Abstract
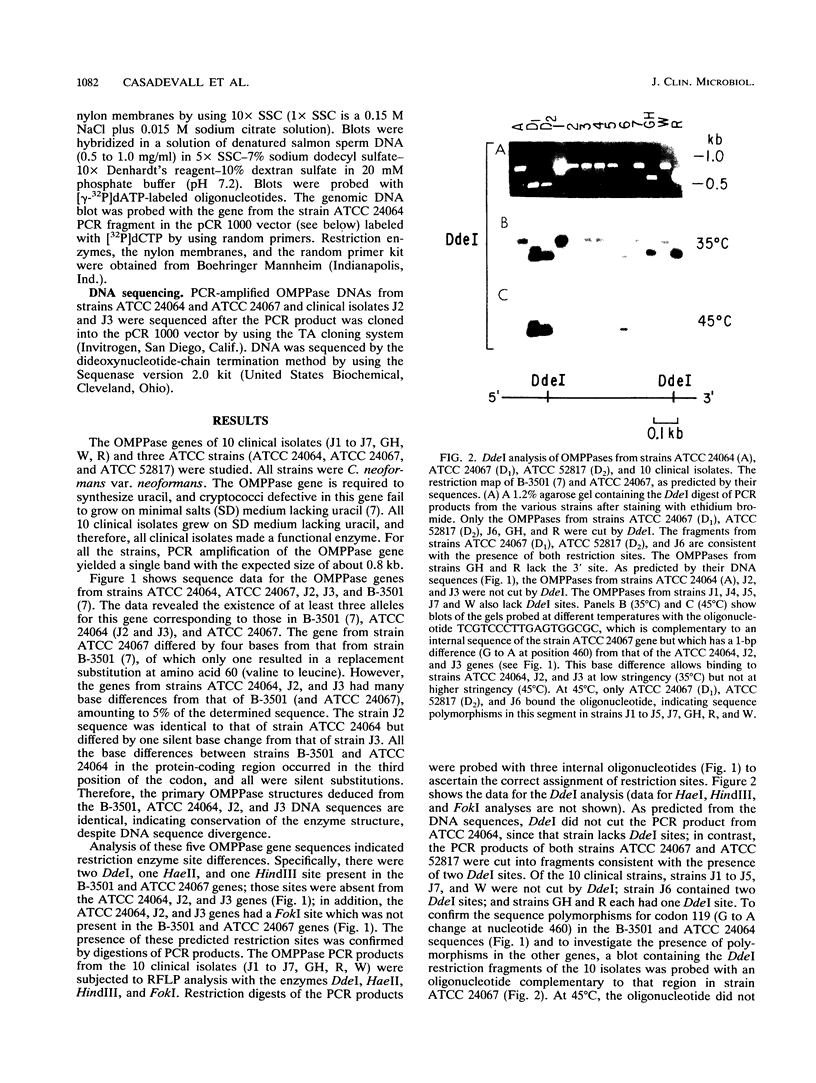
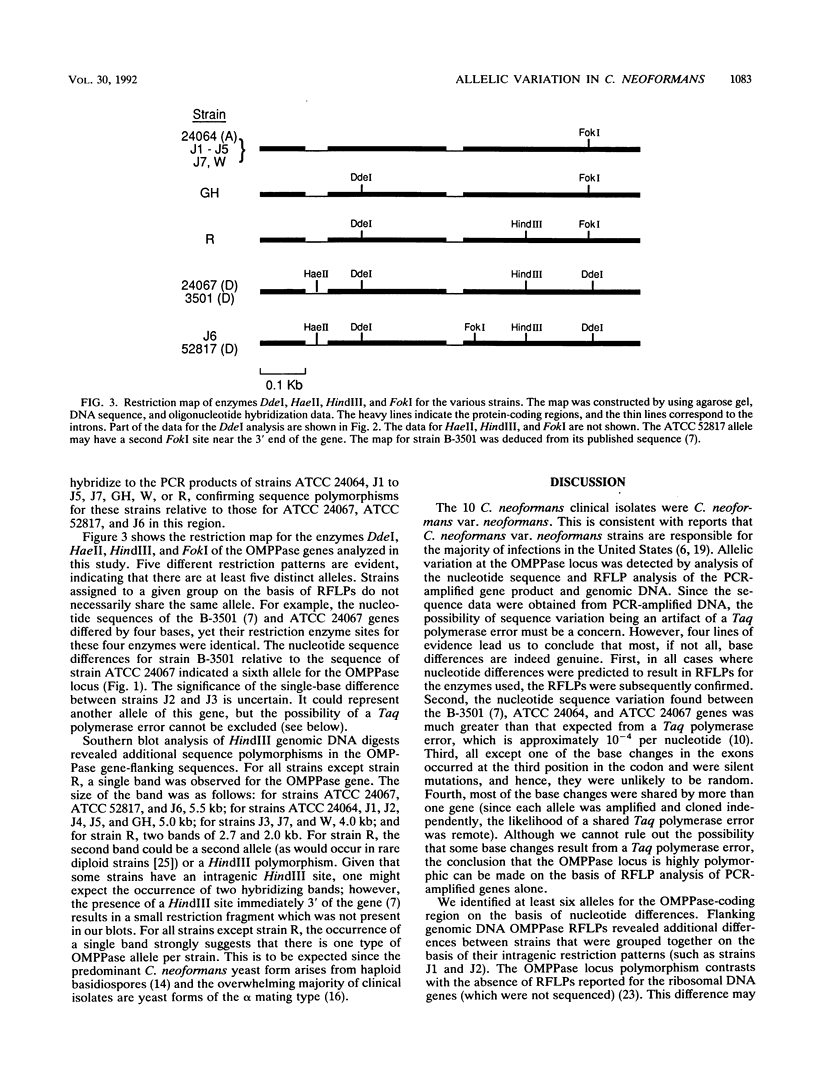
The orotidine monophosphate pyrophosphorylase (OMPPase) gene locus of the DNA of 13 Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans strains, including 10 recent clinical isolates, was studied by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms and nucleotide sequence analysis. The OMPPase locus (URA5) is highly polymorphic, and at least six alleles were identified. The nucleotide sequences of some alleles differed by up to 5%. The majority of the nucleotide polymorphisms in the protein-coding region occurred at the third codon position and were silent. The low frequency of replacement nucleotide substitutions relative to silent nucleotide substitutions implied that there is strong selection against amino acid changes in OMPPase. The allelic variation suggested that there is extensive genomic diversity among C. neoformans clinical isolates from one geographic area. The various alleles are potentially useful markers in the study of the population structure, epidemiology, and pathogenesis of C. neoformans strains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barcak G. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Comparative nucleotide sequence analysis of growth-rate-regulated gnd alleles from natural isolates of Escherichia coli and from Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):372–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.372-379.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisercić M., Feutrier J. Y., Reeves P. R. Nucleotide sequences of the gnd genes from nine natural isolates of Escherichia coli: evidence of intragenic recombination as a contributing factor in the evolution of the polymorphic gnd locus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3894–3900. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3894-3900.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. L., Sande M. A. Infections with Cryptococcus neoformans in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 21;321(12):794–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909213211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kwon-Chung K. J. Isolation of the URA5 gene from Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans and its use as a selective marker for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4538–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. H. Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii in Australia. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):430–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.430-431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. H., Pfeiffer T. J. Ecology, life cycle, and infectious propagule of Cryptococcus neoformans. Lancet. 1990 Oct 13;336(8720):923–925. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92283-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H. A., Gelfand D., Sninsky J. J. Recent advances in the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1643–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.2047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. S., Ayers D. J., Harrell A. C., Nicholas C. C. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of capsule mutants of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1292–1296. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1292-1296.