Abstract
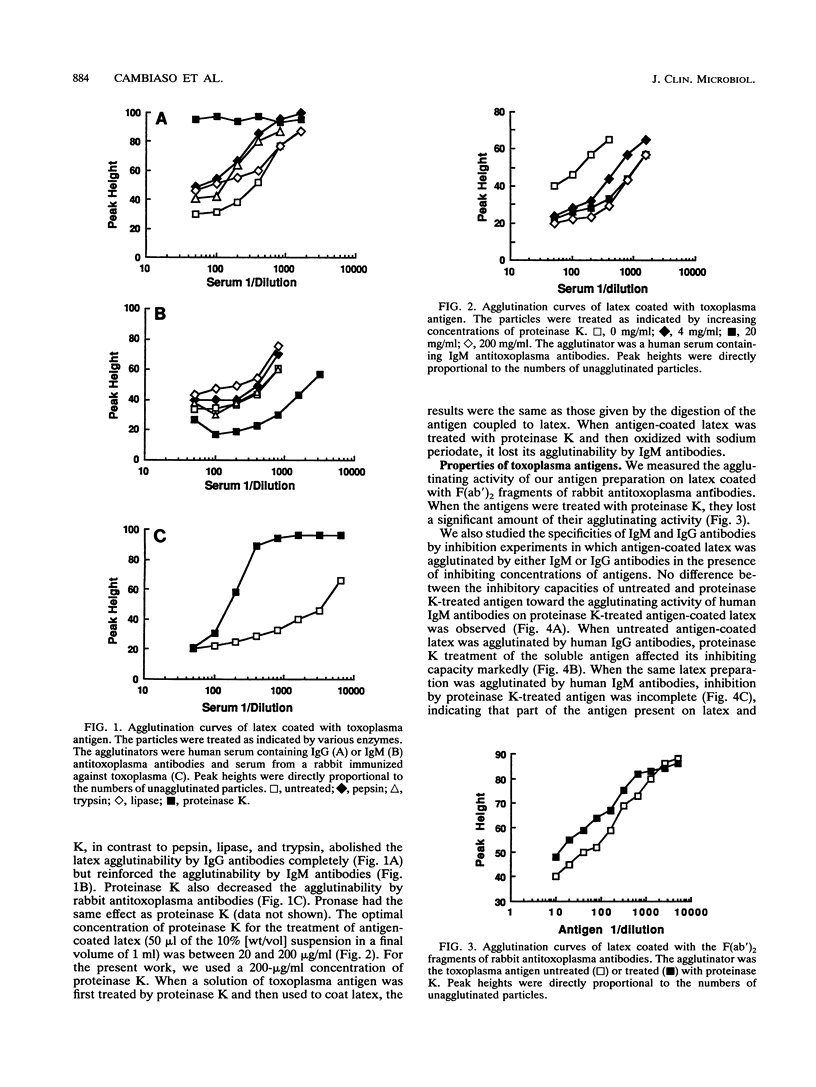
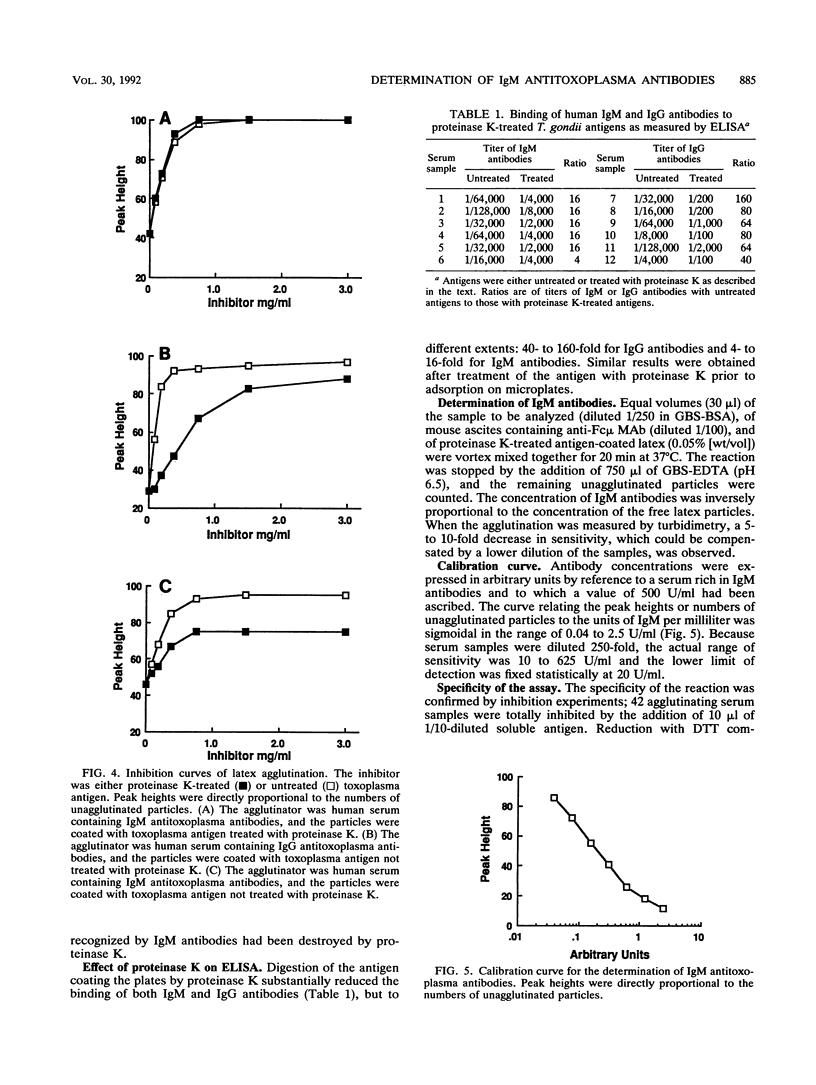
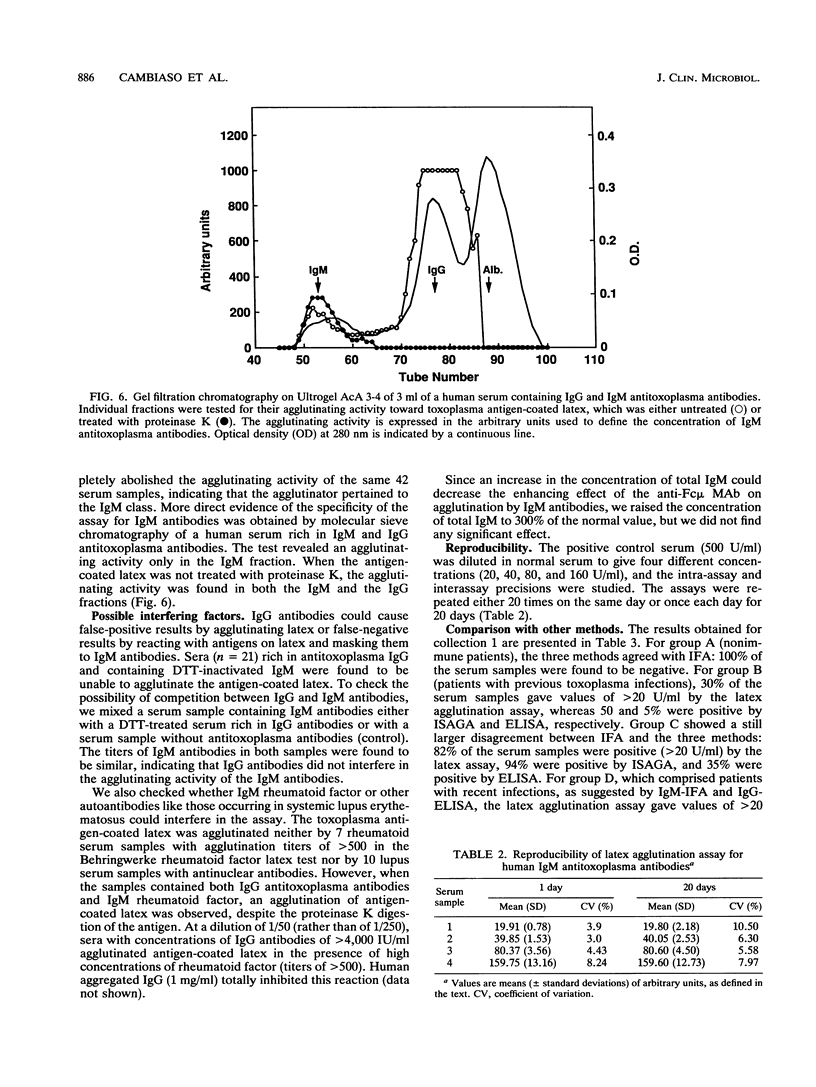
An assay of immunoglobulin M (IgM) antitoxoplasma antibodies which is rapid (less than 30 min), homogeneous, and reliable (interassay coefficient of variation, less than 11%) is proposed. Its principle is based on the observation that a suspension of latex particles coated with toxoplasma antigens, after treatment with proteinase K, becomes less agglutinable by IgG antibodies but more agglutinable by IgM antibodies. The difference between the activities of the two classes of antibodies is increased by the addition of a monoclonal antibody directed against the Fc region of IgM. Agglutination is measured with a special instrument which optically counts the particles that remain free after the reaction. Turbidimetric reading, although less sensitive, is also suitable. No significant interferences either by IgG antitoxoplasma antibodies or by rheumatoid factor or antinuclear antibodies were observed. The sensitivity was similar to that of the immunosorbent agglutination assay.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cambiaso C. L., Leek A. E., De Steenwinkel F., Billen J., Masson P. L. Particle counting immunoassay (PACIA). I. A general method for the determination of antibodies, antigens, and haptens. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Naot Y., Remington J. S. Immunoglobulin M-immunosorbent agglutination assay for diagnosis of infectious diseases: diagnosis of acute congenital and acquired Toxoplasma infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):486–491. