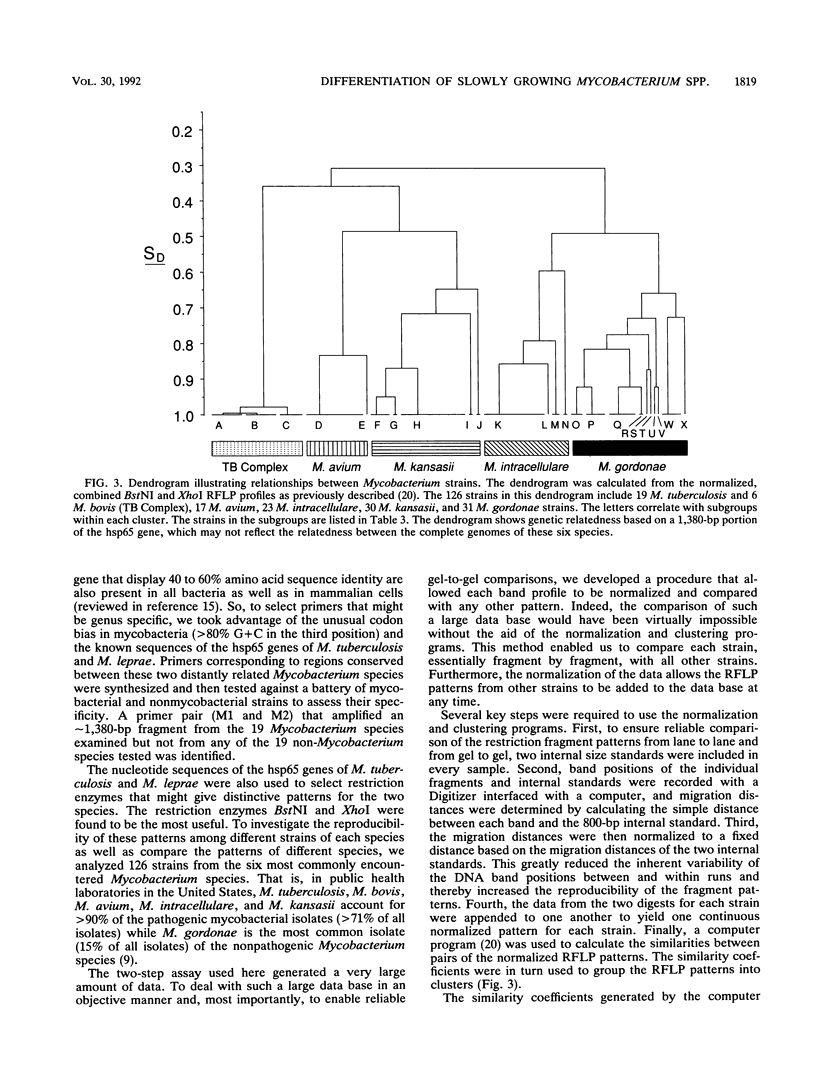
Abstract
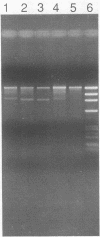
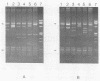
A two-step assay combining a gene amplification step and a restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis was developed to differentiate the Mycobacterium species that account for greater than 90% of potentially pathogenic isolates and greater than 86% of all isolates in clinical laboratories in the United States. These species are M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. avium, M. intracellulare, M. kansasii, and M. gordonae. With lysates of pure cultures as the template, two oligonucleotide primers that amplified an approximately 1,380-bp portion of the hsp65 gene from all 139 strains of 19 Mycobacterium species tested, but not from the 19 non-Mycobacterium species tested, were identified. Digestion of the amplicons from 126 strains of the six most commonly isolated Mycobacterium species with the restriction enzymes BstNI and XhoI in separate reactions generated restriction fragment patterns that were distinctive for each of these species, except for those of M. tuberculosis and M. bovis, which were not distinguishable. By including size standards in each sample, the restriction fragment profiles could be normalized to a fixed distance and the similarities of patterns could be calculated by using a computer-aided comparison program. The availability of this data base should enable the identification of an unknown Mycobacterium strain to the species level by a comparison of the restriction fragment pattern of the unknown with the data base of known patterns.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. F., Bloch A. B., Davidson P. T., Snider D. E., Jr Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 6;324(23):1644–1650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106063242307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noël A., Gicquel B., Lecossier D., Lévy-Frébault V., Nassif X., Hance A. J. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1069–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Nomaguchi H., Anderson D. C., Young R. A., Gillis T. P., Britton W. J., Ivanyi J., Kolk A. H., Closs O., Bloom B. R. Characterization of antibody-reactive epitopes on the 65-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1000–1003. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1000-1003.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Jost K. C., Jr, Kilburn J. O. Identification of mycobacteria by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2468–2472. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2468-2472.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Kilburn J. O. Identification of major slowly growing pathogenic mycobacteria and Mycobacterium gordonae by high-performance liquid chromatography of their mycolic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):50–53. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.50-53.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böddinghaus B., Rogall T., Flohr T., Blöcker H., Böttger E. C. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1751-1759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Cave M. D., Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):977–981. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. W., Patel R. J., Piessens W. F., Wirth D. F. Genus- and species-specific DNA probes to identify mycobacteria using the polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Apr;4(2):87–105. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C., Snider D. E., Jr Isolation of nontuberculous mycobacteria in the United States, 1980. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):829–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Grandchamp B., Lévy-Frébault V., Lecossier D., Rauzier J., Bocart D., Gicquel B. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of mycobacterial DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):843–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., Schuitema A. R., Van Soolingen D., Verstynen C. P., Bik E. M., Thole J. E., Kolk A. H., van Embden J. D. Specific detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1204–1213. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1204-1213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr Mycobacterium avium complex infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 9;324(19):1332–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105093241906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Neupert W. Heat shock proteins hsp60 and hsp70: their roles in folding, assembly and membrane translocation of proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:3–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J., Styblo K., Rouillon A. Tuberculosis in developing countries: burden, intervention and cost. Bull Int Union Tuberc Lung Dis. 1990 Mar;65(1):6–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. J., Fries J. W., Piessens W. F., Wirth D. F. Sequence analysis and amplification by polymerase chain reaction of a cloned DNA fragment for identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):513–518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.513-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. B., Gelber R. H., Shinnick T. M. Rapid and sensitive detection of Mycobacterium leprae using a nested-primer gene amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1913–1917. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1913-1917.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Plikaytis B. B. Numerical analysis of normalized whole-cell protein profiles after sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Sep;132(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-9-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogall T., Flohr T., Böttger E. C. Differentiation of Mycobacterium species by direct sequencing of amplified DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Sep;136(9):1915–1920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-9-1915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Sweetser D., Thole J., van Embden J., Young R. A. The etiologic agents of leprosy and tuberculosis share an immunoreactive protein antigen with the vaccine strain Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1932–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1932-1935.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M. The 65-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1080–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1080-1088.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sritharan V., Barker R. H., Jr A simple method for diagnosing M. tuberculosis infection in clinical samples using PCR. Mol Cell Probes. 1991 Oct;5(5):385–395. doi: 10.1016/s0890-8508(06)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styblo K. Overview and epidemiologic assessment of the current global tuberculosis situation with an emphasis on control in developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11 (Suppl 2):S339–S346. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_2.s339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Keulen W. J., De Bruyn J., Kolk A. H., Groothuis D. G., Berwald L. G., Tiesjema R. H., van Embden J. D. Characterization, sequence determination, and immunogenicity of a 64-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressed in escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1466–1475. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1466-1475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakrus M. A., Reeves M. W., Hunter S. B. Characterization of isolates of Mycobacterium avium serotypes 4 and 8 from patients with AIDS by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1474–1478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1474-1478.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]