Abstract
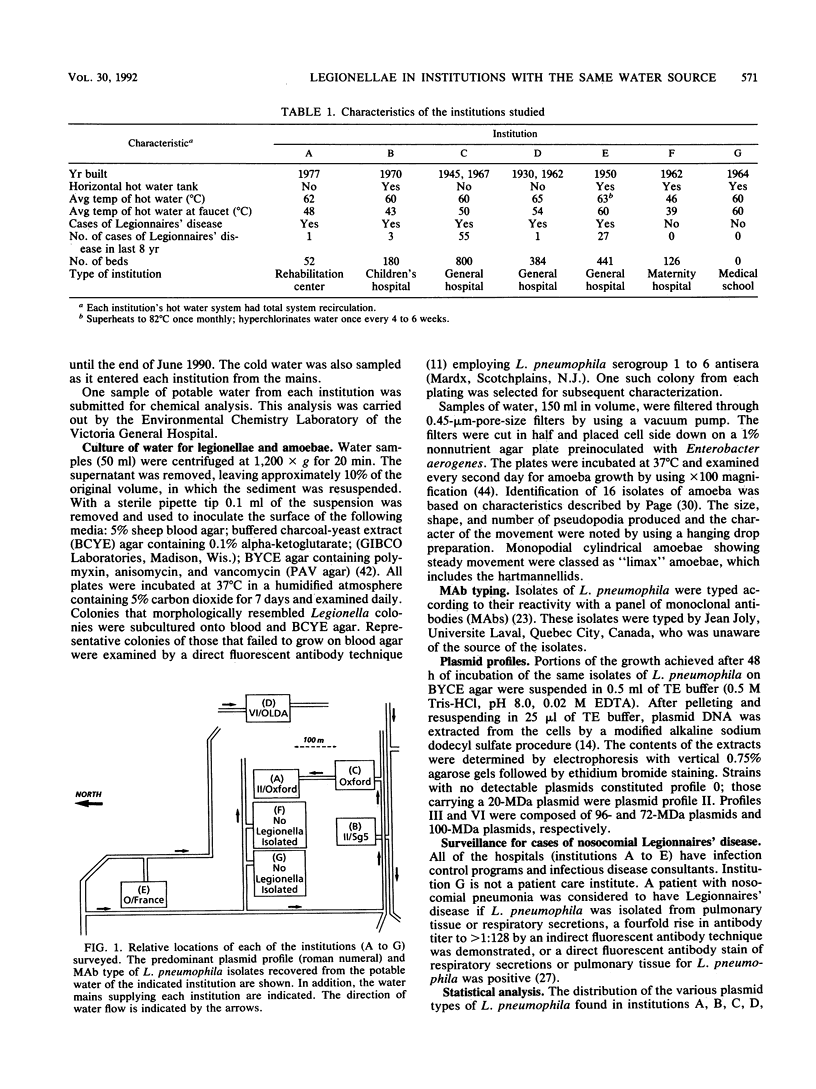
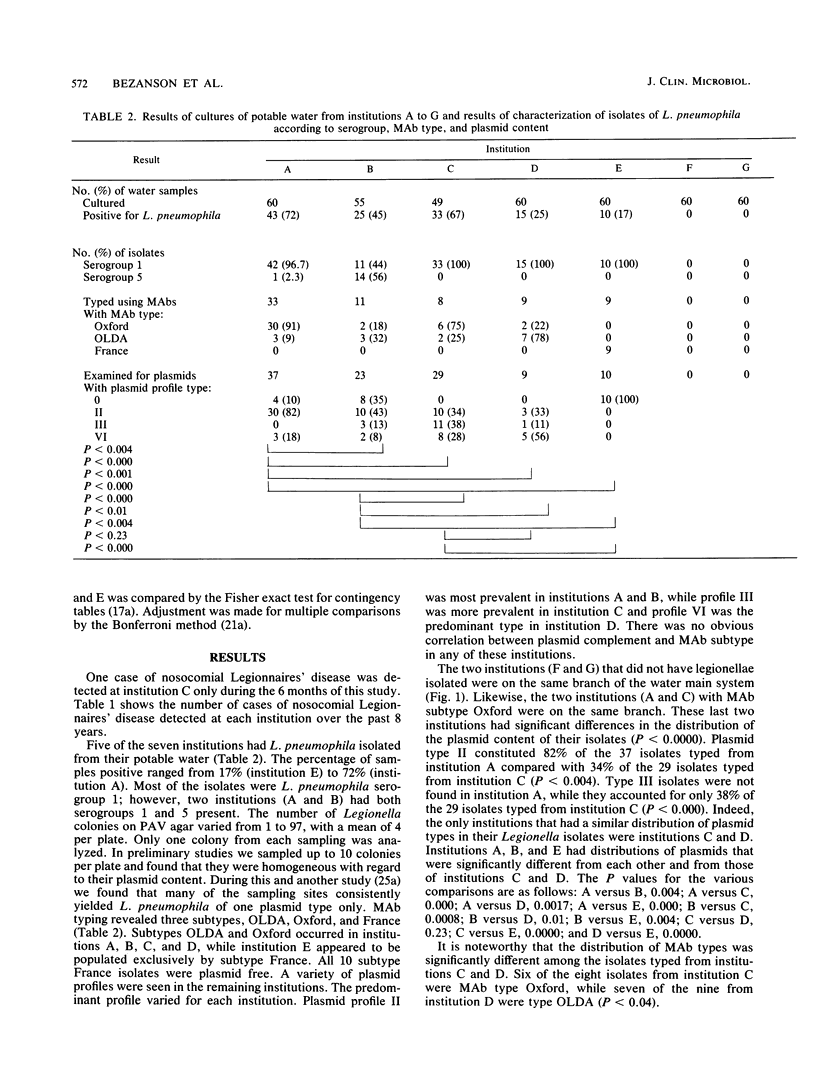
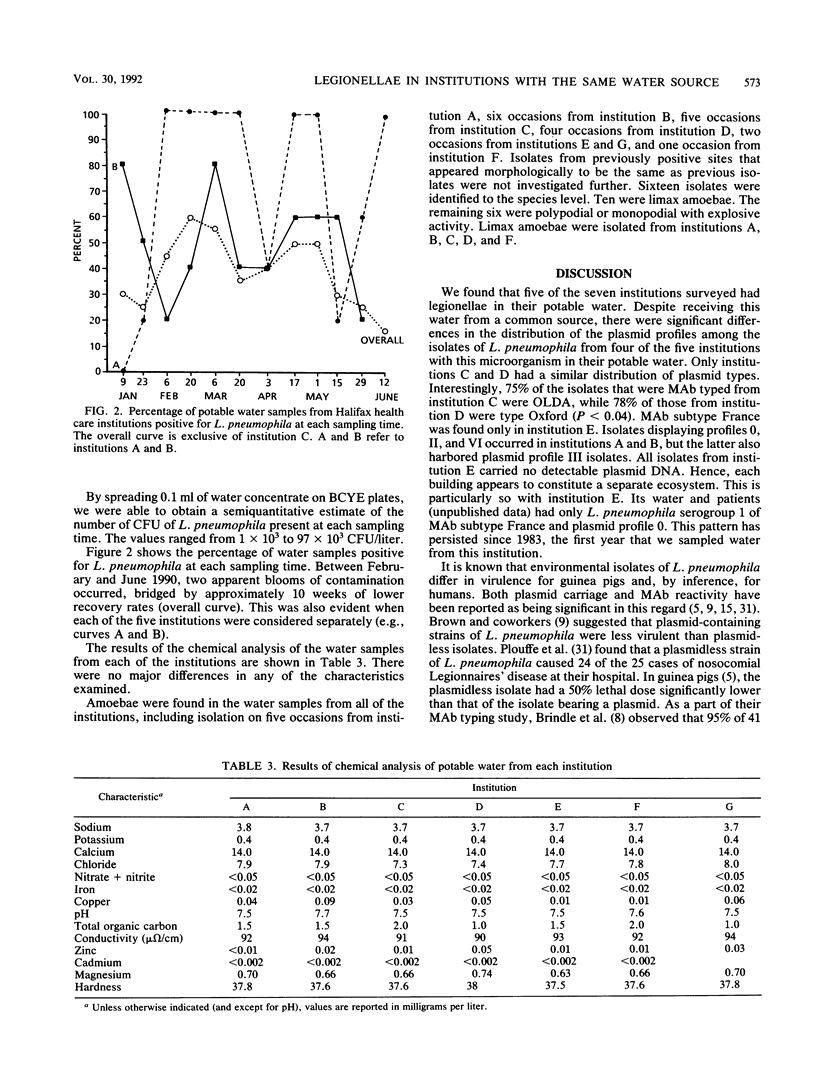
We cultured potable water from seven institutions (six hospitals and one medical school) every 2 weeks for 6 months for Legionella pneumophila. All of the institutions were located close to each other and received water from the same freshwater source. Two institutions (the medical school and hospital F, a maternity hospital) never had L. pneumophila isolated from their potable water. The remaining five had 17 to 72% of their water samples positive for L. pneumophila. Most of the isolates were serogroup 1; however, in hospital B serogroup 5 accounted for 56% of the isolates. Oxford and OLDA monoclonal antibody subtypes of L. pneumophila serogroup 1 coexisted in four of the five institutions, while subtype France only was found in one institution. All 10 isolates from this institution lacked plasmids. The other four institutions had Legionella populations with plasmid profiles II, III, and VI. Two of these institutions also had isolates with no plasmids. The distribution of the plasmid types was significantly different for all institutions except C and D. The distribution of monoclonal antibody subtypes was significantly different for L. pneumophila isolates recovered from institutions C and D. There were no characteristics that distinguished the culture-positive institutions from the culture-negative areas. We conclude that diverse populations of L. pneumophila exist within these institutions despite their geographic proximity and identical potable water source.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnow P. M., Weil D., Para M. F. Prevalence and significance of Legionella pneumophila contamination of residential hot-tap water systems. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):145–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett C. L., Kurtz J. B., Hutchison J. G., Turner G. C., Wright A. E. Legionella in hospital and hotel water supplies. Lancet. 1983 Dec 3;2(8362):1315–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovier H., Fattal B., Shuval H. Seasonal distribution of legionellae isolated from various types of water in Israel. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):644–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best M., Yu V. L., Stout J., Goetz A., Muder R. R., Taylor F. Legionellaceae in the hospital water-supply. Epidemiological link with disease and evaluation of a method for control of nosocomial legionnaires' disease and Pittsburgh pneumonia. Lancet. 1983 Aug 6;2(8345):307–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollin G. E., Plouffe J. F., Para M. F., Prior R. B. Difference in virulence of environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):674–677. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.674-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp C. A., Sumner J. W., Morris G. K., Wells J. G. Isolation of Legionella spp. from environmental water samples by low-pH treatment and use of a selective medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):714–719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.714-719.