Abstract
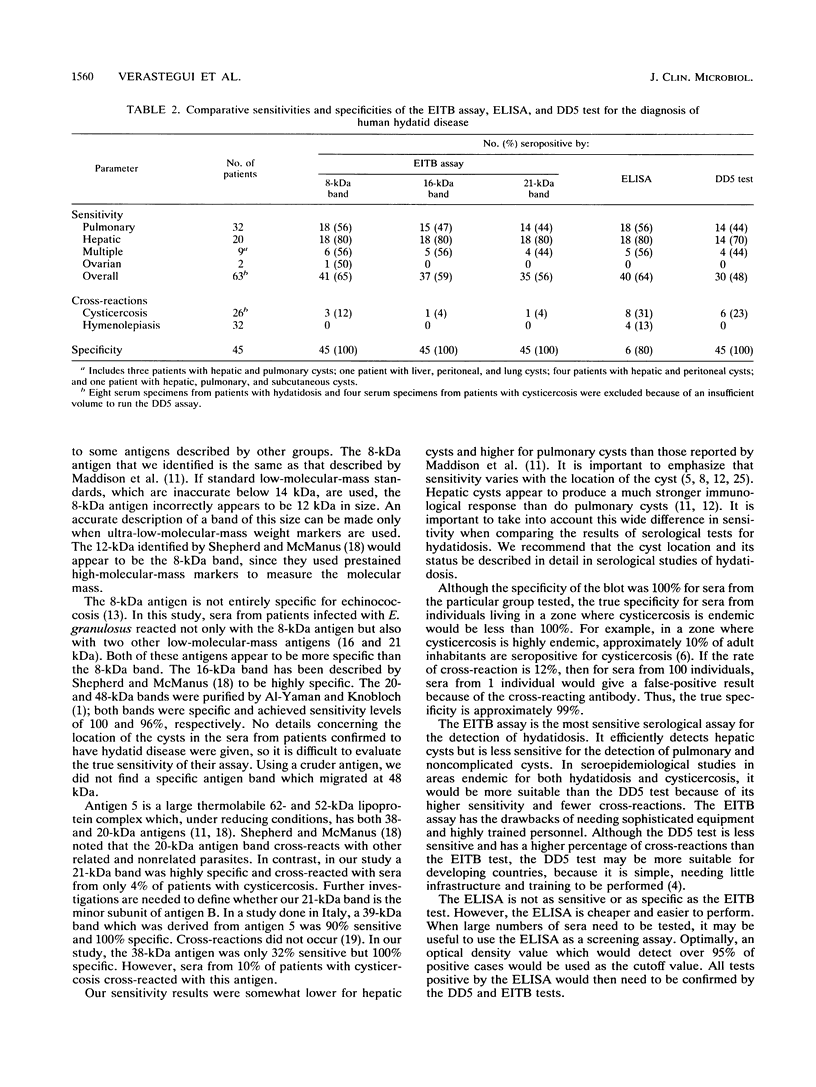
Sera from 71 patients with surgically confirmed hydatid disease (which is caused by Echinococcus granulosus) were studied by an enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot (EITB) assay. Sera from patients either with other cestode infections or with another illness were used as controls. Results of the EITB test for hydatidosis were compared with those of the double-diffusion (DD5) test and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In the EITB assay with bovine lyophilized hydatid fluid, three antigen bands of 8, 16, and 21 kDa were diagnostically important. The sensitivity of the assay by using these antigen bands was 80% for hepatic cysts, 56% for pulmonary cysts, and 56% for cysts located in multiple organs. In sera from controls, the specificity of the EITB assay was 100%. Cross-reactions to the 8-, 16-, and 21-kDa bands occurred, respectively, in 12, 4, and 4% of sera from patients with cysticercosis. No cross-reactions were noted in patients infected with Hymenolepis nana. The ELISA in which swine hydatid fluid was used as the antigen was as sensitive as the EITB test but was less specific (80%) and frequently cross-reacted with sera from patients with other cestode infections. The sensitivity of the DD5 test, which uses sheep hydatid fluid, was low (47%) , but its specificity was as high as that of the EITB assay. However, in patients with cysticercosis, cross-reactions were observed in 23% of sera tested. Despite the higher sensitivity found with the EITB assay, 23% (n = 5) of the serum samples that were positive by the DD5 test were not detected by the EITB assay. The EITB assay offers greater sensitivity and specificity than do the ELISA and the DD5 test. The highest proportion of hydatid cases is detected when the EITB and DD5 tests are run simultaneously.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltorti E. A., Varela-Díaz V. M. Detection of antibodies against Echinococcus granulosus arc 5 antigens by double diffusion test. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(3):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig P. S., Zeyhle E., Romig T. Hydatid disease: research and control in Turkana. II. The role of immunological techniques for the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacona A., Pini C., Vicari G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the serodiagnosis of hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):95–102. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D., De Wit M., De Rycke P. H. Hydatidosis in Belgium: analysis of larval Echinococcus granulosus by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1990 Jun;70(2):121–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson C. N., Romig T., Zeyhle E., Rees P. H., Were J. B. Portable ultrasound scanner versus serology in screening for hydatid cysts in a nomadic population. Lancet. 1987 Aug 1;2(8553):259–261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90839-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Slemenda S. B., Schantz P. M., Fried J. A., Wilson M., Tsang V. C. A specific diagnostic antigen of Echinococcus granulosus with an apparent molecular weight of 8 kDA. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Apr;40(4):377–383. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas M. G., Schantz P. M., Cannon L. T., Sr, Wahlquist S. P. Dot-ELISA for the rapid serodiagnosis of human hydatid disease. Diagn Immunol. 1986;4(6):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz P. M., Shanks D., Wilson M. Serologic cross-reactions with sera from patients with echinococcosis and cysticercosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jul;29(4):609–612. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., McManus D. P. Specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Sep;25(2):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusano A., Ioppolo S., Notargiacomo S., Ortona E., Riganó R., Teggi A., De Rosa F., Vicari G. Detection of antibodies against Echinococcus granulosus major antigens and their subunits by immunoblotting. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Mar-Apr;85(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölander A., Guisantes J. A., Torres-Rodriguez J. M., Schröder H. The diagnosis of human hydatidosis by measurement of specific IgE antibody by enzyme immunoassay. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(2):213–218. doi: 10.3109/00365548909039971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Brand J. A., Boyer A. E. An enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot assay and glycoprotein antigens for diagnosing human cysticercosis (Taenia solium). J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):50–59. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela Díaz V. M., Guarnera E. A., Coltorti E. A. Ventajas y limitaciones de los métodos inmunológicos y de detección por imágenes para el diagnóstico de la hidatidosis. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam. 1986 Apr;100(4):369–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Coltorti E. A., D'Alessandro A. Immunoelectrophoresis tests showing Echinococcus granulosus arc 5 in human cases of Echinococcus vogeli and cysticercosis-multiple myeloma. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 May;27(3):554–557. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Yaman F. M., Knobloch J. Isolation and partial characterization of species-specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Nov;37(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



