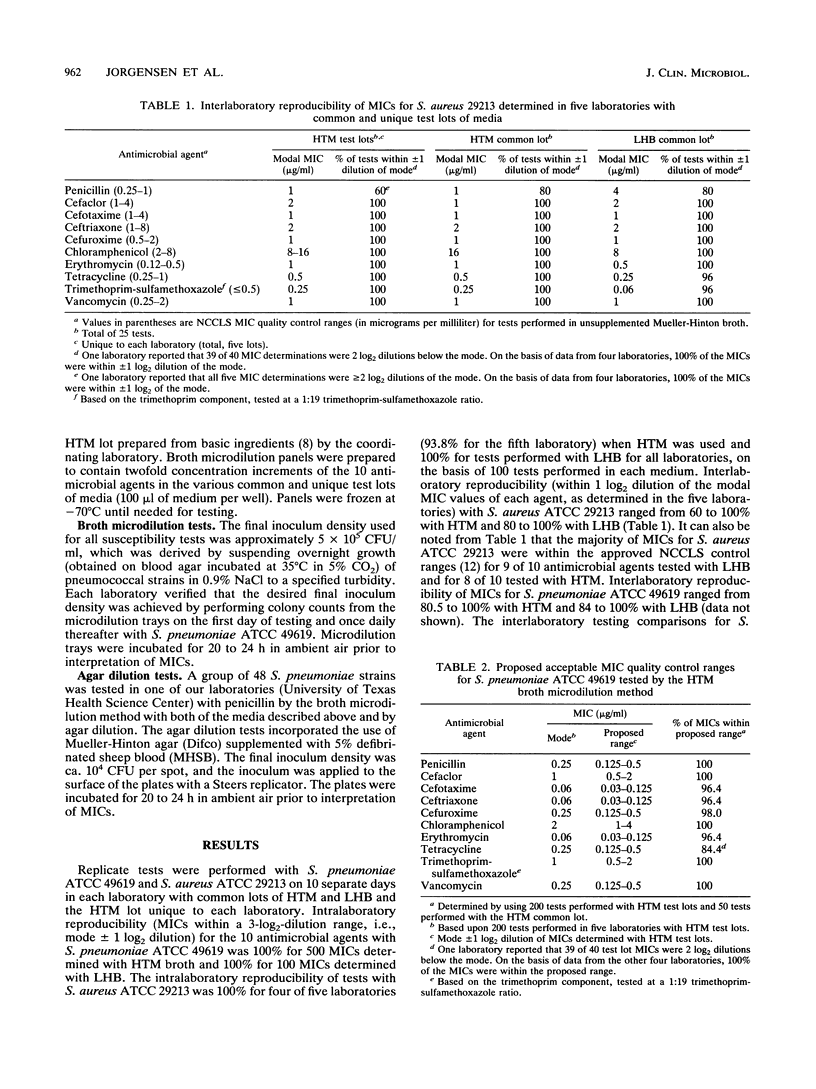
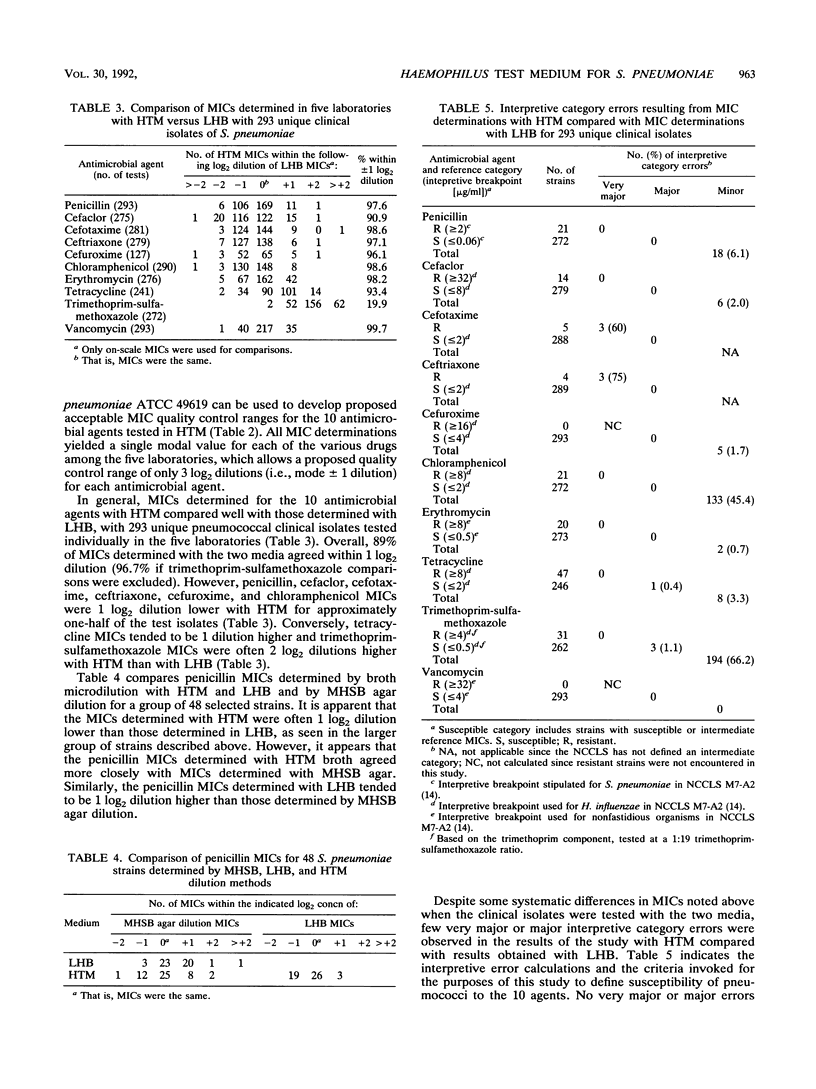
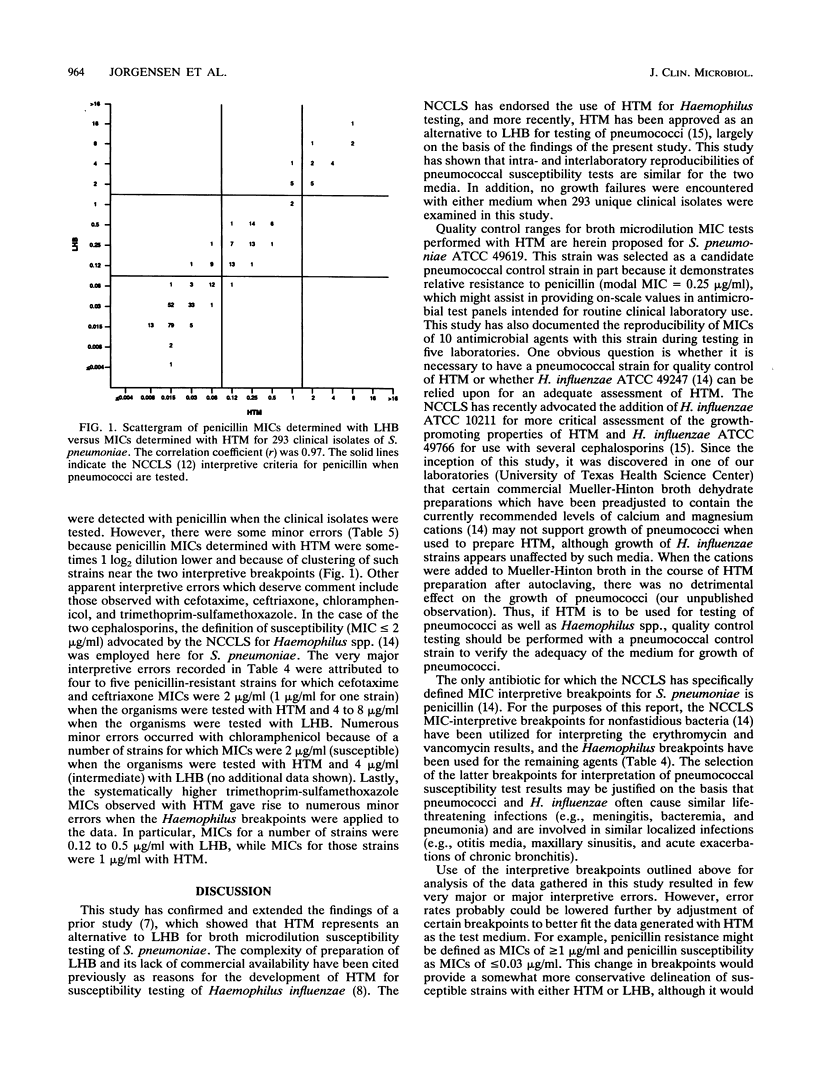
Abstract
A five-laboratory collaborative study was undertaken to determine the precision and accuracy of broth microdilution susceptibility tests of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates performed with Haemophilus test medium (HTM) compared with tests performed with lysed horse blood-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth (LHB). The intra-and interlaboratory reproducibilities of MICs of 10 antimicrobial agents determined with the two media were found to be quite similar and highly reproducible in both media. On the basis of favorable performance in this study, S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 is recommended as a quality control strain to assess the performance of HTM when this medium is used for testing of pneumococci. Testing of 293 unique clinical isolates of S. pneumoniae with both media in the respective participant laboratories allowed a direct comparison of MIC results and a calculation of interpretive error rates. Although there were some slight differences between MICs determined with HTM and MICs determined with LHB, few very major or major errors resulted from testing the clinical isolates against the 10 antimicrobial agents. However, MIC-interpretive criteria specific for S. pneumoniae should be developed and promulgated through a national consensus mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Istre G. R., Humphreys J. T., Albrecht K. D., Thornsberry C., Swenson J. M., Hopkins R. S. Chloramphenicol and penicillin resistance in pneumococci isolated from blood and cerebrospinal fluid: a prevalence study in metropolitan Denver. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):472–475. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.472-475.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istre G. R., Tarpay M., Anderson M., Pryor A., Welch D. Invasive disease due to Streptococcus pneumoniae in an area with a high rate of relative penicillin resistance. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):732–735. