Abstract
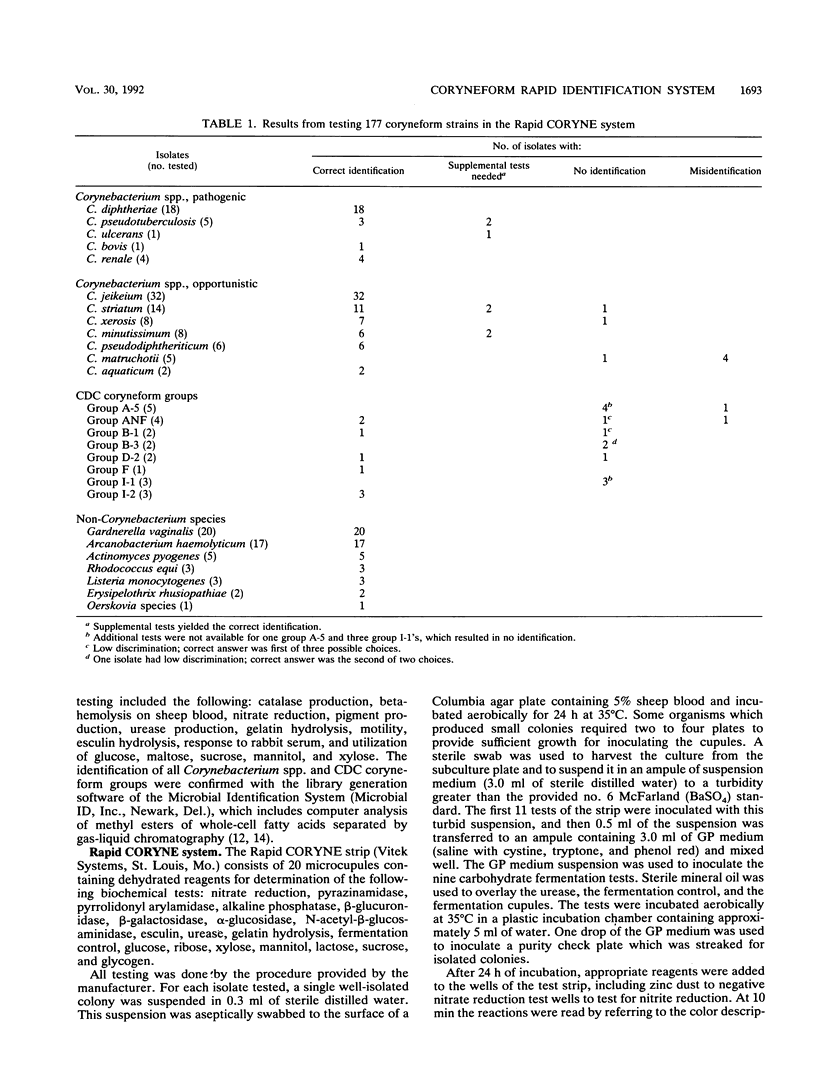
The Rapid CORYNE system for identification of aerobic, nonsporeforming, gram-positive rods was evaluated according to the manufacturer's instructions with 177 organisms. After inoculation with a heavy suspension of growth, strips containing 20 cupules were incubated for 24 h, reagents were added, and the results of 21 biochemical reactions were recorded as numerical profiles. The strains consisted of pathogenic species of the genus Corynebacterium, primarily C. diphtheriae (n = 29), opportunistic species of Corynebacterium including C. jeikeium (n = 75), recognized species of non-corynebacteria such as Gardnerella and Arcanobacterium (n = 51), and Centers for Disease Control (CDC) coryneform groups (n = 22). Results from single tests read after 24 h yielded correct identifications to species level with no additional tests for 26 (89.7%) of the pathogenic species; 64 (85.3%) of the opportunistic organisms; 51 (100%) of the non-corynebacteria, and 8 (36.4%) of the CDC coryneform groups. Supplemental tests produced the correct identification for three additional pathogenic isolates (100% total) and four additional isolates from the opportunistic species (90.6% total). Twelve of the 15 isolates not identified by the system were in the CDC coryneform groups. Four of the six misidentified and one of the unidentified isolates were C. matruchotii, which was not included in the data base. The system is an excellent rapid alternative to conventional biochemical tests.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coyle M. B., Groman N. B., Russell J. Q., Harnisch J. P., Rabin M., Holmes K. K. The molecular epidemiology of three biotypes of Corynebacterium diphtheriae in the Seattle outbreak, 1972-1982. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):670–679. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., Lipsky B. A. Coryneform bacteria in infectious diseases: clinical and laboratory aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):227–246. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freney J., Duperron M. T., Courtier C., Hansen W., Allard F., Boeufgras J. M., Monget D., Fleurette J. Evaluation of API Coryne in comparison with conventional methods for identifying coryneform bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):38–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.38-41.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasmick A. E., Bruckner D. A. Comparison of rapid identification method and conventional substrates for identification of Corynebacterium group JK isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1111–1112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1111-1112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hine J. E., Hill L. R., Lapage S. P. Corynebacterium spp in human disease. Lancet. 1978 Aug 12;2(8085):376–376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. C., Smith I. D., Anstey R. J., Thornley J. H., Rennie R. P. Rapid identification of antibiotic-resistant corynebacteria with the API 20S system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.245-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. R., Tillotson G. S. Identification of Actinomyces (Corynebacterium) pyogenes with the API 20 Strep system. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1865–1866. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1865-1866.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukwaya G. M., Welch D. F. Subgrouping of Pseudomonas cepacia by cellular fatty acid composition. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2640–2646. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2640-2646.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher D. G. Rapid identification of cell wall components as a guide to the classification of aerobic coryneform bacteria from human skin. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Nov;10(4):439–445. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-4-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifkin M., Gil G. M., Engwall C. Rapid identification of group JK and other corynebacteria with the Minitek system. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):177–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.177-180.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson G., Arora M., Robbins M., Holton J. Identification of Corynebacterium jeikeium and Corynebacterium CDC group D2 with the API 20 Strep system. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;7(5):675–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01964252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


