Abstract
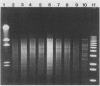
Nocardia isolations increased from 0.7 to 11.7/1,000 acid-fast bacillus and mycological cultures (P less than 0.000001). Only three isolations from one patient represented infection. Pseudoepidemic strain identity was confirmed by DNA fingerprinting; the isolate causing infection was distinct. The end of the pseudoepidemic was associated with changing the needle sterilizer and prolonging needle sterilization time on the BACTEC 460 machine. To our knowledge, this is the first reported Nocardia asteroides pseudoepidemic.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craven D. E., Lichtenberg D. A., Browne K. F., Coffey D. M., Treadwell T. L., McCabe W. R. Pseudobacteremia traced to cross-contamination by an automated blood culture analyzer. Infect Control. 1984 Feb;5(2):75–78. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700058987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier A. R., Rosenow E. C., 3rd, Roberts G. D. Nocardiosis. A review of 25 cases occurring during 24 months. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975 Nov;50(11):657–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhood G. P., Highsmith A. K., Allen J. R., Causey W. A., West C. M., Dixon R. E. Klebsiella pneumoniae pseudobacteremia due to cross-contamination of a radiometric blood culture analyzer. Infect Control. 1981 Nov-Dec;2(6):460–465. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700055727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. R., Miller A. D., Davis A. C. Blood culture cross contamination associated with a radiometric analyzer. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):567–570. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.567-570.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houang E. T., Lovett I. S., Thompson F. D., Harrison A. R., Joekes A. M., Goodfellow M. Nocardia asteroides infection--a transmissible disease. J Hosp Infect. 1980 Mar;1(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(80)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer A., Low D. E., Penner J., Ng J., Goldman C., Simor A. E. Use of molecular typing to study the epidemiology of Serratia marcescens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.55-58.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Goodman N. L., Heifets L., Larsh H. W., Lindner T. H., McClatchy J. K., McGinnis M. R., Siddiqi S. H., Wright P. Evaluation of the BACTEC radiometric method for recovery of mycobacteria and drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from acid-fast smear-positive specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):689–696. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.689-696.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosett W., Hodges G. R. Recent experiences with nocardial infections. Am J Med Sci. 1978 Nov-Dec;276(3):279–285. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197811000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahathevan M., Harvey F. A., Forbes G., O'Grady J., Gimson A., Bragman S., Jensen R., Philpott-Howard J., Williams R., Casewell M. W. Epidemiology, bacteriology and control of an outbreak of Nocardia asteroides infection on a liver unit. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Jun;18 (Suppl A):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90059-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steingrube V. A., Wallace R. J., Jr, Brown B. A., Pang Y., Zeluff B., Steele L. C., Zhang Y. Acquired resistance of Nocardia brasiliensis to clavulanic acid related to a change in beta-lactamase following therapy with amoxicillin-clavulanic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):524–528. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stropnik Z. Isolation of Nocardia asteroides from human skin. Sabouraudia. 1965 Feb;4(1):41–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokars J. I., McNeil M. M., Tablan O. C., Chapin-Robertson K., Patterson J. E., Edberg S. C., Jarvis W. R. Mycobacterium gordonae pseudoinfection associated with a contaminated antimicrobial solution. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2765–2769. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2765-2769.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]