Abstract
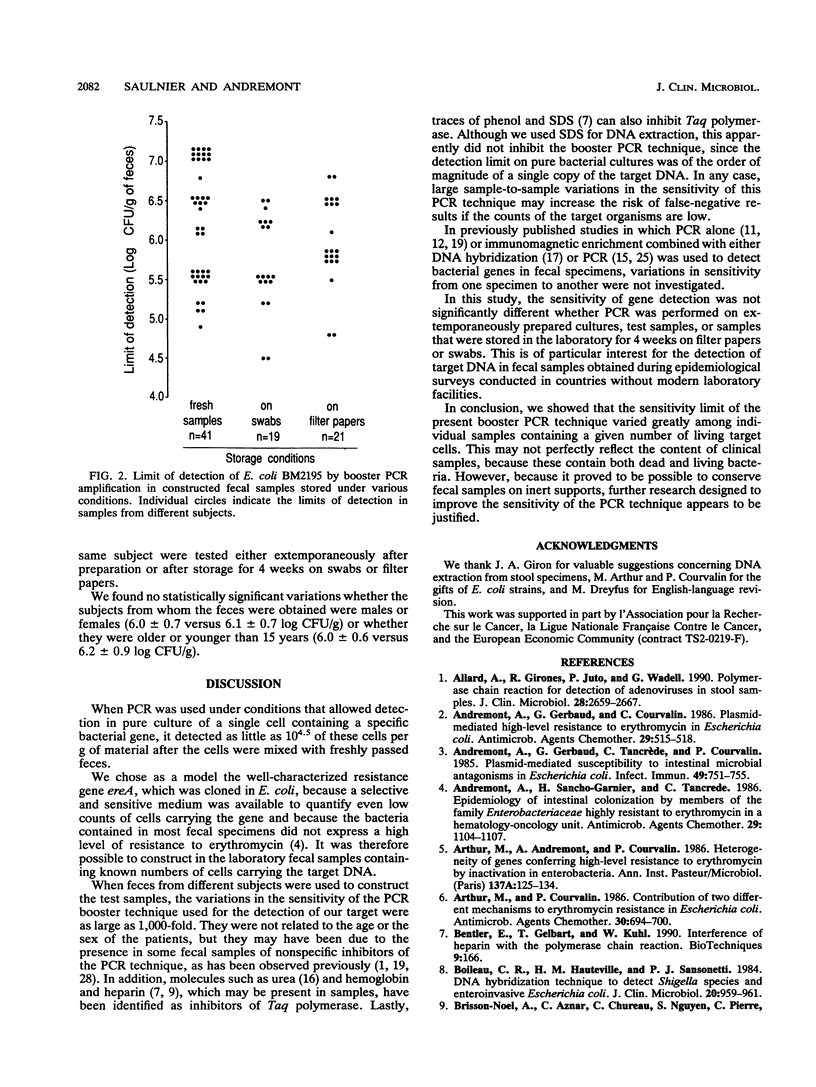
A 321-bp fragment intragenic to the gene ereA carried by Escherichia coli BM2195 was used as a model target to study the conditions under which DNA amplification by booster polymerase chain reaction can be used to detect specific bacterial DNA sequences in fecal specimens. When target E. coli cells were mixed with 41 freshly obtained fecal specimens, the polymerase chain reaction detection limit varied from 4.5 to 7.1 log CFU/g of feces, depending on the individual fecal specimen used to prepare the test sample. These variations were not statistically related to the sex or age of the subject from whom the specimen was obtained. After storage of the samples for 4 weeks at room temperature on swabs or filter papers, no loss in sensitivity was observed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard A., Girones R., Juto P., Wadell G. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of adenoviruses in stool samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2659–2667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2659-2667.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated high-level resistance to erythromycin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):515–518. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Gerbaud G., Tancrède C., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated susceptibility to intestinal microbial antagonisms in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):751–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.751-755.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Sancho-Garnier H., Tancrede C. Epidemiology of intestinal colonization by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae highly resistant to erythromycin in a hematology-oncology unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1104–1107. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Andremont A., Courvalin P. Heterogeneity of genes conferring high-level resistance to erythromycin by inactivation in enterobacteria. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Mar-Apr;137A(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Courvalin P. Contribution of two different mechanisms to erythromycin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):694–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Gelbart T., Kuhl W. Interference of heparin with the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1990 Aug;9(2):166–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boileau C. R., d'Hauteville H. M., Sansonetti P. J. DNA hybridization technique to detect Shigella species and enteroinvasive escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):959–961. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.959-961.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noel A., Aznar C., Chureau C., Nguyen S., Pierre C., Bartoli M., Bonete R., Pialoux G., Gicquel B., Garrigue G. Diagnosis of tuberculosis by DNA amplification in clinical practice evaluation. Lancet. 1991 Aug 10;338(8763):364–366. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R., Diamond M., Hamilton C., Neri M. DNA-DNA hybridization assay for detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1146-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel G., Giron J. A., Valmassoi J., Schoolnik G. K. Multi-gene amplification: simultaneous detection of three virulence genes in diarrhoeal stool. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1729–1734. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel G., Riley L., Giron J. A., Valmassoi J., Friedmann A., Strockbine N., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. K. Detection of Shigella in feces using DNA amplification. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1252–1256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornes E., Wasteson Y., Olsvik O. Detection of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin genes in pig stool specimens by an immobilized, colorimetric, nested polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2375–2379. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2375-2379.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan G., Kangro H. O., Coates P. J., Heath R. B. Inhibitory effects of urine on the polymerase chain reaction for cytomegalovirus DNA. J Clin Pathol. 1991 May;44(5):360–365. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.5.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund A., Wasteson Y., Olsvik O. Immunomagnetic separation and DNA hybridization for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in a piglet model. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2259–2262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2259-2262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ounissi H., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of the gene ereA encoding the erythromycin esterase in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;35(3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Lin S. S., Wu S. Y., Juang W. M., Chang C. H., Lin J. Y. The detection of mycobacterial DNA sequences in uncultured clinical specimens with cloned Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA as probes. Tubercle. 1988 Mar;69(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., McMillan C., Coyle M. B. Whole chromosomal DNA probes for rapid identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1239–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1239-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruano G., Fenton W., Kidd K. K. Biphasic amplification of very dilute DNA samples via 'booster' PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5407–5407. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruano G., Kidd K. K., Stephens J. C. Haplotype of multiple polymorphisms resolved by enzymatic amplification of single DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6296–6300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai H., Nishibuchi M., Ramamurthy T., Bhattacharya S. K., Pal S. C., Takeda Y. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of the cholera enterotoxin operon of Vibrio cholerae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2517–2521. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2517-2521.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Harbour D., McCrae M. A. The application of polymerase chain reaction to the detection of rotaviruses in faeces. J Virol Methods. 1990 Jan;27(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]