Abstract
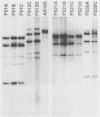
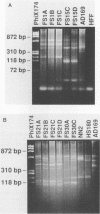
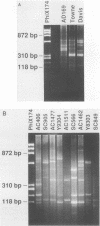
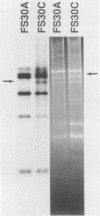
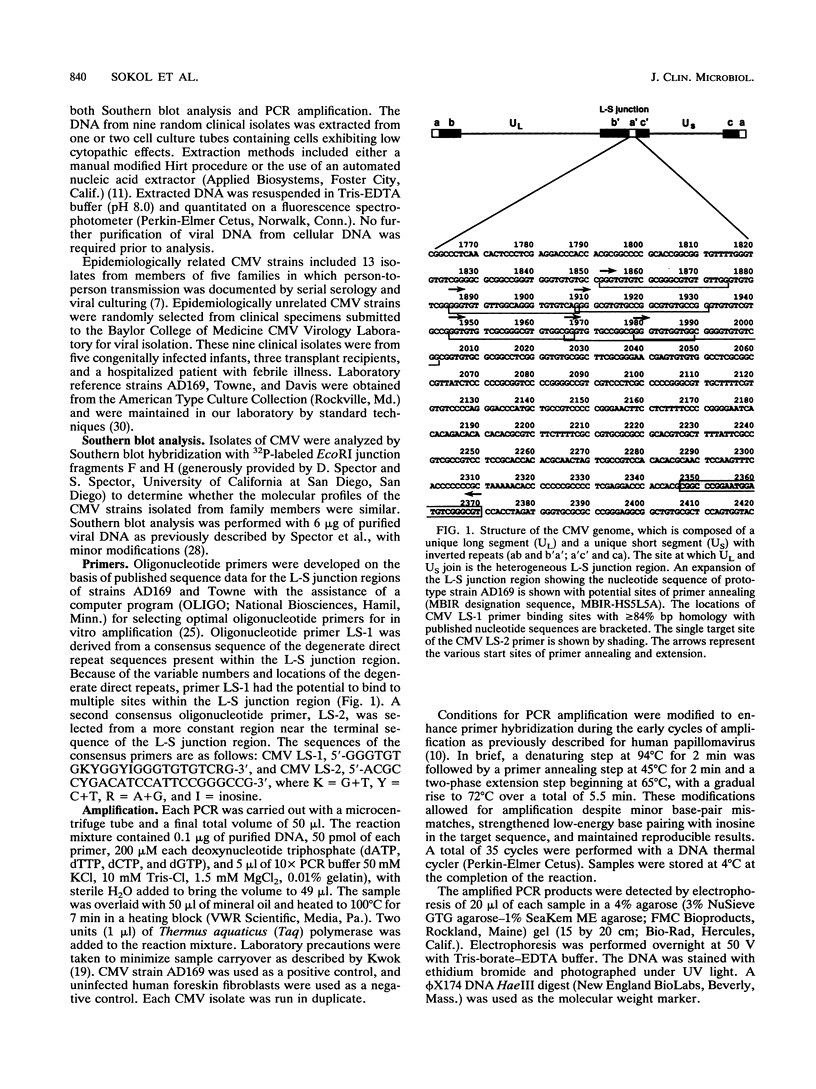
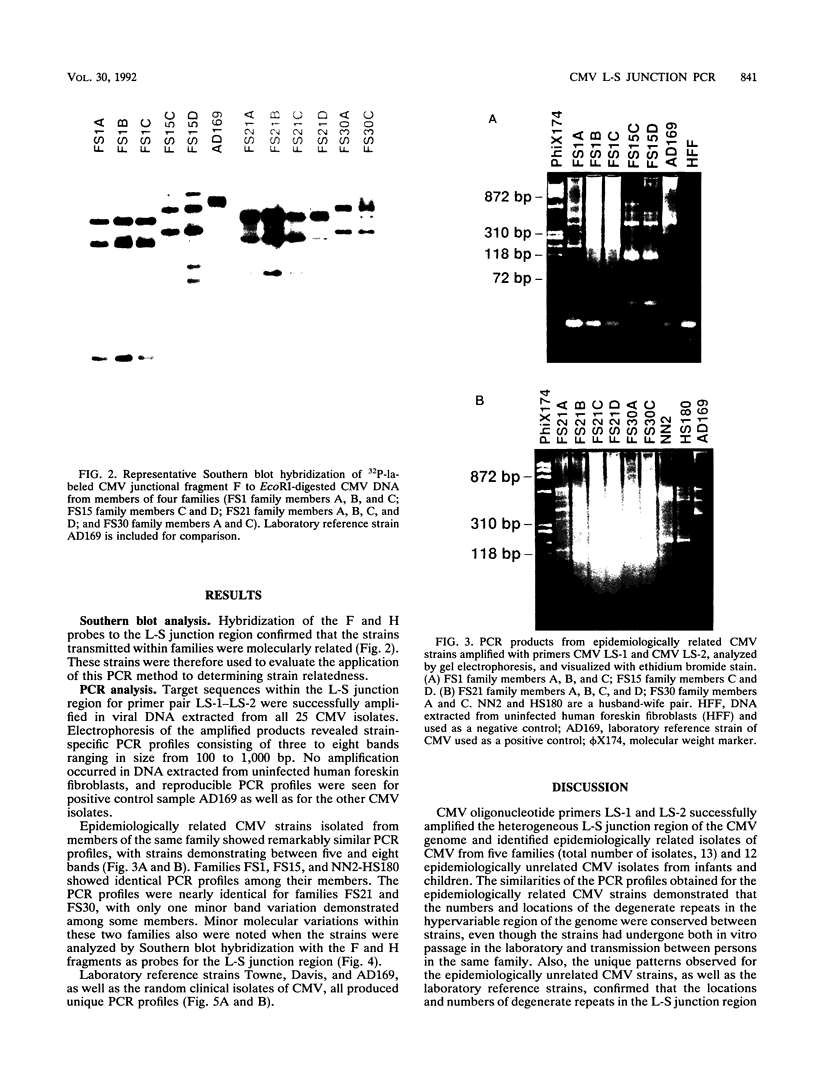
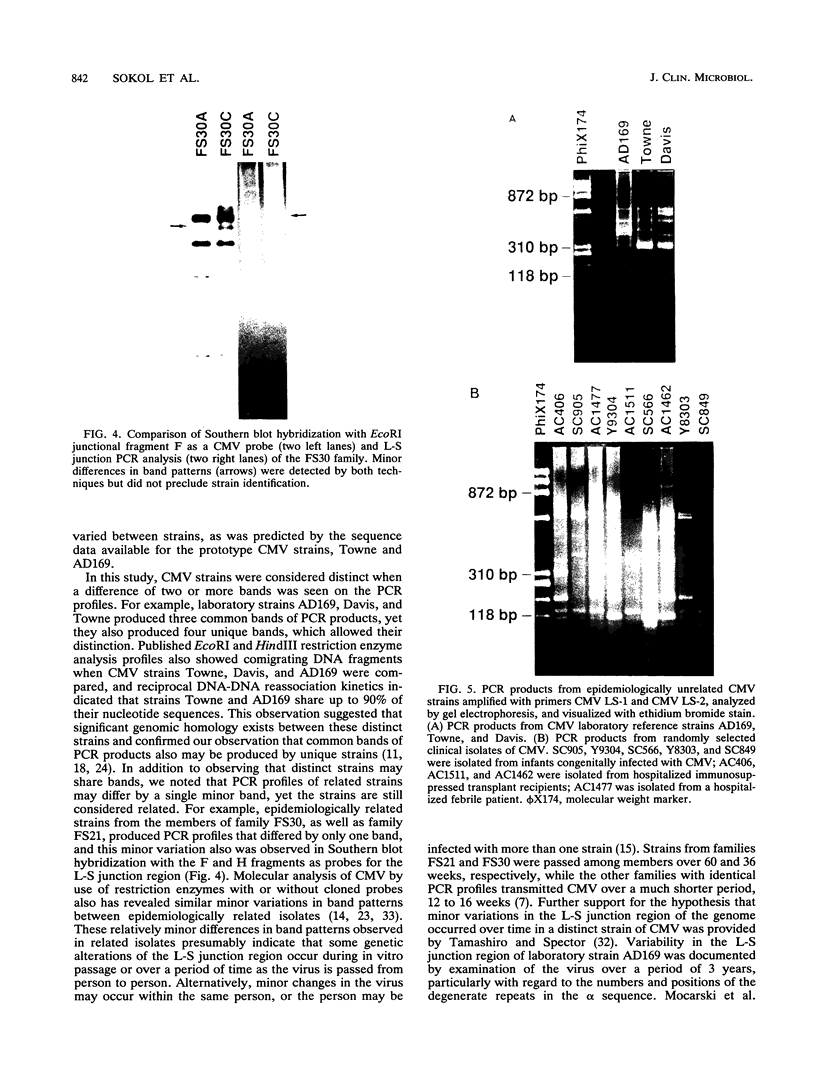
A technique based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was developed to facilitate the study of the epidemiology of cytomegalovirus (CMV). Consensus oligonucleotide primers from repetitive DNA sequences were designed to amplify interspersed repetitive sequences in an area of heterogeneity within the L-S junction region of the CMV genome, and PCR products were detected by gel electrophoresis. Purified CMV DNAs from 25 CMV isolates, 13 from members of five families in which person-to-person transmission was documented, 9 random clinical isolates of CMV, and 3 laboratory reference strains of CMV (Towne, Davis, and AD169), were analyzed. The gel electrophoretic patterns of DNA bands, or PCR profiles, produced by amplification with the L-S primers were unique for epidemiologically unrelated strains and laboratory reference strains, yet similar patterns were observed for epidemiologically related strains isolated from members of the same family. This method of rapid fingerprinting of CMV DNA within the hypervariable L-S junction region by PCR to produce strain-specific, variably sized PCR products should simplify the molecular epidemiologic analysis of CMV.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S. P. The molecular epidemiology of cytomegalovirus transmission among children attending a day care center. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):760–768. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassol S. A., Poon M. C., Pal R., Naylor M. J., Culver-James J., Bowen T. J., Russell J. A., Krawetz S. A., Pon R. T., Hoar D. I. Primer-mediated enzymatic amplification of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA. Application to the early diagnosis of CMV infection in marrow transplant recipients. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1109–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI113990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. W. Acquisition of donor strains of cytomegalovirus by renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 29;314(22):1418–1423. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605293142205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. W. Differentiation of cytomegalovirus strains by restriction analysis of DNA sequences amplified from clinical specimens. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):738–742. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmler G. J., Buffone G. J., Schimbor C. M., May R. A. Detection of cytomegalovirus in urine from newborns by using polymerase chain reaction DNA amplification. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1177–1184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmler G. J., Yow M. D., Spector S. A., Reis S. G., Brady M. T., Anderson D. C., Taber L. H. Nosocomial cytomegalovirus infections within two hospitals caring for infants and children. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):9–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H. A., Gelfand D., Sninsky J. J. Recent advances in the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1643–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.2047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire L., Arella M., Campione-Piccardo J., Lancaster W. D. Amplification of human papillomavirus DNA sequences by using conserved primers. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2660–2665. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2660-2665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Blomberg I. Restriction enzyme analysis of human cytomegalovirus using DNA extracted from infected cells. J Med Virol. 1984;14(4):313–322. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia K., Spector D. H., Lawrie J., Spector S. A. Enzymatic amplification of human cytomegalovirus sequences by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1802–1809. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1802-1809.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Alford C. A., Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Pass R. F. Molecular epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infections in women and their infants. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 23;303(17):958–962. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010233031702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Huong S. M., Tegtmeier G. E., Alford C. Cytomegalovirus: genetic variation of viral genomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:332–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Kilpatrick B. A., Huang Y. T., Pagano J. S. Detection of human cytomegalovirus and analysis of strain variation. Yale J Biol Med. 1976 Mar;49(1):29–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Individual-specific 'fingerprints' of human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):76–79. doi: 10.1038/316076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemble G. W., Mocarski E. S. A host cell protein binds to a highly conserved sequence element (pac-2) within the cytomegalovirus a sequence. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4715–4728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4715-4728.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter S. A., Nelson D. L., Warren S. T., Ledbetter D. H. Rapid isolation of DNA probes within specific chromosome regions by interspersed repetitive sequence polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90477-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Ledbetter S. A., Ledbetter D. H., Ward D. C. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with Alu and L1 polymerase chain reaction probes for rapid characterization of human chromosomes in hybrid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6634–6638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Liu A. C., Spaete R. R. Structure and variability of the a sequence in the genome of human cytomegalovirus (Towne strain). J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2223–2230. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass R. F., Little E. A., Stagno S., Britt W. J., Alford C. A. Young children as a probable source of maternal and congenital cytomegalovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 28;316(22):1366–1370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705283162203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Rhoads R. E. A computer program for choosing optimal oligonucleotides for filter hybridization, sequencing and in vitro amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8543–8551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D., Martin W. J., Appleman M. D., Causey D. M., Leedom J. M., Arnheim N. Detection of cytomegalovirus DNA in peripheral blood of patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1185–1192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. The alpha sequence of the cytomegalovirus genome functions as a cleavage/packaging signal for herpes simplex virus defective genomes. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):817–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.817-824.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Neuman T. R., Hirata K. K. Rapid determination of molecular relatedness of isolates of human cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):755–759. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Spector D. H. Molecular epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infections in premature twin infants and their mother. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;1(6):405–409. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198211000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Filpula D., Friedmann T., Spector D. H. Structure of the heterogeneous L-S junction region of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169 DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):541–548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.541-548.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Spector D. H. Terminal structure and heterogeneity in human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):591–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.591-604.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfert C. M., Huang E. S., Stagno S. Restriction endonuclease analysis of cytomegalovirus deoxyribonucleic acid as an epidemiologic tool. Pediatrics. 1982 Nov;70(5):717–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Huang E. S., Miller M. J., Lin C. H., Ho W. G., Gale R. P., Champlin R. E. Molecular epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infections associated with bone marrow transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jan;102(1):16–20. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-1-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yow M. D., Lakeman A. D., Stagno S., Reynolds R. B., Plavidal F. J. Use of restriction enzymes to investigate the source of a primary cytomegalovirus infection in a pediatric nurse. Pediatrics. 1982 Nov;70(5):713–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Gallez-Hawkins G., Churchill M. A., Morton-Blackshere A., Pande H., Adler S. P., Schmidt G. M., Forman S. J. Comparative analysis of human cytomegalovirus a-sequence in multiple clinical isolates by using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2602–2607. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2602-2607.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]