Abstract
Acquired homozygosity in the form of segmental acquired uniparental disomy (aUPD) has been described in follicular lymphoma (FL) and is usually due to mitotic recombination. SNP array analysis was performed with the use of the Affymetrix 10K 2.0 Gene-chip array on DNA from 185 diagnostic FL patients to assess the prognostic relevance of aUPD. Genetic abnormalities were detected in 118 (65%) of 182 patients. Number of abnormalities was predictive of outcome; more than 3 abnormalities was associated with inferior overall survival (OS; P < .03). Sites of recurrent aUPD were detected on 6p (n = 25), 16p (n = 22), 12q (n = 17), 1p36 (n = 14), 10q (n = 8), and 6q (n = 8). On multivariate analysis aUPD on 1p36 correlated with shorter OS (P = .05). aUPD on 16p was predictive of transformation (P = .03) and correlated with poorer progression-free survival (P = .02). aUPD is frequent at diagnosis of FL and affects probability of disease transformation and clinical outcome.
Introduction
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the most common indolent lymphoma and has marked heterogeneity in outcome,1–3 with frequent transformation to aggressive lymphoma affecting dramatically on overall survival (OS).4,5 The genomic hallmark of FL is t(14;18)(q32;q21) with many secondary abnormalities described,6,7 although few have confirmed prognostic value.6,8,9 The target genes remain largely unidentified.
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays allow detection of copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity (LOH) undetectable by previous methods, termed acquired uniparental disomy (aUPD). We and others have described aUPD in several hematologic malignancies,10,11 including FL.12,13 It is due to mitotic recombination or nondisjunction and may render a cell homozygous for a preexisting abnormality leading to clonal selection. Both FL series profiled to date have shown frequent, nonrandom regions of aUPD; however, its prognostic implication has not been addressed. We aimed to clarify the incidence of aUPD in 185 diagnostic FL patients and correlate this with clinical outcome.
Methods
Patient information
Tumor-extracted DNA from 185 untreated patients with FL presenting between 1974 and 2001 was obtained through the Lymphoma/Leukemia Molecular Profiling Project (LLMPP). Clinical data were available in 169 (93%) of 182 cases (Table S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article), transformation data were available for 141 cases, and 39 patients transformed to aggressive lymphoma. Research ethics committee approval was obtained from the London School of Medicine before initiation of the study.
10K GeneChip assay
SNP array genotyping was performed with the use of the 10K 2.0 GeneChip (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) as previously described.14 Signal intensity data were analyzed by GeneChip DNA analysis software, and GTYPE was used for calling genotypes. GOLF, an in-house software was used for copy number (CN) and UPD estimation (http://bioinformatics.cancerresearchuk.org/∼cazier01/). In the absence of germline controls the definition of aUPD was based on runs of consecutive homozygous markers defined as maximum 2 heterozygous calls in 50 consecutive SNPs. This was described by Gupta et al,15 and briefly this stringent criterion is based on 10K 2.0 data available from 90 independent germline samples from the ColoRectal Tumour Gene Identification (CORGI) study consortium giving a false-positive rate of 3.3%.16 CN was determined based on the log2 ratio of signal intensity from the lymphoma sample versus the pooled signal intensity of 10 unrelated control DNA samples. A ratio below 0.75 and above 1.25 on at least 3 consecutive SNPs was defined as a loss and a gain, respectively. The data were also analyzed with the use of Partek Genomics Suite (Partek, St Louis, MO). Sex chromosomes were excluded from analysis. SNP and gene annotations used National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) genome build 35.
Mutation analysis
Mutation screening was performed for the coding region of ID4, BRD2, HLA DQB1, SOCS1, CDK4, DYRK2, PTEN, and specific exons of NFKB217 (Table S2; protocols available on request).
