Abstract
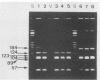
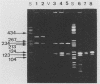
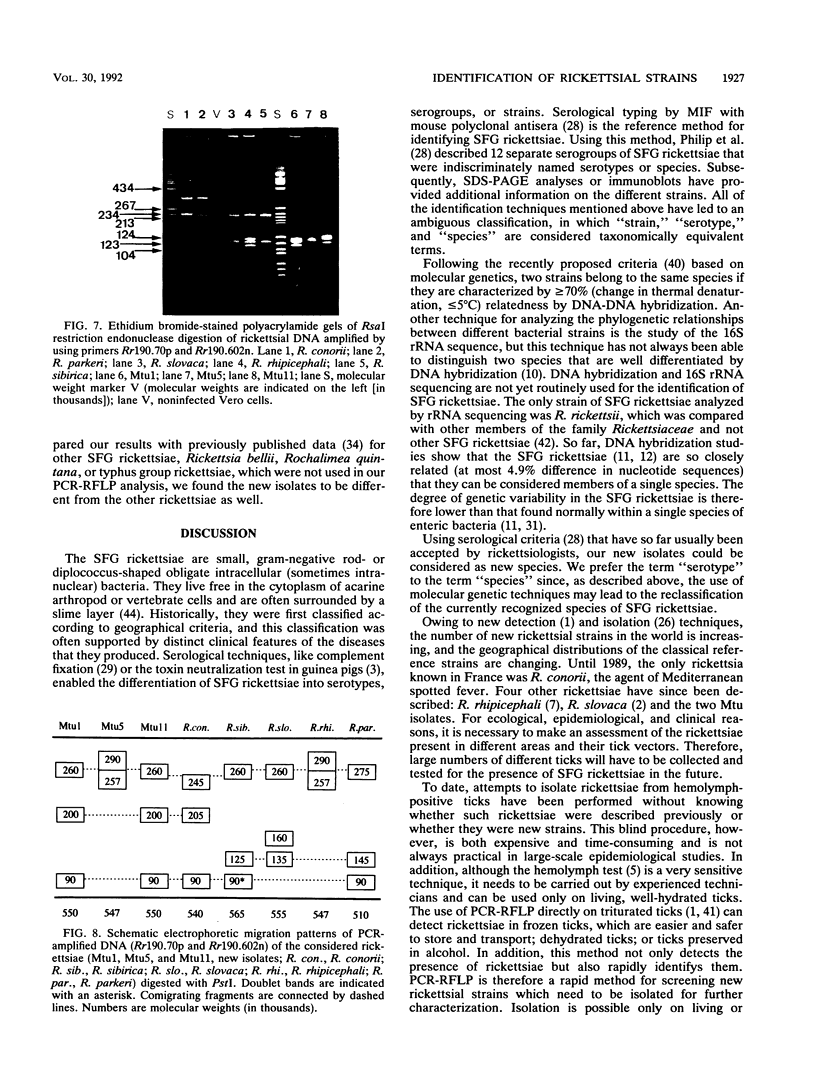
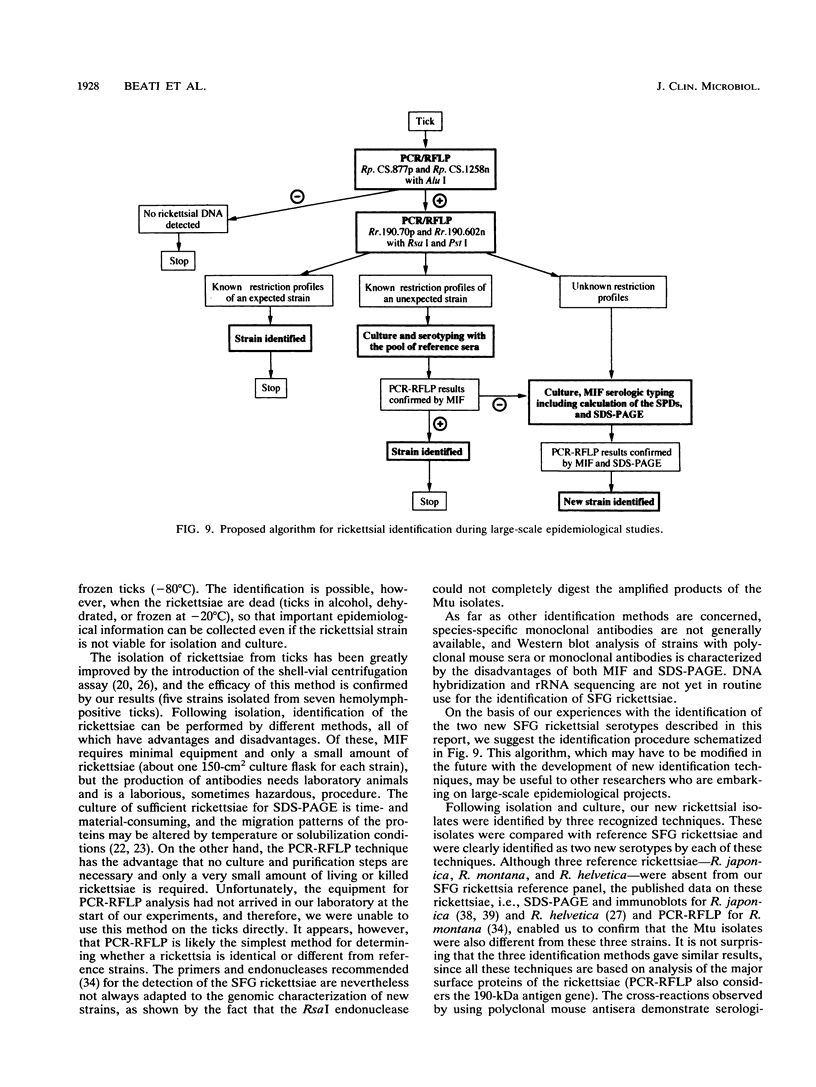
In 1990, 17 adult Rhipicephalus turanicus ticks were collected in the south of France. Two spotted fever group rickettsiae, Mtu1 and Mtu5, were isolated from the hemolymphs of two of these ticks by the centrifugation shell-vial technique by using HEL cells. These isolates were compared with reference spotted fever group rickettsial serotypes by using three identification methods: microimmunofluorescence serologic typing, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), and polymerase chain reaction followed by restriction endonuclease fragment length polymorphism analysis. The results obtained by all these techniques showed that Mtu1 and Mtu5 are each previously undescribed rickettsial serotypes. A comparison of the three methods used to identify the isolates led us to the conclusion that, in large-scale epidemiological studies, the simplest way to identify isolates in ticks is to first use the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis directly on triturated ticks as a screening method to detect interesting rickettsiae, and then attempt to isolate rickettsiae from ticks for identification by microimmunofluorescence and SDS-PAGE, both of which are time-consuming and expensive to carry out.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azad A. F., Webb L., Carl M., Dasch G. A. Detection of rickettsiae in arthropod vectors by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:557–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., STOENNER H. G. Immunologic relationships among the spotted fever group of rickettsias determined by toxin neutralization tests in mice with convalescent animal serums. J Immunol. 1960 Feb;84:171–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. Hemolymph test. A technique for detection of rickettsiae in ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Nov;19(6):1010–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan M. Y., Yu X. J., Walker D. H. Antigenic analysis of Chinese strains of spotted fever group rickettsiae by protein immunoblotting. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Nov;39(5):497–501. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Wisotzkey J. D., Jurtshuk P., Jr How close is close: 16S rRNA sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):166–170. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst P. A., Poetter K. P., Pretzman C., Perlman P. S. Molecular genetics of populations of intracellular bacteria: the spotted fever group rickettsiae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:430–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilot B., Jarry D., Pautou G., Moncada E. Biotopes suburbains à Rhipicephalus turanicus (Pomerancev, Matikasvili, Lototzki, 1940) (Acarina, Ixodoidea): étude préliminaire. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1977 May-Jun;52(3):353–362. doi: 10.1051/parasite/1977523353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilot B., Laforge M. L., Pichot J., Raoult D. Relationships between the Rhipicephalus sanguineus complex ecology and Mediterranean spotted fever epidemiology in France. Eur J Epidemiol. 