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.486-491.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Remington J. S. Direct agglutination test for diagnosis of Toxoplasma infection: method for increasing sensitivity and specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):562–568. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.562-568.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., TURK J. L. Direct agglutination test for Toxoplasma gondii. Lancet. 1959 Dec 12;2(7111):1068–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanti L. M., Cambiaso C. L., Cornu C. J., Lamy M. E., Masson P. L. Immunoassay of hepatitis B surface antigen by particle counting after pepsin digestion. J Virol Methods. 1987 Dec;18(4):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Cambiaso C. L., Collet-Cassart D., Magnusson C. G., Richards C. B., Sindic C. J. Particle counting immunoassay (PACIA). Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):106–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mineo J. R., Camargo M. E., Ferreira A. W. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii polysaccharides in human toxoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):283–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.283-287.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Guptill D. R., Mullenax J., Remington J. S. Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii antigens that react with human immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):331–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.331-338.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. I. Diagnostic significance in congenital cases and a method for their rapid demonstration. Pediatrics. 1968 Jun;41(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ise Y., Iida T., Suzuki T., Shimada K., Nishioka K. Detection of toxoplasma IgM antibody by passive latex agglutination reaction. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Aug 3;101(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Mullenax J., Araujo F. G., Erlich H. A., Remington J. S. Western Blot analysis of the antigens of Toxoplasma gondii recognized by human IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner L. J., Chatterton J. M., Joss A. W., Moir I. L., Ho-Yen D. O. The use of an IgM immunosorbent agglutination assay to diagnose congenital toxoplasmosis. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Feb;28(2):125–128. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-2-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtsbaeder S., Nguyen B. T., Calvin-Preval M. C. Respective role of antibodies and immune macrophages during acquired immunity against toxoplasmosis in mice. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1975 Jun-Jul;126C(4):461–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Coulie P. Monoclonal anti-IgG autoantibodies derived from lipopolysaccharide-activated spleen cells of 129/Sv mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):219–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