Statistical analysis
The Fisher exact test and the Mann-Whitney U test were used to determine the association with clinical characteristics. OS was defined as the time from diagnosis to death or, for patients remaining alive, the time from diagnosis to last contact. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the time from diagnosis to first clinical progression, transformation, or death from any cause or, for patients remaining alive and disease-free, the time from diagnosis to last contact. Transformation to aggressive lymphoma was defined histologically or by clinical criteria. Kaplan-Meier survival estimates were obtained, and the log-rank test was used to compare differences between the groups with UPD versus those without. Multivariate Cox regression was used to determine whether regions of recurrent abnormality remained independently predictive of PFS and OS after adjusting for the International Prognostic Index (IPI). Statistical significance was set at P values less than .05.
Results and discussion
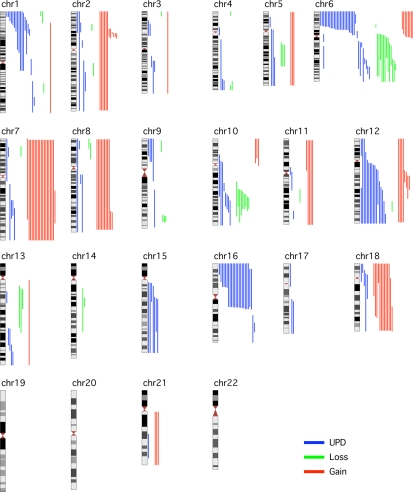
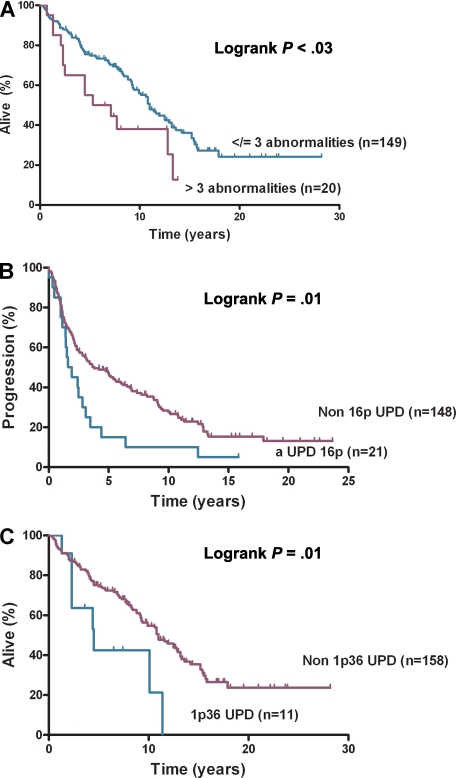
This study of 185 diagnostic FL cases addresses the clinical effect of aUPD, using the well-characterized LLMPP cases.18 It confirms earlier reports that aUPD is frequent at diagnosis of FL, occurs nonrandomly at recurring chromosomal locations,12,13 and now shows that aUPD is clinically important. SNP genotype call rates were greater than 90% for 182 of 185 cases analyzed. Abnormalities, including CN and copy-neutral changes, were detected in 118 (65%) of 182 cases (Figure 1). The number of abnormalities ranged from 0 to 9 (median, 1) with median LOH size of 48 Mb (range, 3.4-241 Mb). The 20 cases with more than 3 abnormalities at diagnosis had inferior OS (P = .03) compared with those with no more than 3 abnormalities (n = 149) (Figure 2A). aUPD was seen in 96 (81%) of 118 abnormal cases. Sites of recurrent aUPD were detected on chromosome 6p (n = 25), 16p (n = 22), 1p (n = 16), 12q (n = 17), 10q (n = 8), and 6q (n = 8). aUPD6p was observed in 25 (14%) of 182 cases (Table S3), and, as shown previously,13 aUPD6p was associated with aUPD1p (P = .002). aUPD16p occurred in 22 (12%) of 182 cases (Table S4) and in 10 of 22 cases transformed to aggressive lymphoma (P < .03).
Figure 1.
Global view of LOH, including aUPDs, losses, and gains in 182 FL samples across the 22 autosomes with the use of GOLF. Aberrations (gain in red, loss in green, and aUPD in blue) for individual samples are shown to the right of the chromosome.
Figure 2.
