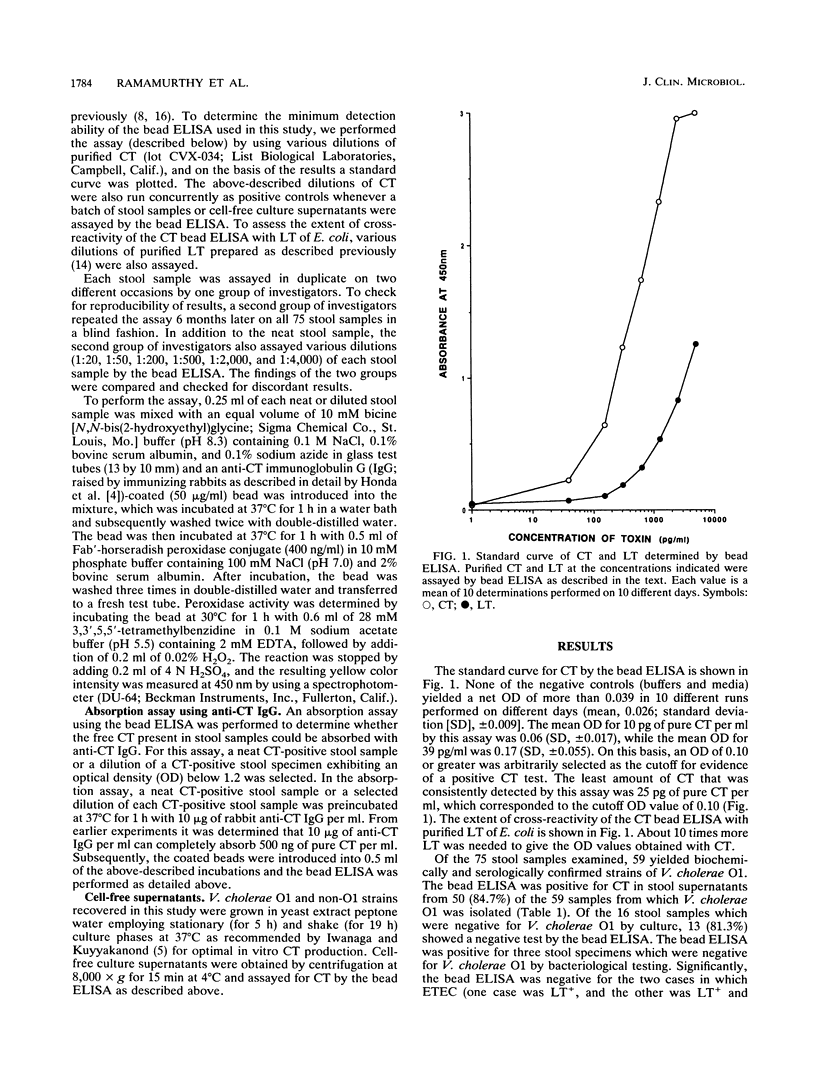
Abstract
A highly sensitive bead enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (bead ELISA) for detection of cholera toxin (CT) was evaluated for direct detection of CT from stool specimens of patients with acute secretory diarrhea. Of the 75 stool samples examined, 59 yielded biochemically, and serologically confirmed strains of Vibrio cholerae O1. The bead ELISA was positive for CT in stool supernatants in 50 (84.7%) of the 59 samples from which V. cholerae O1 was isolated. In addition, the bead ELISA was positive for three stool specimens which were negative by culture. The free CT present in 48 of the 50 stool samples positive by culture for V. cholerae O1 and for CT by bead ELISA was completely absorbed by anti-CT immunoglobulin G. All of the 59 strains of V. cholerae O1 biotype eltor isolated in this study produced in vitro CT. The concentration of CT present in the bead ELISA-positive stool samples ranged between 26 pg/ml and greater than 100 ng/ml. This evaluation study demonstrates that the bead ELISA is a sensitive and simple method for direct detection of CT in nonsterile stool samples, and we recommend routine use of this assay for detection of CT in stool samples and culture supernatants in clinical and reference laboratories.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida R. J., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Sowers E. G., Puhr N. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Wachsmuth I. K. Comparison of a latex agglutination assay and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting cholera toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.128-130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Verheart L., Ulyanco C. V., Santiago L. T. Detection of heat-labile enterotoxin-like activity in stools of patients with cholera and Escherichia coli diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):343–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.343-344.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Modified Elek test for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.1-5.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of special antibodies which react only with homologous enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):333–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.333-336.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga M., Kuyyakanond T. Large production of cholera toxin by Vibrio cholerae O1 in yeast extract peptone water. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2314–2316. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2314-2316.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Yolken R. H., Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L., Greenberg H. B., Huq I., Black R. W. Detection of Escherichia coli enterotoxins in stools. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.108-113.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., DuPont H. L., Wood L. V., Ericsson C. D. Comparison of methods to detect Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin in stool and cell-free culture supernatants. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.798-802.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku Y., Uesaka Y., Hirayama T., Takeda Y. Development of a highly sensitive bead-ELISA to detect bacterial protein toxins. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(8):807–816. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. Differential inhibitory effects of cholera toxoids and ganglioside on the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):1009–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthy T., Pal A., Nair G. B., Pal S. C., Takeda T., Takeda Y. Experience with toxin bead ELISA in cholera outbreak. Lancet. 1990 Aug 11;336(8711):375–376. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91917-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Saha M. R., Nair G. B., Das P., Niyogi S. K., De S. P., Bhattacharya S. K., Datta P., Dutta D., Pal S. C. Etiological spectrum of acute diarrhoea in hospitalised patients in Calcutta. Indian J Med Res. 1985 Oct;82:286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strombeck D. R., Harrold D. Binding of cholera toxin to mucins and inhibition by gastric mucin. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1266–1272. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1266-1272.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Taga S., Miwatani T. In vitro formation of hybrid toxins between subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and those of cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.341-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesaka Y., Otsuka Y., Kashida M., Oku Y., Horigome K., Nair G. B., Pal S. C., Yamasaki S., Takeda Y. Detection of cholera toxin by a highly sensitive bead-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb01641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Greenberg H. B., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):439–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



