Abstract
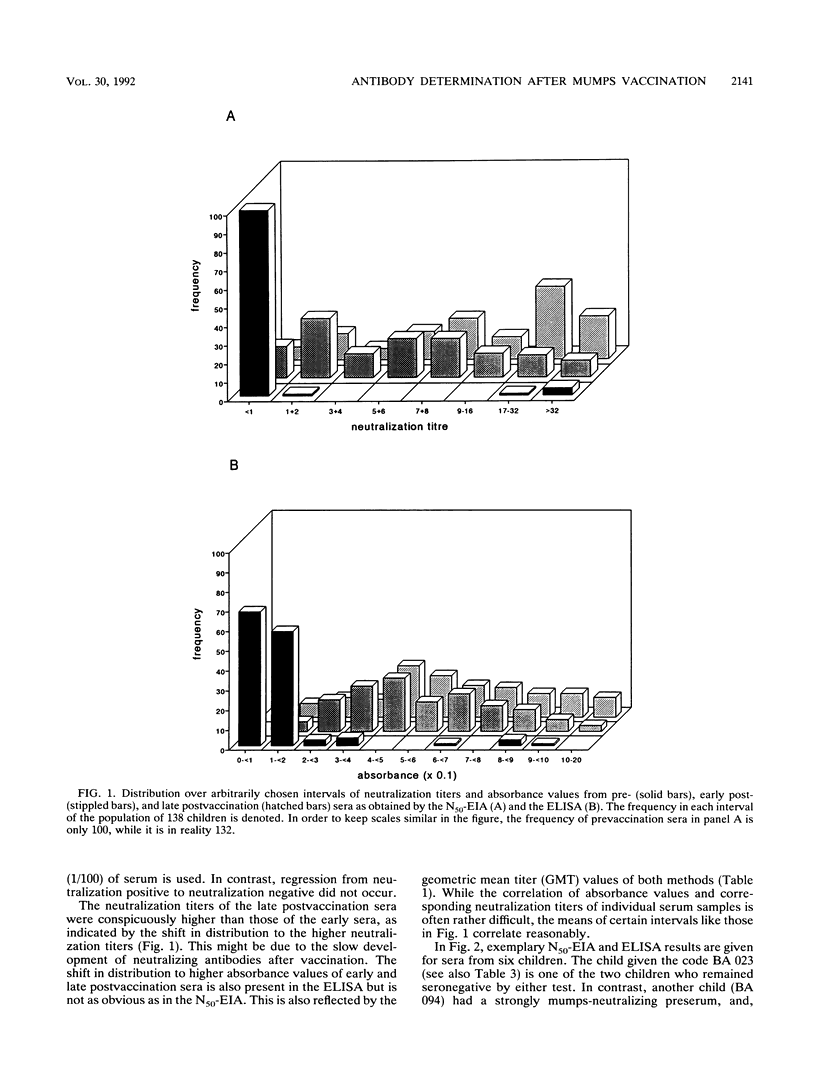
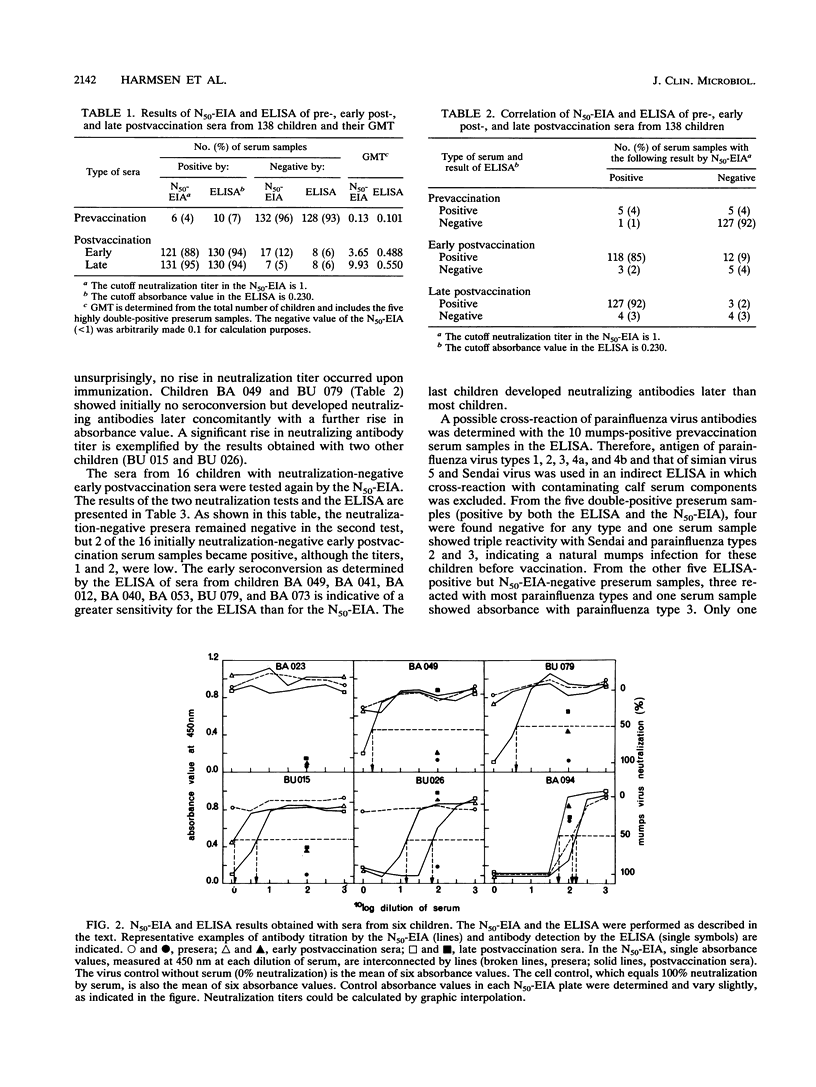
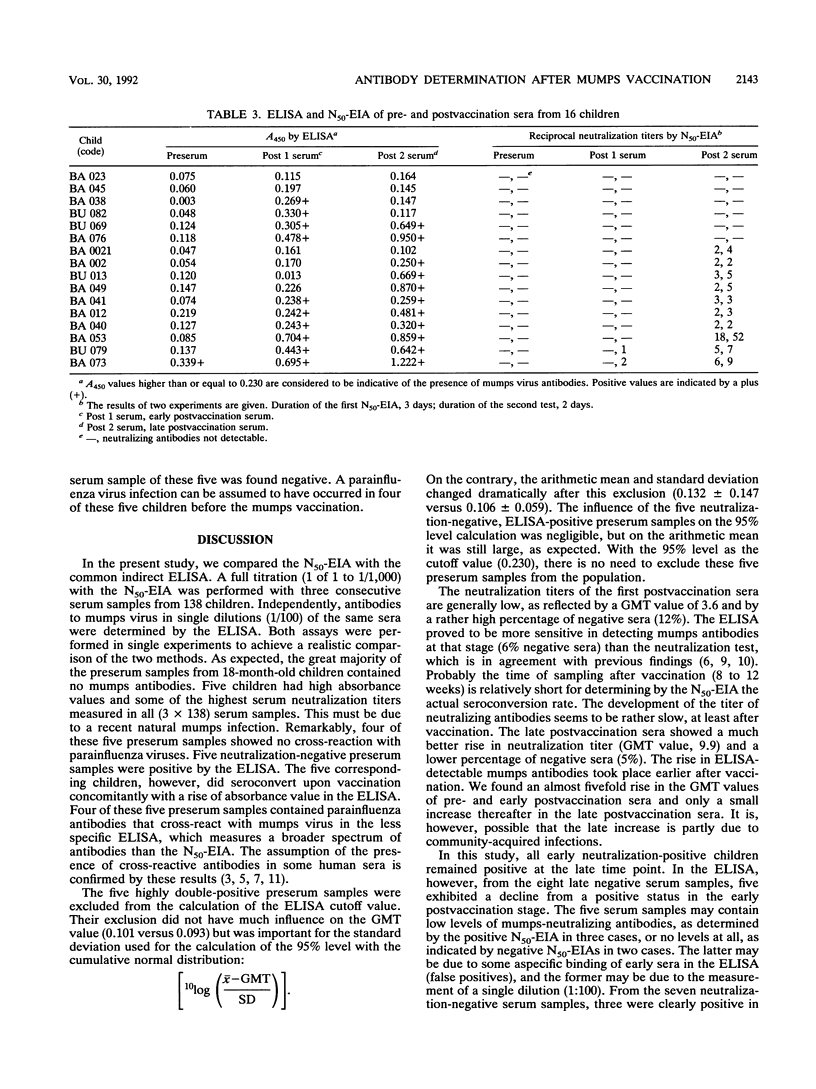
A 50% neutralization enzyme immunoassay (N50-EIA) was compared with an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for determining mumps virus antibodies in three consecutive serum samples from 138 children vaccinated with a live mumps vaccine at the age (in years) of 1.5. By the N50-EIA, most (132 of 138) preserum samples did not show neutralizing activity. Eight to 12 weeks after vaccination, 17 of the children were still negative, but only 7 remained so after 2.5 years, resulting in a seroconversion rate of 125 of 132 (95%). Over the same period, the neutralization geometric mean titer rose from 3.6 to 9.9. By an indirect ELISA, 128 of 138 preserum samples were found negative. The early and late postvaccination sera of 8 children were ELISA negative, resulting in a seroconversion rate of 120 of 128 (94%). Only two children remained seronegative by both methods. Seven of the late postvaccination serum samples yielded noncorresponding results, reflecting 95% correlation between both methods. Due to cross-reactivity with parainfluenza viruses, the ELISA proved to be less specific, but on the other hand, it showed a greater sensitivity than the N50-EIA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ennis F. A., Douglas R. D., Stewart G. L., Hopps H. E., Meyer H. M., Jr A plaque neutralization test for determining mumps antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):896–899. