Abstract
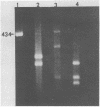
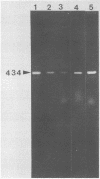
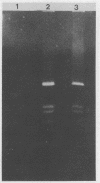
The recent discovery of cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis) infected with a typhuslike rickettsia (designated the ELB agent) raises the question of whether similar rickettsial infections exist in wild cat flea populations. We verified the presence of the ELB agent and Rickettsia typhi in urban and suburban areas of Los Angeles, Calif. Opossums trapped in close proximity to the residences of human murine typhus cases in Los Angeles county and other areas within the city of Los Angeles were tested for the presence of typhus group rickettsiae by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The presence of rickettsiae in the spleen tissues of three opossums (n = 9) and in 66 opossum fleas (n = 205) was determined by PCR and was verified by dot blot and Southern transfer hybridization. Further analysis of the amplified PCR products generated by a series of primer pairs derived from either the 17-kDa antigen gene or the citrate synthase gene revealed that both R. typhi and the ELB agent were present in the tested samples. Dual infection was not noted in the samples; however, the fleas were infected with either R. typhi or the ELB agent. The presence of the ELB agent in the cat flea population may have implications for public health. Whether this agent is responsible for the mild cases of human murine typhus in urban and suburban areas of Los Angeles or in other endemic foci remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. R., Schmidtmann E. T., Azad A. F. Infection of colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché), with a rickettsia-like microorganism. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Oct;43(4):400–409. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams W. H., Emmons R. W., Brooks J. E. The changing ecology of murine (endemic) typhus in Southern California. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Mar;19(2):311–318. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Regnery R. L., Carlone G. M., Tzianabos T., McDade J. E., Fu Z. Y., Bellini W. J. Sequence analysis of the 17-kilodalton-antigen gene from Rickettsia rickettsii. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2385–2390. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2385-2390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Tzianabos T. Comparative sequence analysis of a genus-common rickettsial antigen gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5199–5201. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5199-5201.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:553–569. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F., Sacci J. B., Jr, Nelson W. M., Dasch G. A., Schmidtmann E. T., Carl M. Genetic characterization and transovarial transmission of a typhus-like rickettsia found in cat fleas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):43–46. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F., Webb L., Carl M., Dasch G. A. Detection of rickettsiae in arthropod vectors by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:557–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhang-Azad A., Traub R., Baqar S. Transovarial transmission of murine typhus rickettsiae in Xenopsylla cheopis fleas. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):543–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3966162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhang-Azad A., Traub R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Rickettsia mooseri infection in the fleas Leptopsylla segnis and Xenopsylla cheopis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Nov;32(6):1392–1400. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Spruill C. L., Plikaytis B. D. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1576–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1576-1589.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schriefer M. E., Sacci J. B., Jr, Wirtz R. A., Azad A. F. Detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified malarial DNA in infected blood and individual mosquitoes. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Oct;73(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R., Wisseman C. L. The ecology of murine typhus-a critical review. Trop Dis Bull. 1978 Apr;75(4):237–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L., Carl M., Malloy D. C., Dasch G. A., Azad A. F. Detection of murine typhus infection in fleas by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):530–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.530-534.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Williamson L. R., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3564-3572.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]