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiman R. F., Fields B. S., Sanden G. N., Volmer L., Meier A., Spika J. S. Association of shower use with Legionnaires' disease. Possible role of amoebae. JAMA. 1990 Jun 6;263(21):2924–2926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle R. J., Stannett P. J., Tobin J. O. Legionella pneumophila: monoclonal antibody typing of clinical and environmental isolates. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):235–239. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Vickers R. M., Elder E. M., Lema M., Garrity G. M. Plasmid and surface antigen markers of endemic and epidemic Legionella pneumophila strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):230–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.230-235.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbourne J. S., Trew R. M. Presence of Legionella in London's water supplies. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):633–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dournon E., Bibb W. F., Rajagopalan P., Desplaces N., McKinney R. M. Monoclonal antibody reactivity as a virulence marker for Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 strains. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):496–501. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Nakahama C., Tobin J. O., Calarco K., Beer K. B., Joly J. R., Selander R. K. Paleoepidemiologic investigation of Legionnaires disease at Wadsworth Veterans Administration Hospital by using three typing methods for comparison of legionellae from clinical and environmental sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1121-1126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiguet M., Pierre J., Brun P., Berthelot G., Gottot S., Gibert C., Valleron A. J. Epidemiological survey of a major outbreak of nosocomial legionellosis. Int J Epidemiol. 1987 Sep;16(3):466–471. doi: 10.1093/ije/16.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T. G., Saunders N. A., Haththotuwa A., Hallas G., Birtles R. J., Taylor A. G. Phenotypic variation amongst genotypically homogeneous Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 isolates: implications for the investigation of outbreaks of Legionnaires' disease. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):171–180. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800059331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C. M., Massanari R. M., Wenzel R. P., Pfaller M. A., Moyer N. P., Hall N. Legionnaires' disease associated with a hospital water system. A five-year progress report on continuous hyperchlorination. JAMA. 1988 Apr 22;259(16):2423–2427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., Chen Y. Y., Ramsay D. Serogrouping and subtyping of Legionella pneumophila with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1040–1046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1040-1046.