1990 Dec;6(4):357–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00151708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilot B., Pautou G. L'évolution des populations de tiques (Ixodidae et Argasidae) en relation avec l'artificialisation des milieux dans les Alpes françaises. Acta Trop. 1982 Dec;39(4):337–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilot B., Pautou G. Répartititon et intérêt épidémiologique de Rhipicepohalus turanicus (Pomerantsev, Matikasvili, Lototzki, 1940) (Acarina, Ixodoidea). Ecologie de cette espèce dans le Midi méditerranéen français. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1981;56(5):547–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Raoult D., Fox J., Han Y., Elliott L. B., Rawlings J. Cross-reaction of immune sera from patients with rickettsial diseases. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jul;29(3):199–202. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-3-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. J., Mason P. R. Serological typing of spotted fever group Rickettsia isolates from Zimbabwe. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2302–2304. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2302-2304.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. J., Raoult D., Mason P. R. Isolation of spotted fever group rickettsias from triturated ticks using a modification of the centrifugation-shell vial technique. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 May-Jun;85(3):397–398. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90303-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Lenz B., Walker D. H. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize heat-labile epitopes on surface proteins of spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2587–2593. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2587-2593.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Walker D. H. Biological characterization of major polypeptides on the surface of spotted fever group rickettsiae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:389–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C. E., Jr, Walters V. D. Comparative electrophoresis of spotted fever group rickettsial proteins. Life Sci. 1978 Feb;22(7):583–587. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Raoult D., Gilot B. Isolation by a sensitive centrifugation cell culture system of 52 strains of spotted fever group rickettsiae from ticks collected in France. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1597–1599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1597-1599.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rageau J. Répartition géographique et rôle pathogènes des tiques (acariens: Argasidae et Ixodidae) en France. Wiad Parazytol. 