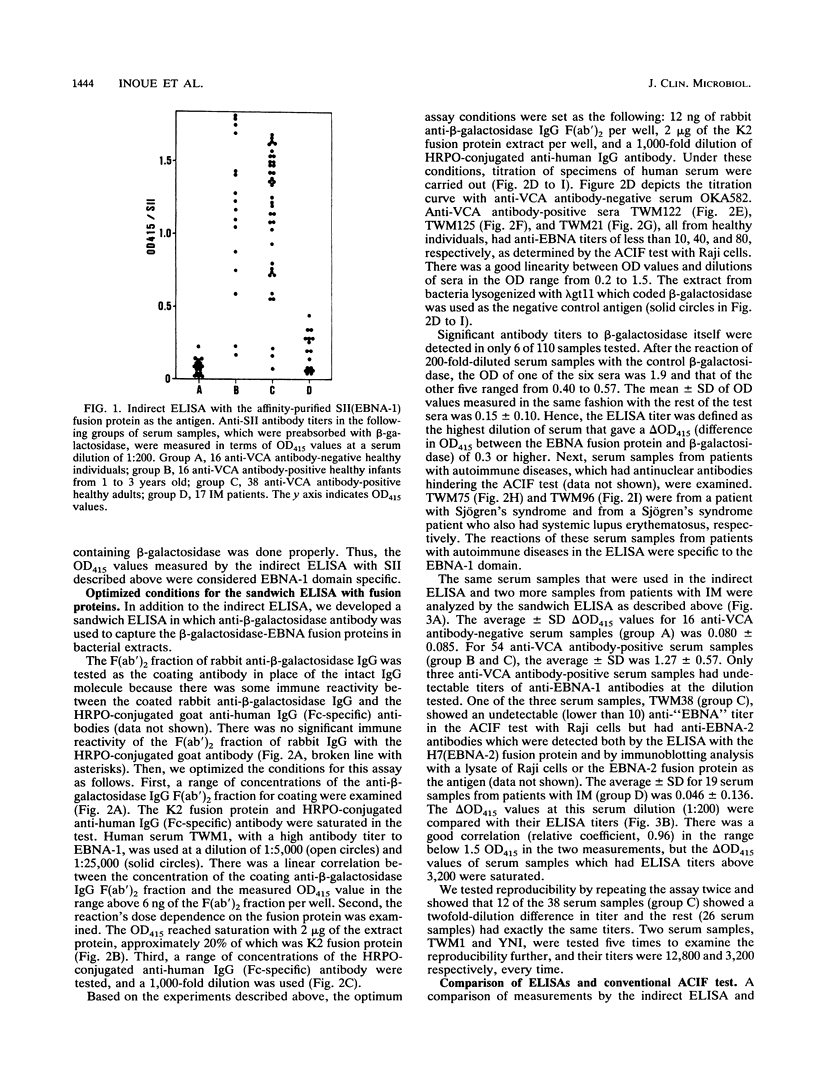
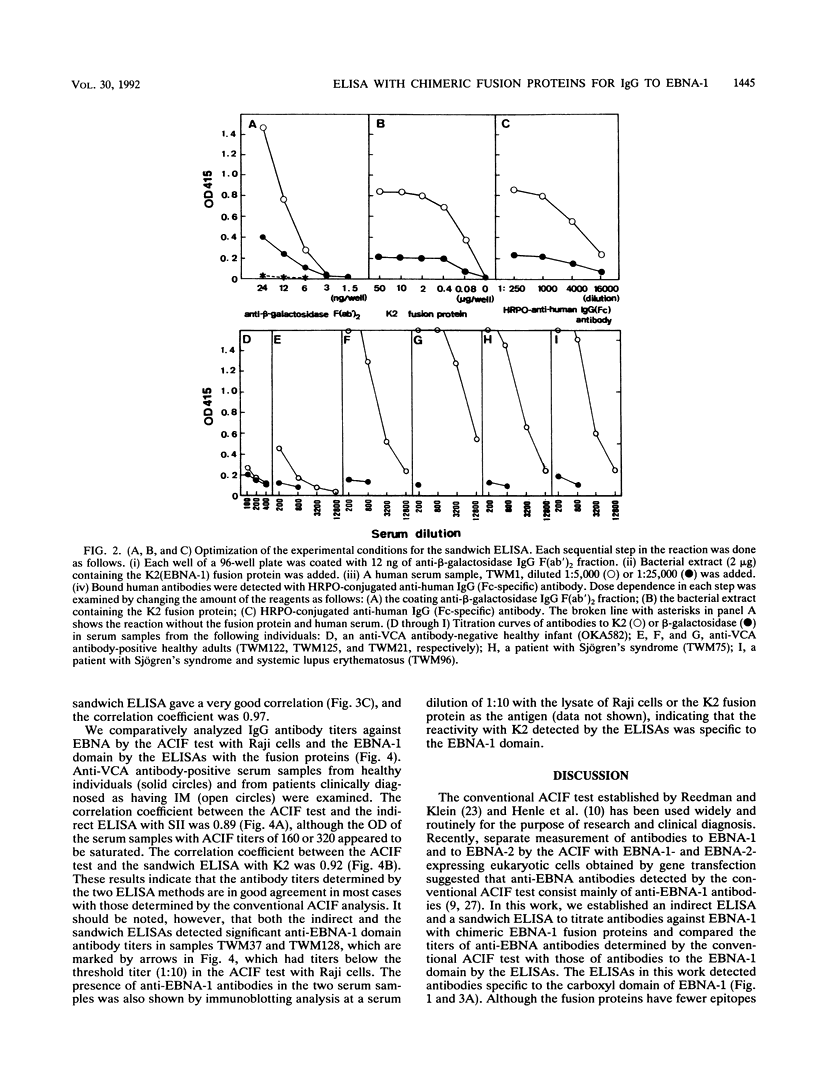
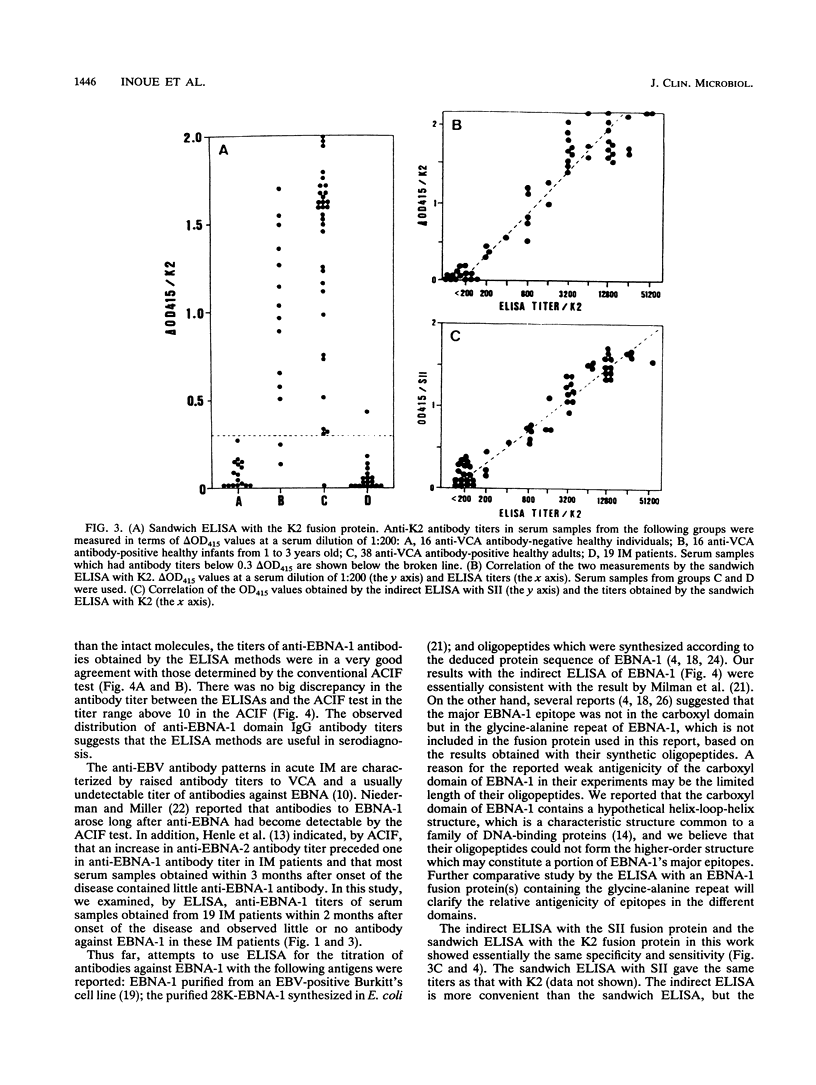
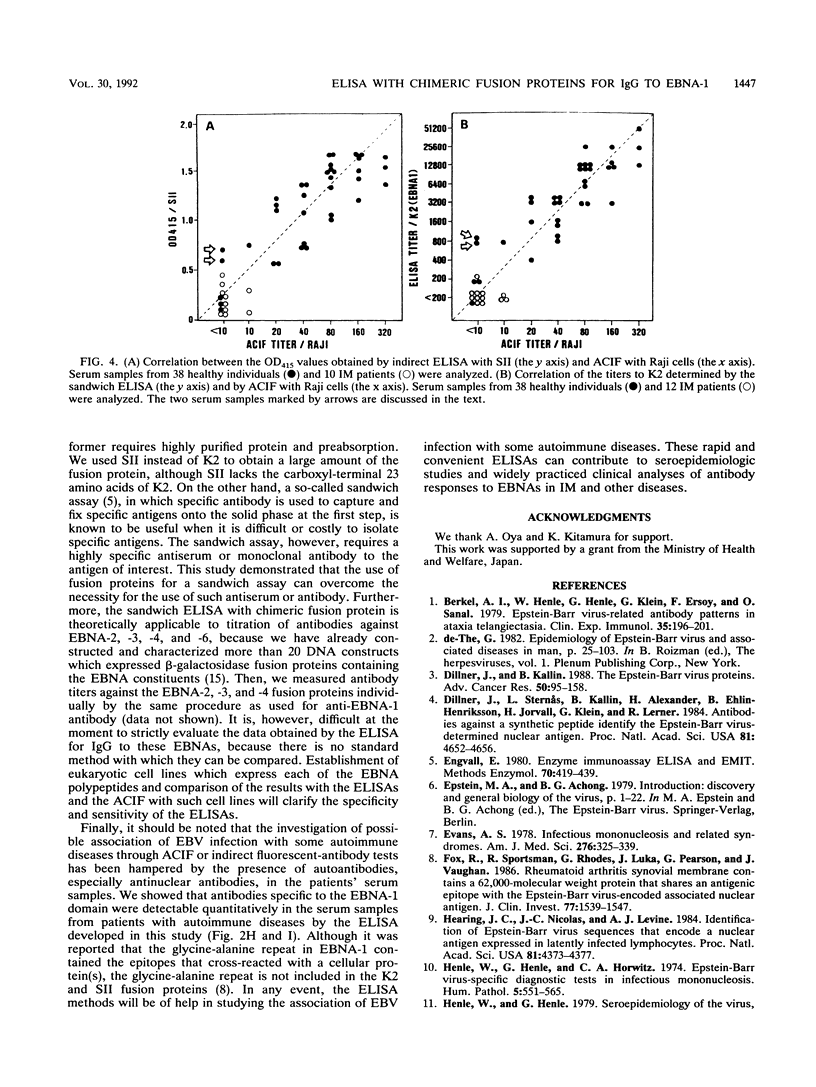
Abstract
Two new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) with chimeric fusion polypeptides for the detection of human antibodies specific to Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA-1) are described. One is an indirect ELISA with affinity-purified beta-galactosidase-EBNA-1 fusion protein as the antigen. The other is a "sandwich" assay based on the use of anti-beta-galactosidase antibody to capture beta-galactosidase-EBNA-1 fusion proteins in bacterial extracts. A good correlation was shown between antibody titers determined by the ELISA with the EBNA-1 fusion proteins and those determined by a conventional anticomplement immunofluorescence test which is being widely performed with Raji cells for the purpose of research and clinical diagnosis. The advantage of the ELISAs for seroepidemiologic studies on Epstein-Barr virus was demonstrated by sensitive detection of marginal immunoglobulin G antibody to the EBNA-1 domain in serum samples from patients with infectious mononucleosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkel A. I., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G., Ersoy F., Sanal O. Epstein-Barr virus-related antibody patterns in ataxia-telangiectasia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Feb;35(2):196–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B. The Epstein-Barr virus proteins. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;50:95–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S. Infectious mononucleosis and related syndromes. Am J Med Sci. 1978 Nov-Dec;276(3):325–339. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197811000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R., Sportsman R., Rhodes G., Luka J., Pearson G., Vaughan J. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane contains a 62,000-molecular-weight protein that shares an antigenic epitope with the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded associated nuclear antigen. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1539–1547. doi: 10.1172/JCI112469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing J. C., Nicolas J. C., Levine A. J. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus sequences that encode a nuclear antigen expressed in latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4373–4377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. E., Horwitz C. A. Epstein-Barr virus specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol. 1974 Sep;5(5):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Andersson J., Ernberg I., Klein G., Horwitz C. A., Marklund G., Rymo L., Wellinder C., Straus S. E. Antibody responses to Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA)-1 and EBNA-2 in acute and chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):570–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue N., Harada S., Honma T., Kitamura T., Yanagi K. The domain of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 essential for binding to oriP region has a sequence fitted for the hypothetical basic-helix-loop-helix structure. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90651-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue N., Harada S., Yanagi K. Synthesis of fusion proteins of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens in E. coli and their antigenicity. J Virol Methods. 1991 Feb-Mar;31(2-3):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90168-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Li Y., Kochoumian L. Preparation of protein conjugates via intermolecular disulfide bond formation. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1499–1506. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Kallin B., Dillner J., Andersson J., Jägdahl L., Lindvall A., Wahren B. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with two synthetic peptides of Epstein-Barr virus for diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):903–909. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Chase R. C., Pearson G. R. A sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against the major EBV-associated antigens. I. Correlation between ELISA and immunofluorescence titers using purified antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Szigeti R., Ernberg I., Masucci G., Klein G., Chessels J., Sieff C., Lie S., Glomstein A., Businco L. Cellular immune defects to Epstein-Barr virus-determined antigens in young males. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4284–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Scott A. L., Cho M. S., Hartman S. C., Ades D. K., Hayward G. S., Ki P. F., August J. T., Hayward S. D. Carboxyl-terminal domain of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen is highly immunogenic in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6300–6304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman J. C., Miller G. Kinetics of the antibody response to BamHI-K nuclear antigen in uncomplicated infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):346–349. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Carson D. A., Valbracht J., Houghten R., Vaughan J. H. Human immune responses to synthetic peptides from the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpold H., Rhodes G. H., Bloch P. L., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. The glycine-alanine repeating region is the major epitope of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA-1). J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneurin J. M., Lavoue M. F., Genoulaz O., Bornkamm G. W., Lenoir G. M. Antibody response against the Epstein-Barr virus-coded nuclear antigen2 (EBNA2) in different groups of individuals. Int J Cancer. 1987 Sep 15;40(3):349–353. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer E., Lenoir G. M., Virelizier J. L., Griscelli C. Epstein-Barr serology in immunodeficiencies: an attempt to correlate with immune abnormalities in Wiskott-Aldrich and Chediak-Higashi syndromes and ataxia telangiectasia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):249–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