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M. Nucleotide polymorphism at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):412–417. doi: 10.1038/304412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new genus, filobasidiella, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1975 Nov-Dec;67(6):1197–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new species of Filobasidiella, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans B and C serotypes. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):943–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Bennett J. E. Distribution of alpha and alpha mating types of Cryptococcus neoformans among natural and clinical isolates. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):337–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. Morphogenesis of Filobasidiella neoformans, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):821–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Polacheck I., Bennett J. E. Improved diagnostic medium for separation of Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans (serotypes A and D) and Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii (serotypes B and C). J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):535–537. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.535-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppel K., Crawford D., Beutler B. A tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-IgG heavy chain chimeric protein as a bivalent antagonist of TNF activity. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1483–1489. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo B. I., Barbour A. G. Cloning of 18S and 25S rDNAs from the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5596–5600. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5596-5600.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi M. G., Drutz D. J., Howell A., Sande M. A., Wofsy C. B., Hadley W. K. Serotypes of Cryptococcus neoformans in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):642–642. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrin R. E., Lancaster L. A., Davis C. E., Braude A. I. Differentiation of Cryptococcus neoformans serotypes by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;86(2):204–208. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibayrenc M., Kjellberg F., Arnaud J., Oury B., Brenière S. F., Dardé M. L., Ayala F. J. Are eukaryotic microorganisms clonal or sexual? A population genetics vantage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5129–5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma A., Kwon-Chung K. J. Restriction fragment polymorphism in mitochondrial DNA of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3353–3362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys R., Hester M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4238–4246. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L. The genetics of medically important fungi. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(2):99–170. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Jacobson E. S. Occurrence of diploid strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1231–1232. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1231-1232.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuger A., Louie E., Holzman R. S., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J. Cryptococcal disease in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Diagnostic features and outcome of treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Feb;104(2):234–240. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-2-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