1972;18(4):707–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph D., Pretzman C., Daugherty N., Poetter K. Genetic relationships among the members of the family rickettsiaceae as shown by DNA restriction fragment polymorphism analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:541–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Dasch G. A. Line blot and western blot immunoassays for diagnosis of Mediterranean spotted fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2073–2079. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2073-2079.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Toga B., Chaudet H., Chiche-Portiche C. Rickettsial antibody in southern France: antibodies to Rickettsia conorii and Coxiella burnetii among urban, suburban and semi-rural blood donors. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1987;81(1):80–81. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(87)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Spruill C. L., Plikaytis B. D. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1576–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1576-1589.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. G., Wisseman C. L., Jr Tick-borne rickettsiae of the spotted fever group in West Pakistan. II. Serological classification of isolates from West Pakistan and Thailand: evidence for two new species. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Jan;97(1):55–64. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J. Some contributions of electron microscopy to the study of the rickettsiae. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 May;7(3):200–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00145667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarasevich I. V., Makarova V. A., Fetisova N. F., Stepanov A. V., Miskarova E. D., Raoult D. Studies of a "new" rickettsiosis "Astrakhan" spotted fever. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 May;7(3):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00145681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Yu X. J., Uchiyama T., Walker D. H. Identification of a unique spotted fever group rickettsia from humans in Japan. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1122–1126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Uchida T., Walker D. H. Species-specific monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsia japonica, a newly identified spotted fever group rickettsia. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1177–1180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1177-1180.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L., Carl M., Malloy D. C., Dasch G. A., Azad A. F. Detection of murine typhus infection in fleas by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):530–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.530-534.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Dobson M. E., Samuel J. E., Dasch G. A., Mallavia L. P., Baca O., Mandelco L., Sechrest J. E., Weiss E., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic diversity of the Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4202–4206. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4202-4206.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]