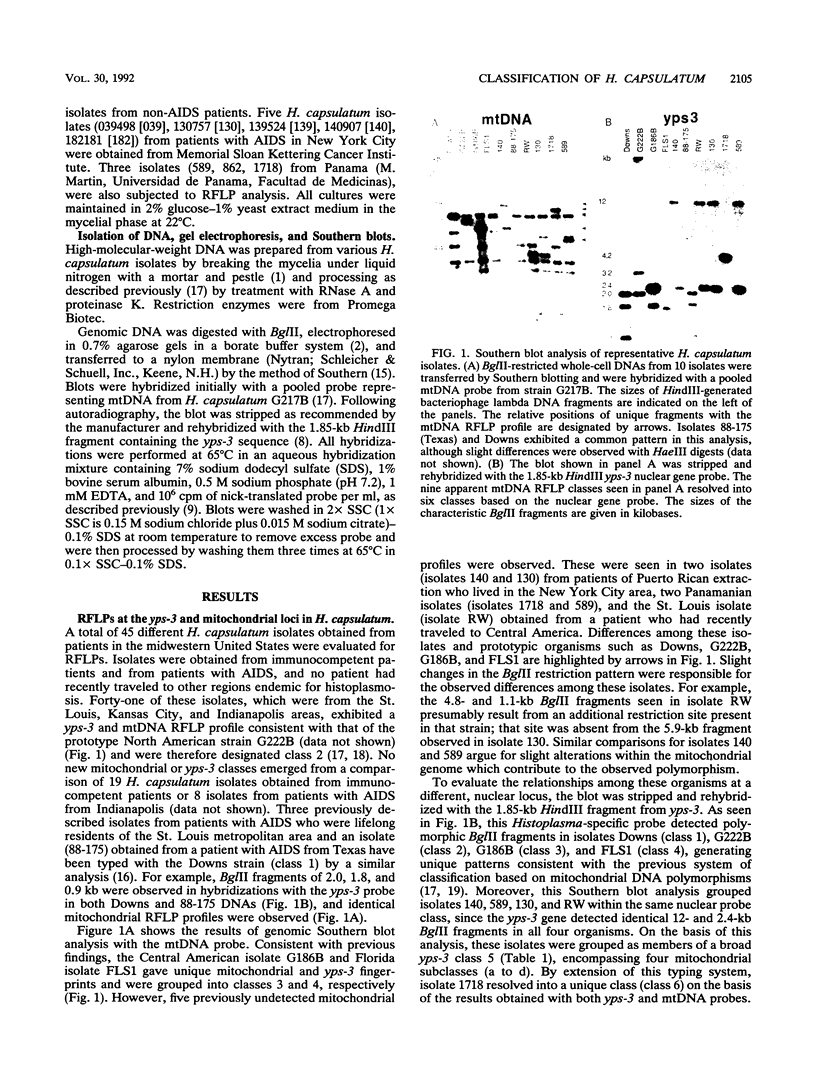
Abstract
We previously described yps-3, a Histoplasma-specific nuclear gene probe useful in the identification of Histoplasma capsulatum. By using restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) of DNA detected by the yps-3 gene and mitochondrial DNA, 76 clinical and soil isolates of H. capsulatum were classified. The majority of North American isolates obtained from endemic regions of the midwestern United States were members of the previously characterized class 2, although four clinical isolates from different patients with AIDS from that region were grouped in class 1 with the temperature-sensitive Downs strain. A Florida soil isolate (FLS1) was placed in class 4 on the basis of RFLP with both probes. Two American Type Culture Collection strains (G184B and G186B) from Panama were grouped into class 3 by this analysis. A group of five H. capsulatum isolates obtained from patients with AIDS in New York City were typed into a new class 5 on the basis of yps-3 polymorphisms; those organisms fell into two broad mitochondrial DNA patterns, designated 5b and 5c. Two new isolates from Panama were also members of this broad yps-3 class 5 group, but they exhibited a distinct mitochondrial DNA profile (class 5a). A sixth class was detected in DNA obtained from a patient with AIDS from Panama; that DNA had unique RFLP profiles with respect to both probes. These observations suggest that the Histoplasma-specific yps-3 gene probe is a sensitive tool for typing H. capsulatum in clinical specimens. Additionally, these studies provide molecular support for the hypothesis that AIDS-associated histoplasmosis in nonendemic areas is due to reactivation of a previously acquired infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. General method for cloning Neurospora crassa nuclear genes by complementation of mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2272–2278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. New molecular techniques for microbial epidemiology and the diagnosis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):595–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. H., Pfeiffer T. J. Natural habitat of Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1642–1644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1642-1644.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser V. J., Keath E. J., Powderly W. G. Two cases of blastomycosis from a common source: use of DNA restriction analysis to identify strains. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1378–1381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R. Histoplasmosis and AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):623–626. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. C., Khardori N., Najjar A. F., Butt F., Mansell P. W., Sarosi G. A. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Aug;85(2):152–158. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Painter A. A., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Variable expression of a yeast-phase-specific gene in Histoplasma capsulatum strains differing in thermotolerance and virulence. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1384-1390.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Spitzer E. D., Painter A. A., Travis S. J., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. DNA probe for the identification of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2369–2372. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2369-2372.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Bennett J. E. Epidemiologic differences between the two varieties of Cryptococcus neoformans. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Jul;120(1):123–130. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell W., Goldberg D. M., Neu H. C. Histoplasmosis in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1986 Dec;81(6):974–978. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., McManus E. J., Riggsby W. S., Jones J. M. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):214–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer E. D., Keath E. J., Travis S. J., Painter A. A., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Temperature-sensitive variants of Histoplasma capsulatum isolated from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):258–261. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer E. D., Lasker B. A., Travis S. J., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Use of mitochondrial and ribosomal DNA polymorphisms to classify clinical and soil isolates of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1409–1412. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1409-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma A., Kwon-Chung K. J. Restriction fragment polymorphism in mitochondrial DNA of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3353–3362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent R. D., Goewert R., Goldman W. E., Kobayashi G. S., Lambowitz A. M., Medoff G. Classification of Histoplasma capsulatum isolates by restriction fragment polymorphisms. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):813–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.813-818.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]