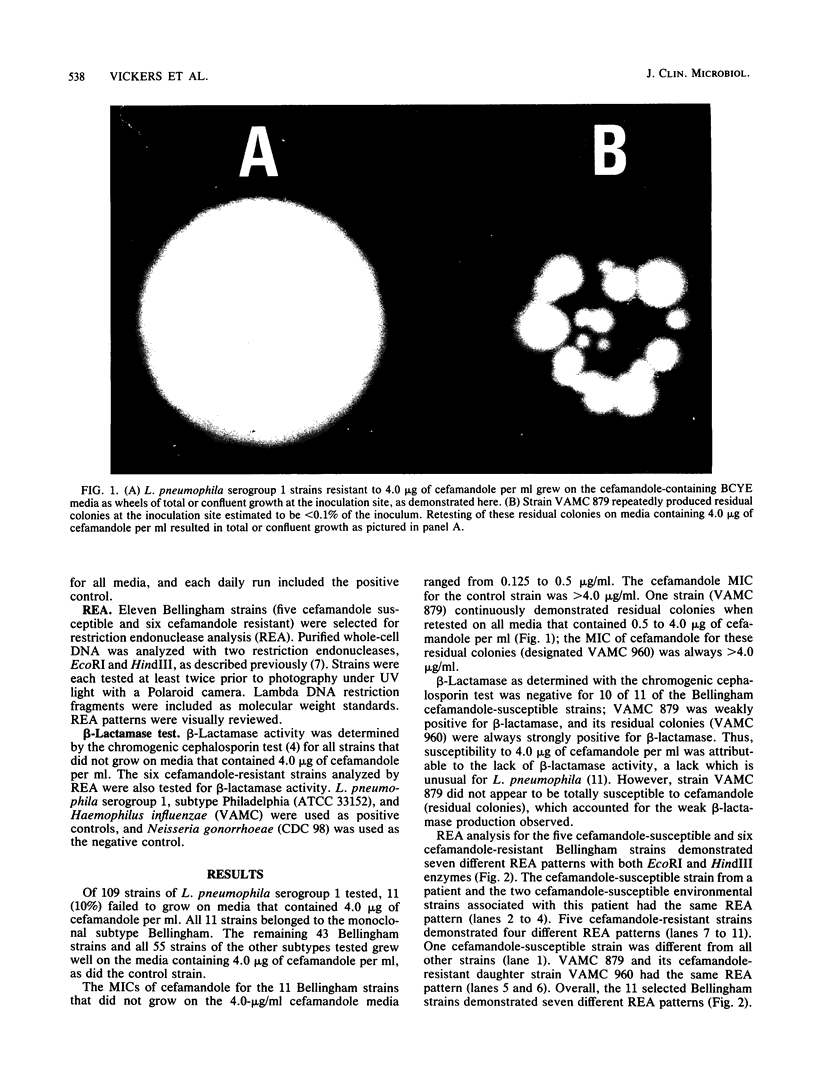
The standard selective Legionella medium that contains cefamandole failed to grow legionella pneumophila serogroup 1, subtype Bellingham, from a sputum sample from a patient with nosocomial Legionnaires' disease; the isolate did grow on a similar selective medium that substitutes vancomycin for cefamandole. Two Bellingham isolates from this patient's hospital environment also failed to grow when tested on the cefamandole medium. We tested 106 additional L. pneumophila serogroup 1 isolates that belonged to nine different monoclonal antibody subtypes and demonstrated that susceptibility to cefamandole was rare (10%) and limited to the Bellingham subtype. The diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease may be missed unless the culture protocol includes both a nonselective medium and a selective medium that does not contain cefamandole. In vitro susceptibility to cefamandole also provided an epidemiologic marker that linked a water source for a patient to nosocomial Legionnaires' disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dournon E., Bibb W. F., Rajagopalan P., Desplaces N., McKinney R. M. Monoclonal antibody reactivity as a virulence marker for Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 strains. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):496–501. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., McKinney R. M., Tobin J. O., Bibb W. F., Watkins I. D., Ramsay D. Development of a standardized subgrouping scheme for Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.768-771.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. E., Joly J., Para M., Plouffe J., Ciesielski C., Blaser M. J., Yu V. L. Comparison of molecular methods for subtyping patients and epidemiologically linked environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):486–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N. J., Woods T., Bibb W., McKinney R. M. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella species by restriction endonuclease and alloenzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1875-1880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers R. M., Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Rihs J. D. Manual of culture methodology for Legionella. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Dec;2(4):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins I. D., Tobin J. O., Dennis P. J., Brown W., Newnham R., Kurtz J. B. Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 subgrouping by monoclonal antibodies--an epidemiological tool. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):211–216. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J. Similar DNA restriction endonuclease profiles in strains of Legionella pneumophila from different serogroups. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1838–1841. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1838-1841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]