Abstract
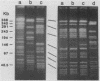
A large diarrhea outbreak due to enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) serogroup O143 occurring in Houston, Tex., provided the opportunity to investigate aspects of the molecular epidemiology of this and related organisms. This was done by comparing the plasmid patterns and the chromosomal restriction endonuclease digestion patterns by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) of EIEC from the outbreak, other E. coli from the same serogoup (O143), and EIEC isolated from other patients with diarrhea. Among the isolates studied, there was marked restriction fragment length polymorphism. All 3 non-O143 EIEC isolates had very different restriction endonuclease digestion patterns, as did 5 of 5 O143 non-EIEC isolates and 6 of 15 O143 EIEC isolates. Four Houston outbreak O143 EIEC isolates had the same restriction pattern as an O143 EIEC strain isolated 2 months before in Mexico and was nearly identical to another two O143 EIEC Mexican isolates. These related strains also had the same plasmid pattern; however, the presence of only a few plasmid bands, versus the 21 to 30 chromosomal bands seen with PFGE, suggests that plasmid patterns could be a less specific way to distinguish different strains. These results demonstrate that PFGE can distinguish between different E. coli strains of the same serogroup and phenotype. This technique can also identify relatedness within O143 EIEC, and our data suggest the spread of a strain of EIEC from Mexico to Houston, where it caused a large outbreak. PFGE may be useful to study the epidemiology of EIEC.
Full text
PDF
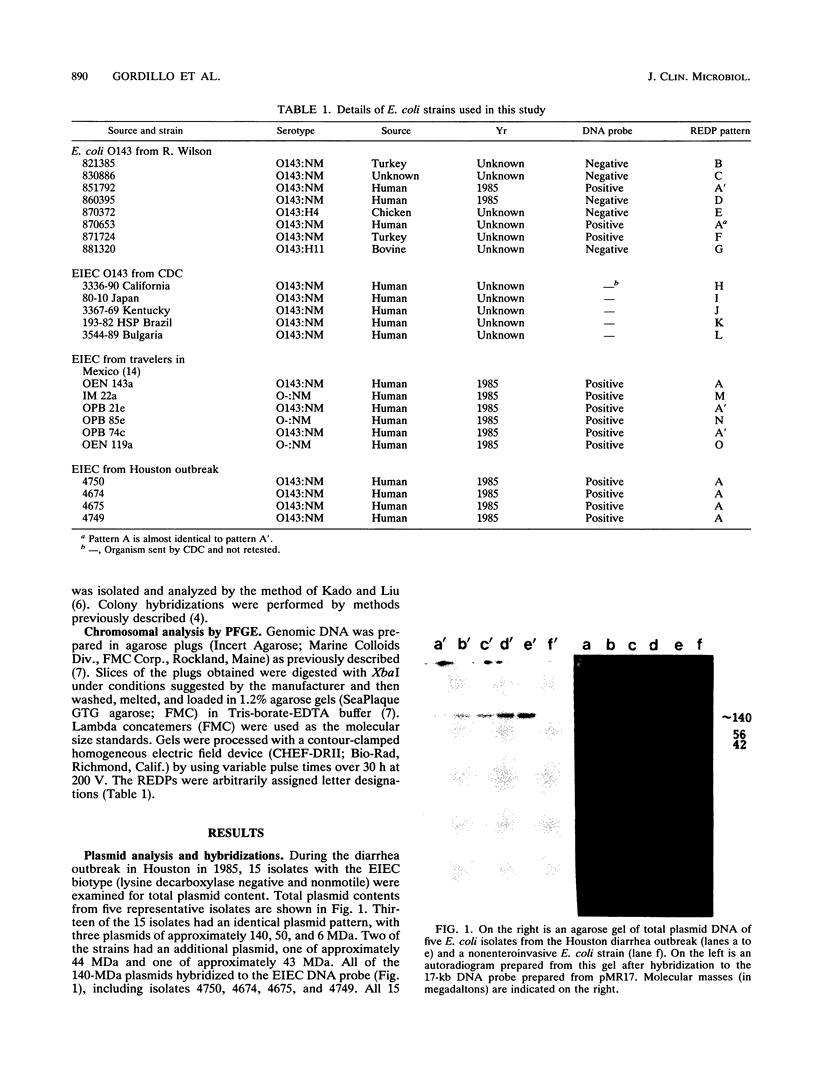



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Orskov I., Orskov F., Zimmermann S., Prada J., Gelderblom H., Stephan R., Whittam T. S. Clonal diversity and virulence factors in strains of Escherichia coli of the classic enteropathogenic serogroup O114. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Orskov I., Orskov F., Svanborg Eden C., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity in relation to serotype in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.407-413.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Duensing T. D. Rapid field inversion gel electrophoresis in combination with an rRNA gene probe in the epidemiological evaluation of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):426–429. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.426-429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R., Mariano J., Wells J. G., Payne B. J., Donnell H. D., Cohen M. L. Person-to-person transmission in an outbreak of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Aug;122(2):245–252. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Heath J. D., Sharma B. R., Weinstock G. M. Comparison of genomic DNAs of different enterococcal isolates using restriction endonucleases with infrequent recognition sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2059–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2059-2063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Markowitz S. M., Lopardo H. A., Patterson J. E., Zervos M. J., Rubeglio E., Eliopoulos G. M., Rice L. B., Goldstein F. W. Evidence for clonal spread of a single strain of beta-lactamase-producing Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis to six hospitals in five states. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):780–785. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Farrar W. E., Jr, McGee Z. A., Schaffner W. Evolution of a plasmid mediating resistance to multiple antimicrobial agents during a prolonged epidemic of nosocomial infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):170–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. D., Wells J. G., Yashuk J., Puhr N., Blake P. A. Outbreak of invasive Escherichia coli gastroenteritis on a cruise ship. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Mar;33(2):281–284. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati L., Piffaretti J. C. Molecular typing of Shigella strains using pulsed field gel electrophoresis and genome hybridization with insertion sequences. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jun;142(5):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90182-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Echeverria P., Pál T., Sethabutr O., Saiborisuth S., Sricharmorn S., Rowe B., Cross J. The role of Shigella spp., enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, and other enteropathogens as causes of childhood dysentery in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1132–1138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulloch E. F., Jr, Ryan K. J., Formal S. B., Franklin F. A. Invasive enteropathic Escherichia coli dysentery. An outbreak in 28 adults. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jul;79(1):13–17. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanger A. R., Murray B. E., Echeverria P., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L. Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli in travelers with diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):640–642. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]