Survival and progression-free survival. (A) Overall survival by number of abnormalities, (B) progression-free survival by aUPD 16p, and (C) overall survival by aUPD 1p36.
aUPD16p correlated with poorer PFS (P = .01) (Figure 2B) but not OS and remained significant after adjusting for IPI (hazard ratio [HR], 1.80; confidence interval [CI], 1.09-2.98; P = .02). The association of aUPD16p with transformation (P = .03) represents a potential new risk factor for this event with a trend seen toward shorter time to transformation with aUPD16p (HR, 1.94; CI, 0.92-4.13; P = .08). Loss of 1p36 has been previously associated with poorer OS in FL.6 aUPD1p was present in 16 (9%) of 182 cases, and analysis showed that patients with aUPD1p36 (n = 14) had inferior OS (P = .01; Figure 2C) and PFS (P = .05 log-rank test). On multivariate analysis aUPD1p36 correlated with poorer OS after adjusting for IPI (HR, 2.10; CI, 1.00-4.43; P = .05) but not for PFS (HR, 1.70; CI, 0.90-3.18; P = .10). aUPD12q was present in 17 (9%) of 182 cases, 10q abnormalities (loss [n = 9] and aUPD [n = 8]) were seen in 17 (9%) of 182 cases, and chromosome 6q abnormalities were identified in 21 (11%) of 182 cases (loss [n = 13] and aUPD [n = 8]). Loss of 6q and inferior outcome have been shown previously in FL9; no significant associations were seen here for OS, PFS, or transformation with 6p, 6q, 10q, or 12q abnormalities. Recurrent regions of gain were identified on chromosome 2p (involving REL), chromosome 7, 8q, 12q (involving MDM2), and 18q, areas of gain previously described in FL.19–21 No statistically significant associations were seen here with clinical outcome. The regions of aUPD, copy number loss, and gain were verified with the use of Partek Genomic Suite.
The recurring regions of abnormality seen here showed considerable overlap with previous analysis that used cell-sorted FL samples, but the frequency of abnormalities was higher.13 This finding suggests that in FL purified tumor populations are preferred for accurate genotyping because DNA from nontumor cells will interfere with the detection of abnormalities. It is probable that some of the “normal” cases in this study may have low malignant cell content, below the threshold of detection of this array. Identification of gene lesions made homozygous has proven difficult in FL; in this series none of the target genes screened were mutated (Table S1), and it is probable that other selective mechanisms are important.22 The regions identified here were invariably large, pointing toward clonal events, but this may be an underestimate. Comparison of tumor and germline DNA is required to distinguish smaller somatic UPD from inherited events.23 This study focuses on recurrent regions of LOH making it less likely to detect a rarely reported constitutional abnormality.24 The use of higher resolution platforms may identify cases with more localized aberrations suitable for further characterization by next-generation sequencing.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Cancer Research UK, the Medical Research Council, and the National Institutes of Health (SPEC grant 5UO1CA114778). D.O. is supported by a Medical Research Council Clinical Research Fellow grant. C.O. is a Cancer Research UK Barts-Cambridge Molecular Pathology Clinical Research Fellow.
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: D.O. designed the study, performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; C.O., Y.Y., and D.W. performed research; M.G., R.W., J.G., B.D.Y., and J.-B.C. analyzed data; A.R., G.O., L.M.R., H.H., N.A.J., E.C., W.C.C., and R.D.G. collected data; and L.M.S., T.A.L., and J.F. designed the study and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Derville O'Shea, Centre for Medical Oncology, Barts and The London School of Medicine, Charterhouse Square, London EC1M6BQ, United Kingdom; e-mail: derville.oshea@cancer.org.uk.