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. A., Shelton S., Nelson J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Relatively penicillin-resistant pneumococcal infections in pediatric patients. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):129–132. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198403000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Koornhof H. J., Robins-Browne R. M., Stevenson C. M., Vermaak Z. A., Freiman I., Miller G. B., Witcomb M. A., Isaäcson M., Ward J. I. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 5;299(14):735–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810052991402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Doern G. V., Maher L. A., Howell A. W., Redding J. S. Antimicrobial resistance among respiratory isolates of Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2075–2080. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Doern G. V., Thornsberry C., Preston D. A., Redding J. S., Maher L. A., Tubert T. Susceptibility of multiply resistant Haemophilus influenzae to newer antimicrobial agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;9(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Maher L. A., Howell A. W. Use of Haemophilus test medium for broth microdilution antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):430–434. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.430-434.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Redding J. S., Maher L. A., Howell A. W. Improved medium for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2105–2113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2105-2113.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P. Pneumococcal resistance to antibiotics. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Apr;3(2):171–196. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton A., Gulyas M., Munoz R., Tomasz A. Extremely high incidence of antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Hungary. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):542–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. W., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Relationship between in vitro susceptibility test results for chloramphenicol and production of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase by Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Aerococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2387–2390. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2387-2390.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz R., Coffey T. J., Daniels M., Dowson C. G., Laible G., Casal J., Hakenbeck R., Jacobs M., Musser J. M., Spratt B. G. Intercontinental spread of a multiresistant clone of serotype 23F Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):302–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallares R., Gudiol F., Liñares J., Ariza J., Rufi G., Murgui L., Dorca J., Viladrich P. F. Risk factors and response to antibiotic therapy in adults with bacteremic pneumonia caused by penicillin-resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 2;317(1):18–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707023170104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Lukaszewski M., Cross A., Al-Ibrahim M., Baltch A. L., Smith R. P., Geiseler P. J., Nadler J., Richmond A. S. Antibiotic-resistant isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae from clinical specimens: a cluster of serotype 19A organisms in Brooklyn, New York. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):78–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaegen J., Glupczynski Y., Verbist L., Blogie M., Vandeven J., Yourassowsky E., Vandepitte J. Capsular types and antibiotic sensitivity of pneumococci isolated from patients with serious infections in Belgium 1980 to 1988. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;9(6):390–395. doi: 10.1007/BF01979467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viladrich P. F., Gudiol F., Liñares J., Rufi G., Ariza J., Pallares R. Characteristics and antibiotic therapy of adult meningitis due to penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Am J Med. 1988 May;84(5):839–846. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten R. D., Markiewicz Z., Gilbert D. N. Meningitis due to penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in adults. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):118–124. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



