Abstract
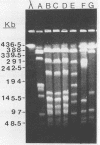
Campylobacter hyointestinalis was isolated from five members of the same family who had previously consumed raw milk. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of genomic DNAs from the five strains, after digestion with restriction endonuclease SalI, revealed that three strains had identical genome patterns and therefore appeared to be related, whereas the other two had completely different genome patterns and appeared to be unrelated. We report here for the first time the isolation of C. hyointestinalis from family members who had consumed raw milk. Our study also demonstrates the usefulness of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for epidemiologic studies of this unusual campylobacter.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Hutchinson D. N., Coates D. Blood-free selective medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):169–171. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.169-171.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang N., Taylor D. E. Use of pulsed-field agarose gel electrophoresis to size genomes of Campylobacter species and to construct a SalI map of Campylobacter jejuni UA580. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5211–5217. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5211-5217.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Griffin P. M., Barrett T. J., Schmid G. P., Baker C. N., Lambert M. A., Brenner D. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis associated with human gastrointestinal disease in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.685-691.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki T., Takeuchi N., Liu S. L., Kai A., Yamamoto H., Yabuuchi E. Small-scale DNA preparation for rapid genetic identification of Campylobacter species without radioisotope. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(2):141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Ward G. E., Chang K., Kurtz H. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis (new species) isolated from swine with lesions of proliferative ileitis. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Mar;44(3):361–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill B. D., Thomas R. J., Mackenzie A. R. Campylobacter hyointestinalis-associated enteritis in Moluccan rusa deer (Cervus timorensis subsp. Moluccensis). J Comp Pathol. 1987 Nov;97(6):687–694. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(87)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyama S., Ohta M., Shimokata K., Kato N., Takeuchi J. Genomic DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiological marker for study of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2690–2695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2690-2695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minet J., Grosbois B., Megraud F. Campylobacter hyointestinalis: an opportunistic enteropathogen? J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2659–2660. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2659-2660.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. G., Singh K. V., Murray B. E. DNA fingerprinting of Enterococcus faecium by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis may be a useful epidemiologic tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2752–2757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2752-2757.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Firehammer B. D., Border M. M., Shoop D. S. Prevalence of enteric pathogens in the feces of healthy beef calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Aug;45(8):1544–1548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya T., Kubo M., Watase H. Campylobacter species isolated from swine with lesions of proliferative enteritis. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Apr;47(2):285–294. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic-Uroic T., Patton C. M., Nicholson M. A., Kiehlbauch J. A. Evaluation of the indoxyl acetate hydrolysis test for rapid differentiation of Campylobacter, Helicobacter, and Wolinella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2335–2339. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2335-2339.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Fennell C. L., Tenover F. C., Wezenberg J. M., Perine P. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Campylobacter cinaedi (sp. nov.) and Campylobacter fennelliae (sp. nov.): two new Campylobacter species associated with enteric disease in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Chang N., Taylor D. E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli genomic DNA and its epidemiologic application. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]