Abstract
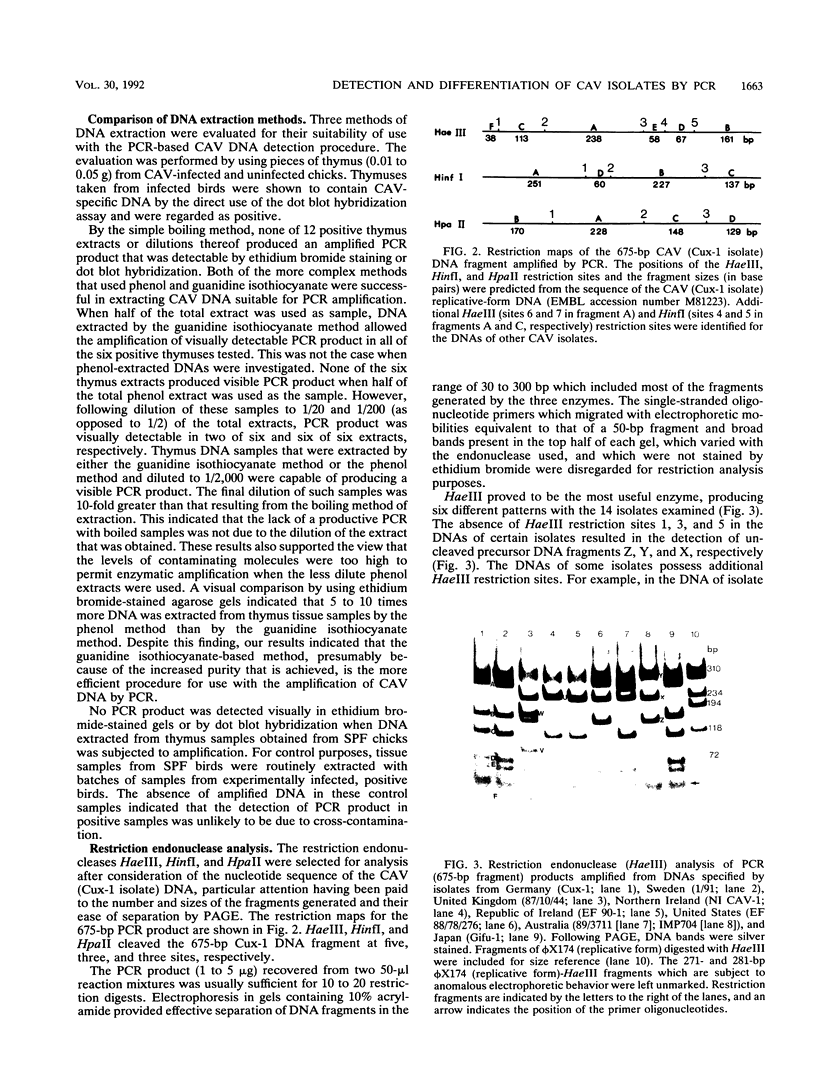
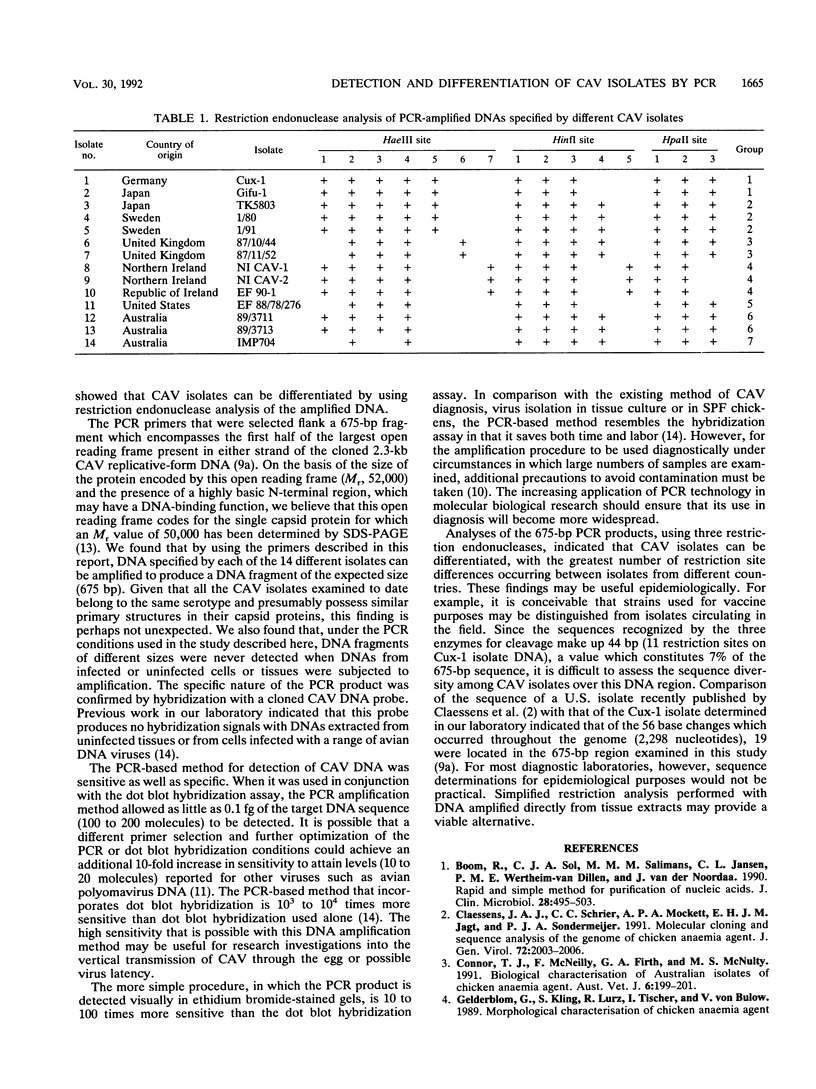
Complementary oligonucleotide primers which flank a 675-bp DNA fragment encompassing part of the putative gene for the capsid protein of chicken anemia virus (CAV) were used for the enzymatic amplification of CAV DNA by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Application of a dot blot hybridization assay by using a 32P-labeled cloned CAV DNA probe allowed PCR product amplified from as little as 0.1 fg of the target DNA sequence to be detected. When it was used for PCR amplification, DNA extracted from thymus tissue by a guanidine isothiocyanate-based method proved to be more efficient than that extracted by methods involving phenol or boiling. DNAs specified by 14 CAV isolates originating in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Germany, Sweden, the United States, Japan, and Australia were amplified. Restriction endonuclease analysis of the PCR-amplified DNAs with the enzymes HaeIII, HinfI, and HpaII indicated that the 14 CAV isolates can be assigned to seven groups, with isolates from different countries usually exhibiting the greatest number of restriction site differences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claessens J. A., Schrier C. C., Mockett A. P., Jagt E. H., Sondermeijer P. J. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the genome of chicken anaemia agent. J Gen Virol. 1991 Aug;72(Pt 8):2003–2006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-8-2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor T. J., McNeilly F., Firth G. A., McNulty M. S. Biological characterisation of Australian isolates of chicken anaemia agent. Aust Vet J. 1991 Jun;68(6):199–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1991.tb03192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Connor T. J., McNeilly F., Spackman D. Chicken anemia agent in the United States: isolation of the virus and detection of antibody in broiler breeder flocks. Avian Dis. 1989 Oct-Dec;33(4):691–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H. Polymerase chain reaction: trenches to benches. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1281–1285. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1281-1285.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phalen D. N., Wilson V. G., Graham D. L. Polymerase chain reaction assay for avian polyomavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1030-1037.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., Creelan J. L., Mackie D. P., Rixon F., McNulty M. S. Purification and biochemical characterization of chicken anaemia agent. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):819–823. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., Creelan J. L., McNulty M. S. Dot blot hybridization assay for chicken anemia agent using a cloned DNA probe. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):933–939. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.933-939.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., Niagro F. D., Ritchie B. W., Curran W., Allan G. M., Lukert P. D., Latimer K. S., Steffens W. L., 3rd, McNulty M. S. Comparison of three animal viruses with circular single-stranded DNA genomes. Arch Virol. 1991;117(1-2):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01310498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]