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis F. A. Immunity to mumps in an institutional epidemic. Correlation of insusceptibility to mumps with serum plaque neutralizing and hemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):654–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikmann G., Mordhorst C. H. Serological diagnosis of mumps and parainfluenza type-1 virus infections by enzyme immunoassay, with a comparison of two different approaches for detection of mumps IgG antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Aug;94(4):157–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R., Weibel R. E., Buynak E. B., Stokes J., Jr, Whitman J. E., Jr Live attenuated mumps-virus vaccine. IV. Protective efficacy as measured in a field evaluation. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 2;276(5):252–258. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702022760502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen O. P., Meurman O. H. Avidity of IgG antibodies against mumps, parainfluenza 2 and Newcastle disease viruses after mumps infection. J Virol Methods. 1986 Aug;14(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Shekarchi I., Tzan N., Madden D. L., Sever J. L. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for mumps virus antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Mar;160(3):363–367. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O., Hänninen P., Krishna R. V., Ziegler T. Determination of IgG- and IgM-class antibodies to mumps virus by solid-phase enzyme immunoassay. J Virol Methods. 1982 May;4(4-5):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata H., Hishiyama M., Sugiura A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay compared with neutralization tests for evaluation of live mumps vaccines. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.21-25.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehab Z. M., Brunell P. A., Cobb E. Epidemiological standardization of a test for susceptibility to mumps. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):810–812. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukkonen P., Väisänen O., Penttinen K. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for mumps and parainfluenza type 1 immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):319–323. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.319-323.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenvoort J. H., Harmsen M., Boutahar-Trouw B. J., Kraaijeveld C. A., Winkler K. C. Epidemiology of mumps in the Netherlands. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Dec;85(3):313–326. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tiel F. H., Kraaijeveld C. A., Baller J., Harmsen T., Oosterlaken T. A., Snippe H. Enzyme immunoassay of mumps virus in cell culture with peroxidase-labelled virus specific monoclonal antibodies and its application for determination of antibodies. J Virol Methods. 1988 Oct;22(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