References
- 1.Gallagher CJ, Gregory WM, Jones AE, et al. Follicular lymphoma: prognostic factors for response and survival. J Clin Oncol. 1986;4:1470–1480. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.10.1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fisher RI, LeBlanc M, Press OW, Maloney DG, Unger JM, Miller TP. New treatment options have changed the survival of patients with follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8447–8452. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liu Q, Fayad L, Cabanillas F, et al. Improvement of overall and failure-free survival in stage IV follicular lymphoma: 25 years of treatment experience at The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1582–1589. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.3696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bastion Y, Sebban C, Berger F, et al. Incidence, predictive factors, and outcome of lymphoma transformation in follicular lymphoma patients. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:1587–1594. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.4.1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Montoto S, Davies AJ, Matthews J, et al. Risk and clinical implications of transformation of follicular lymphoma to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2426–2433. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.3260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hoglund M, Sehn L, Connors JM, et al. Identification of cytogenetic subgroups and karyotypic pathways of clonal evolution in follicular lymphomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2004;39:195–204. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Horsman DE, Connors JM, Pantzar T, Gascoyne RD. Analysis of secondary chromosomal alterations in 165 cases of follicular lymphoma with t(14;18). Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001;30:375–382. doi: 10.1002/gcc.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tilly H, Rossi A, Stamatoullas A, et al. Prognostic value of chromosomal abnormalities in follicular lymphoma. Blood. 1994;84:1043–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Viardot A, Moller P, Hogel J, et al. Clinicopathologic correlations of genomic gains and losses in follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4523–4530. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Raghavan M, Lillington DM, Skoulakis S, et al. Genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism analysis reveals frequent partial uniparental disomy due to somatic recombination in acute myeloid leukemias. Cancer Res. 2005;65:375–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Walker BA, Leone PE, Jenner MW, et al. Integration of global SNP-based mapping and expression arrays reveals key regions, mechanisms, and genes important in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Blood. 2006;108:1733–1743. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-005496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fitzgibbon J, Iqbal S, Davies A, et al. Genome-wide detection of recurring sites of uniparental disomy in follicular and transformed follicular lymphoma. Leukemia. 2007;21:1514–1520. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ross CW, Ouillette PD, Saddler CM, Shedden KA, Malek SN. Comprehensive analysis of copy number and allele status identifies multiple chromosome defects underlying follicular lymphoma pathogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4777–4785. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Matsuzaki H, Loi H, Dong S, et al. Parallel genotyping of over 10,000 SNPs using a one-primer assay on a high-density oligonucleotide array. Genome Res. 2004;14:414–425. doi: 10.1101/gr.2014904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gupta M, Raghavan M, Gale RE, et al. Novel regions of acquired uniparental disomy discovered in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2008 doi: 10.1002/gcc.20573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kemp Z, Carvajal-Carmona L, Spain S, et al. Evidence for a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 3q21-q24 from a high-density SNP genome-wide linkage scan. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:2903–2910. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Neri A, Fracchiolla NS, Migliazza A, Trecca D, Lombardi L. The involvement of the candidate proto-oncogene NFKB2/lyt-10 in lymphoid malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996;23:43–48. doi: 10.3109/10428199609054800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dave SS, Wright G, Tan B, et al. Prediction of survival in follicular lymphoma based on molecular features of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2159–2169. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa041869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schwaenen C, Viardot A, Berger H, et al. Microarray-based genomic profiling reveals novel genomic aberrations in follicular lymphoma which associate with patient survival and gene expression status. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:39–54. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cheung KJ, Shah SP, Steidl C, et al. Genome-wide profiling of follicular lymphoma by array comparative genomic hybridization reveals prognostically significant DNA copy number imbalances. Blood. 2009;113:137–148. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-140616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Viardot A, Barth TF, Moller P, Dohner H, Bentz M. Cytogenetic evolution of follicular lymphoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2003;13:183–190. doi: 10.1016/s1044-579x(03)00014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Milani L, Gupta M, Andersen M, et al. Allelic imbalance in gene expression as a guide to cis-acting regulatory single nucleotide polymorphisms in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:e34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gondek LP, Tiu R, O'Keefe CL, Sekeres MA, Theil KS, Maciejewski JP. Chromosomal lesions and uniparental disomy detected by SNP arrays in MDS, MDS/MPD, and MDS-derived AML. Blood. 2008;111:1534–1542. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-092304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.O'Keefe CL, Gondek LP, Tiu R, et al. Identification of chromosomal abnormalities in healthy bone marrow using 250K SNP arrays [abstract]. Blood. 2006;108 Abstract 2076. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.