Abstract
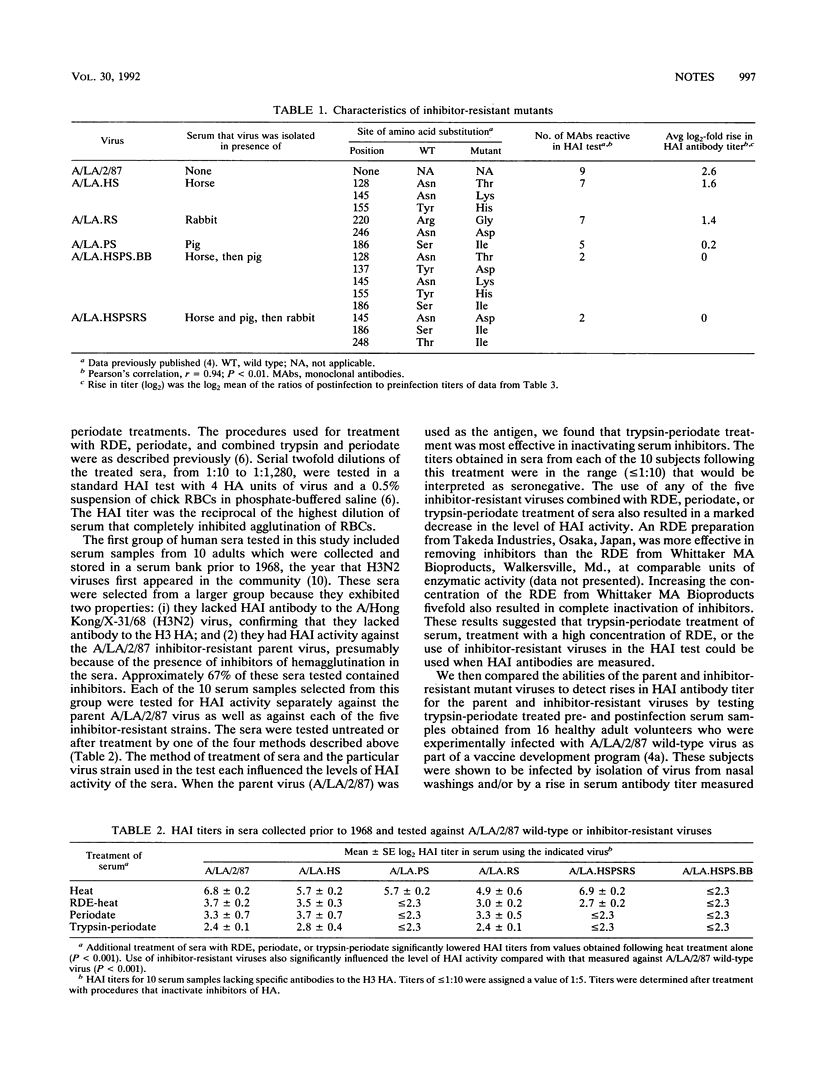
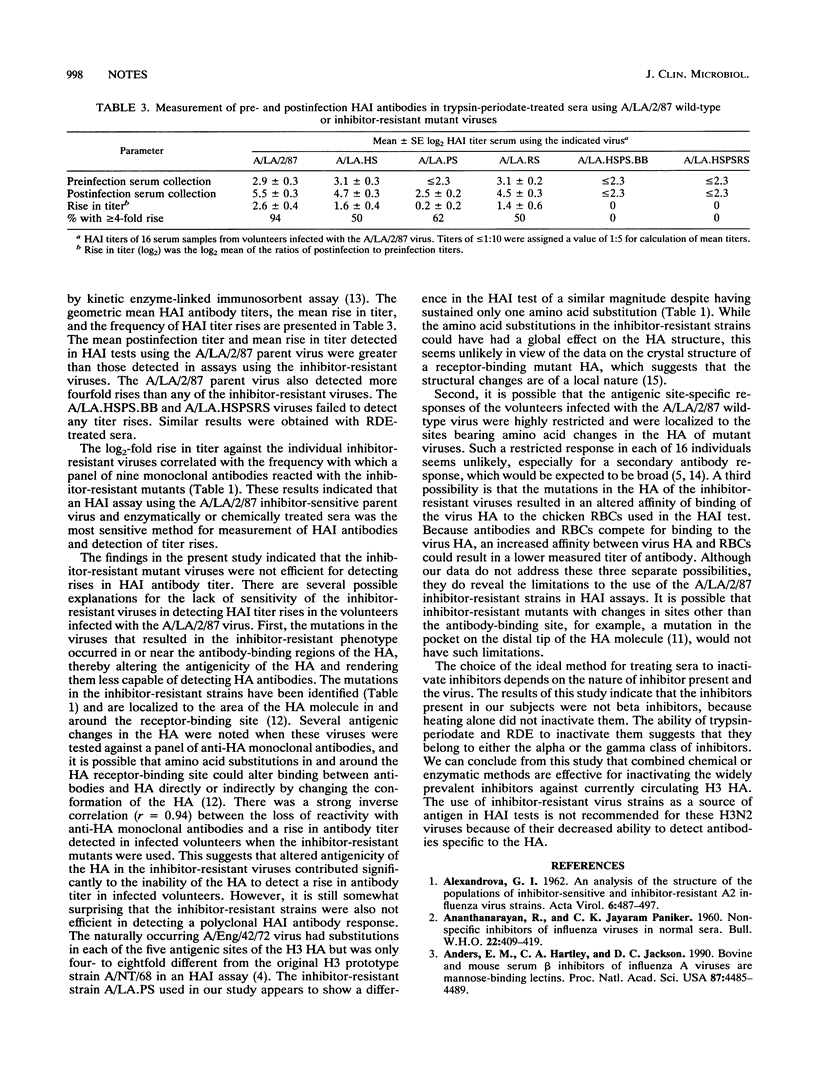
The A/Los Angeles/2/87 (H3N2) (A/LA/2/87) virus is sensitive to inhibitors of hemagglutination present in certain human sera. It was found that the effect of these inhibitors could be removed by treating sera with high-concentration receptor-destroying enzyme or trypsin-periodate or by using inhibitor-resistant viruses in the hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) test. Inhibitor-resistant viruses were not effective for detecting rises in antibody titers in the sera of volunteers infected with the A/LA/2/87 wild-type virus, while rises in antibody titer were readily detected in sera treated with trypsin-periodate and tested against A/LA/2/87 wild-type virus in an HAI test. It is therefore suggested that chemical or enzymatic methods be used to inactivate serum inhibitors and that standard virus be used in the HAI test for the currently circulating H3N2 viruses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDROVA G. I. An analysis of the structure of the populations of inhibitor-sensitive and inhibitor-resistant A2 influenza virus strains. Acta Virol. 1962 Nov;6:487–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANANTHANARAYAN R., PANIKER C. K. Non-specific inhibitors of influenza viruses in normal sera. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;22:409–419. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders E. M., Hartley C. A., Jackson D. C. Bovine and mouse serum beta inhibitors of influenza A viruses are mannose-binding lectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4485–4489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Sleigh M. J., Cox N. J., Kendal A. P. Antigenic drift in influenza virus H3 hemagglutinin from 1968 to 1980: multiple evolutionary pathways and sequential amino acid changes at key antigenic sites. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.52-60.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krizanová O., Rathová V. Serum inhibitors of myxoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;47:125–151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46160-6_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers G. N., Paulson J. C., Daniels R. S., Skehel J. J., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Single amino acid substitutions in influenza haemagglutinin change receptor binding specificity. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):76–78. doi: 10.1038/304076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan-Poirier K. A., Kawaoka Y. Distinct glycoprotein inhibitors of influenza A virus in different animal sera. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):389–395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.389-395.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. H., Banks S., Murphy B. R. Determination of antibody response to influenza virus surface glycoproteins by kinetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2034–2040. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2034-2040.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. L., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Comparative analyses of the specificities of anti-influenza hemagglutinin antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):124–128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.124-128.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyke Coelingh K. L., Winter C. C., Tierney E. L., Hall S. L., London W. T., Kim H. W., Chanock R. M., Murphy B. R. Antibody responses of humans and nonhuman primates to individual antigenic sites of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase and fusion glycoproteins after primary infection or reinfection with parainfluenza type 3 virus. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3833–3843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3833-3843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