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Saux N. M., Sekla L., McLeod J., Parker S., Rush D., Jeffery J. R., Brunham R. C. Epidemic of nosocomial Legionnaires' disease in renal transplant recipients: a case-control and environmental study. CMAJ. 1989 May 1;140(9):1047–1053. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Stout J. E., Yu V. L. Factors predisposing to Legionella pneumophila colonization in residential water systems. Arch Environ Health. 1988 Jan-Feb;43(1):59–62. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1988.9934375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., George J., Macdonald S., Haase D. Are health care workers at risk for infection during an outbreak of nosocomial Legionnaires' disease? Am J Infect Control. 1986 Oct;14(5):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(86)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., MacDonald S., Clarke K., Haldane D. Nosocomial legionnaires' disease: lessons from a four-year prospective study. Am J Infect Control. 1991 Apr;19(2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(91)90043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Redus M. A., Dowdle W. R. Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1197–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Yu V. L., McClure J. K., Kroboth F. J., Kominos S. D., Lumish R. M. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease uncovered in a prospective pneumonia study. JAMA. 1983 Jun 17;249(23):3184–3188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Para M. F., Maher W. E., Hackman B., Webster L. Subtypes of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 associated with different attack rates. Lancet. 1983 Sep 17;2(8351):649–650. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92531-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Hutner S. H., George J. R., Harrell W. K. Metal requirements of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.688-695.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro C. D., Burge S. H., Palmer S. R., Tobin J. O., Watkins I. D. Legionella pneumophila in a hospital water system following a nosocomial outbreak: prevalence, monoclonal antibody subgrouping and effect of control measures. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Jun;98(3):253–262. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800062002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Current views on the relationships between amoebae, legionellae and man. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):678–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield G. M., Locci R. Colonization of components of a model hot water system by Legionella pneumophila. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;58(2):151–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Ceraso M., Stephenson T. E., Wolford R. S., Wadowsky R. M., McNamara A. M., Yee R. B. Effects of metals on Legionella pneumophila growth in drinking water plumbing systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1149–1154. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1149-1154.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Kuchta J. M., Oleck B. M., Lipovich M. J., Wolford R. S., Wadowsky R. M., McNamara A. M., Sykora J. L., Keleti G. Survival and multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in municipal drinking water systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):979–986. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.979-986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. E., Joly J., Para M., Plouffe J., Ciesielski C., Blaser M. J., Yu V. L. Comparison of molecular methods for subtyping patients and epidemiologically linked environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):486–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J., Best M., Brown A., Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. Ubiquitousness of Legionella pneumophila in the water supply of a hospital with endemic Legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 25;306(8):466–468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202253060807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker S. B., Bennett J. V., Tsai T. F., Fraser D. W., McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Williams K. H., Jr, Stuart W. H., Dull H. B., Eickhoff T. C. An outbreak in 1965 of severe respiratory illness caused by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):512–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobiansky L., Drath A., Dubery B., Koornhof H. J. Seasonality of Legionella isolates from environmental sources. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):640–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers R. M., Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Rihs J. D. Manual of culture methodology for Legionella. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Dec;2(4):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers R. M., Yu V. L., Hanna S. S., Muraca P., Diven W., Carmen N., Taylor F. B. Determinants of Legionella pneumophila contamination of water distribution systems: 15-hospital prospective study. Infect Control. 1987 Sep;8(9):357–363. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700067412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Butler L. J., Cook M. K., Verma S. M., Paul M. A., Fields B. S., Keleti G., Sykora J. L., Yee R. B. Growth-supporting activity for Legionella pneumophila in tap water cultures and implication of hartmannellid amoebae as growth factors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2677–2682. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2677-2682.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo A. H., Yu V. L., Goetz A. Potential in-hospital modes of transmission of Legionella pneumophila. Demonstration experiments for dissemination by showers, humidifiers, and rinsing of ventilation bag apparatus. Am J Med. 1986 Apr;80(4):567–573. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90809-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



