Abstract
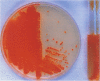
A methotrexate-containing medium for the detection of beta-hemolytic group B streptococci from clinical specimens on the basis of detection of pigment is described. The medium contained peptone, starch, serum, MgSO4, glucose, pyruvate, methotrexate (as pigment enhancer), phosphate-morpholine-propanesulfonic acid buffer, and selective agents. The recovery of beta-hemolytic group B streptococci was comparable to that obtained with selective broth.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher D. P., Wilson S., Fischer G. W. Comparison of commercially available group B streptococcal latex agglutination assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2895–2896. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2895-2896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Rosa M., Villareal R., Vega D., Miranda C., Martinezbrocal A. Granada medium for detection and identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):779–785. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.779-785.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam A. K. Rapid recognition of group-B Streptococci. Lancet. 1977 Jan 29;1(8005):256–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt K., Jacobs N. J. Characterization and incidence of pigment production by human clinical group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):105–107. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.105-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt K., Jacobs N. J. Improved medium for detecting pigment production by group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):379–380. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.379-380.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M. A., Bent J. M., West A. B. Detection and identification of group B streptococci by use of pigment production. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;36(3):350–352. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson K. M., Forsgren A. Evaluation of culture methods for isolation of group B streptococci. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;6(2):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon E. P., Noble M. A., Luther E. R., Wort A. J., Bent J., Swift M. Evaluation of a rapid method for the detection of vaginal group B streptococci in women in labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Mar 1;148(5):575–578. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(84)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapsall J. W. Pigment production by Lancefield-group-B streptococci (Streptococcus agalactiae). J Med Microbiol. 1986 Feb;21(1):75–81. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A. A selective and differential medium for group B streptococci. Med Lab Sci. 1982 Apr;39(2):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. E., Hammerberg O., Lyn P., Peng H. Q., Hunter D., Richardson H. Rapid detection of group B streptococcal carriage in parturient women using a modified starch serum medium. Clin Invest Med. 1988 Feb;11(1):52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Richardson H. A rapid method for detection of group B streptococcal colonization: testing at the bedside. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;76(5 Pt 1):882–885. doi: 10.1097/00006250-199011000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]