Abstract
Human babesiosis, which is caused by infection with the intraerythrocytic malarialike protozoan Babesia microti, has recently been diagnosed with increasing frequency in residents of New England. Diagnosis is difficult because of the small size of the parasite and the sparse parasitemia that is characteristic of most infections with this pathogen. We generated B. microti-specific DNA sequence information by universal primer amplification of a portion of the eukaryotic 16S-like gene; this was followed by direct DNA sequence analysis. Specific primers were synthesized on the basis of this sequence information for use in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The PCR-based system demonstrates a strong bias for detection of B. microti as opposed to Babesia gibsoni and does not amplify vertebrate DNA. The analytical sensitivity of the system is approximately three merozoites. Blood specimens from 12 patients with clinically diagnosed and parasitologically confirmed babesiosis from Nantucket Island, Mass., were PCR positive in a blinded test of this procedure. Thus, DNA amplification may provide an adjunct to conventional methods for the diagnosis of human babesiosis and may provide a new means of monitoring therapy or enhancing epidemiological surveillance for this emerging pathogen.
Full text
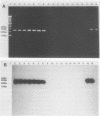
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Mintz E. D., Gadbaw J. J., Magnarelli L. A. Babesia microti, human babesiosis, and Borrelia burgdorferi in Connecticut. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2779–2783. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2779-2783.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. H., Jr, Suebsaeng L., Rooney W., Wirth D. F. Detection of Plasmodium falciparum infection in human patients: a comparison of the DNA probe method to microscopic diagnosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3):266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., MacDonald A., Grunwaldt E., Giron J. A. Serological evidence for simultaneous occurrences of Lyme disease and babesiosis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):473–477. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt F., Healy G. R., Welch M. Human babesiosis: the isolation of Babesia microti in golden hamsters. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):934–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Gutell R., Noller H. F., Wool I. G. The nucleotide sequence of a rat 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene and a proposal for the secondary structure of 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm E. S., Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Sulzer A. J., Healy G. R. Babesia microti infection in man: evaluation of an indirect immunofluorescent antibody test. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Jan;27(1 Pt 1):14–19. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. S., Rogers E. T., Egan E. L. Babesiosis: under-reporting or case-clustering? Postgrad Med J. 1989 Aug;65(766):591–593. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.65.766.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad P. A., Thomford J. W., Marsh A., Telford S. R., 3rd, Anderson J. F., Spielman A., Sabin E. A., Yamane I., Persing D. H. Ribosomal DNA probe for differentiation of Babesia microti and B. gibsoni isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1210–1215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1210-1215.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad P., Thomford J., Yamane I., Whiting J., Bosma L., Uno T., Holshuh H. J., Shelly S. Hemolytic anemia caused by Babesia gibsoni infection in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1991 Sep 1;199(5):601–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammin G. J., Spielman A., Benach J. L., Piesman J. The rising incidence of clinical Babesia microti infection. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):398–400. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkind P., Piesman J., Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Spielman A., Juranek D. D. Methods for detecting Babesia microti infection in wild rodents. J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;66(1):107–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filstein M. R., Benach J. L., White D. J., Brody B. A., Goldman W. D., Bakal C. W., Schwartz R. S. Serosurvey for human babesiosis in New York. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):518–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R., Speilman A., Gleason N. Human babesiosis: reservoir in infection on Nantucket Island. Science. 1976 Apr 30;192(4238):479–480. doi: 10.1126/science.769166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R., Walzer P. D., Sulzer A. J. A case of asymptomatic babesiosis in Georgia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 May;25(3):376–378. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Thilly W. G. Fidelity of DNA polymerases in DNA amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9253–9257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause P. J., Telford S. R., 3rd, Ryan R., Hurta A. B., Kwasnik I., Luger S., Niederman J., Gerber M., Spielman A. Geographical and temporal distribution of babesial infection in Connecticut. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.1-4.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Schoen R. T., Moore T. L., Dodge D. E., White T. J., Persing D. H. Failure of multitarget detection of Borrelia burgdorferi-associated DNA sequences in synovial fluids of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a cautionary note. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Feb;35(2):246–247. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather T. N., Telford S. R., 3rd, Moore S. I., Spielman A. Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti: efficiency of transmission from reservoirs to vector ticks (Ixodes dammini). Exp Parasitol. 1990 Jan;70(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90085-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum F. S., Maden B. E. Human 18 S ribosomal RNA sequence inferred from DNA sequence. Variations in 18 S sequences and secondary modification patterns between vertebrates. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):725–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2320725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., de la Cruz V. F., Lal A. A., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Primary sequences of two small subunit ribosomal RNA genes from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Feb;28(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz E. D., Anderson J. F., Cable R. G., Hadler J. L. Transfusion-transmitted babesiosis: a case report from a new endemic area. Transfusion. 1991 May;31(4):365–368. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1991.31491213305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Landry M. L. In vitro amplification techniques for the detection of nucleic acids: new tools for the diagnostic laboratory. Yale J Biol Med. 1989 Mar-Apr;62(2):159–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Telford S. R., 3rd, Rys P. N., Dodge D. E., White T. J., Malawista S. E., Spielman A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Ixodes dammini ticks. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1420–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2402635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Lewengrub S., Rudzinska M. A., Spielman A. Babesia microti: prolonged survival of salavarian piroplasms in nymphal Ixodes dammini. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Dec;64(3):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Mather T. N., Telford S. R., 3rd, Spielman A. Concurrent Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti infection in nymphal Ixodes dammini. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):446–447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.446-447.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Spielman A. Human babesiosis on Nantucket Island: prevalence of Babesia microti in ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):742–746. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovsky M. A., Lindberg L. E., Syrek A. L., Page P. L. Prevalence of Babesia antibody in a selected blood donor population. Transfusion. 1988 Jan-Feb;28(1):59–61. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1988.28188127955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy G. R., Chakrabarti D., Yowell C. A., Dame J. B. Sequence microheterogeneity of the three small subunit ribosomal RNA genes of Babesia bigemina: expression in erythrocyte culture. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3641–3645. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruano G., Kidd K. K. Coupled amplification and sequencing of genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2815–2819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Juranek D. D., Chisholm E. S., Snow P. C., Healy G. R., Sulzer A. J. Human babesiosis on Nantucket Island. Evidence for self-limited and subclinical infections. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 13;297(15):825–827. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710132971511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Evans A. T., Popovsky M., Mills L., Spielman A. Transfusion-acquired babesiosis and failure of antibiotic treatment. JAMA. 1986 Nov 21;256(19):2726–2727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A. Human babesiosis on Nantucket Island: transmission by nymphal Ixodes ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Nov;25(6):784–787. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A., Wilson M. L., Levine J. F., Piesman J. Ecology of Ixodes dammini-borne human babesiosis and Lyme disease. Annu Rev Entomol. 1985;30:439–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.30.010185.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Weber G. Untersuchungen zur Ubertragung (transstadial, transovarial) von Babesia microti, Stamm "Hannover I", in Ixodes ricinus. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1981 Dec;32(4):228–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Partial sequence of the asexually expressed SU rRNA gene of Plasmodium vivax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2135–2135. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]