Abstract
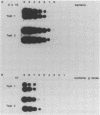
Three assays for the specific detection of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis by dot spot hybridization of polymerase chain reaction products were applied to fecal samples of dairy cattle. The first two tests used polymerase chain reaction primers and a DNA probe derived from M. paratuberculosis-specific sequences of the 16S rRNA gene and insertion element IS900, respectively. These two tests were carried out on spiked fecal samples to determine the detection limits. The 16S rRNA test was able to detect 10(7) bacteria per g of feces, and the IS900 test detected 10(4) to 10(5) per g of feces. Next, we studied the usefulness of these tests in a control program for paratuberculosis. Therefore, the tests and a third, commercially available, test (IDEXX Corp.) were used twice with an interval of 3 months on fecal samples of 87 cows from two dairy herds with a history of Johne's disease. We compared the results of these tests with those of culturing. This showed that the tests are specific but that the sensitivity ranged from 3 to 23%. Further improvement of the sensitivity is needed before the tests can be used in a control program to eradicate Johne's disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beerwerth W. Die Züchtung von Mykobakterien aus dem Kot der Haustiere und ihre Bedeutung für die Epidemiologie und Bekämpfung der Tuberkulose. Prax Pneumol. 1967 Apr;21(4):189–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedictus G., Dijkhuizen A. A., Stelwagen J. Economic losses due to paratuberculosis in dairy cattle. Vet Rec. 1987 Aug 15;121(7):142–146. doi: 10.1136/vr.121.7.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgrove G. S., Thoen C. O., Blackburn B. O., Murphy C. D. Paratuberculosis in cattle: a comparison of three serologic tests with results of fecal culture. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Feb;19(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Sockett D. C., Ridge S., Cox J. C. Evaluation of a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Johne's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):272–276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.272-276.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudswaard J., Gilmour N. J., Dijkstra R. G., van Beek J. J. Diagnosis of Johne's disease in cattle: a comparison of five serological tests under field conditions. Vet Rec. 1976 Jun 5;98(23):461–462. doi: 10.1136/vr.98.23.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley S. S., Splitter G. A., Welch R. A. Development of a diagnostic test for Johne's disease using a DNA hybridization probe. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1582–1587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1582-1587.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen J. B. An improved medium for culture of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis from bovine faeces. Acta Vet Scand. 1982;23(3):325–335. doi: 10.1186/BF03546784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. B., Moyle A. I., Himes E. M. Experimental vaccination of cattle against paratuberculosis (Johne's disease) with killed bacterial vaccines: a controlled field study. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Jan;39(1):65–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Larsen A. B., Kopecky K. E. Comparison of examination and test methods for early detection of paratuberculous cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Aug;29(8):1533–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. R., Mack W. N., Coates K. J., Hill J., Gill I., Sheldrick P. The sensitivity and specificity of a modified ELISA for the diagnosis of Johne's disease from a field trial in cattle. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Nov;25(2-3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A., Moriarty K. M., Scott D. B. A cloned DNA probe for the detection of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. N Z Vet J. 1989 Jun;37(2):47–50. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1989.35556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary P. H., Andersen P. R., Green E., Hermon-Taylor J., McFadden J. J. Use of highly specific DNA probes and the polymerase chain reaction to detect Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in Johne's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.933-937.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilesmith J. W. Johne's disease: a retrospective study of vaccinated herds in Great Britain. Br Vet J. 1982 Jul-Aug;138(4):321–331. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)31037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lisle G. W., Samagh B. S., Duncan J. R. Bovine paratuberculosis II. A comparison of fecal culture and the antibody response. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Apr;44(2):183–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Giessen J. W., Eger A., Haagsma J., Haring R. M., Gaastra W., van der Zeijst B. A. Amplification of 16S rRNA sequences to detect Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Apr;36(4):255–263. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-4-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]