Abstract
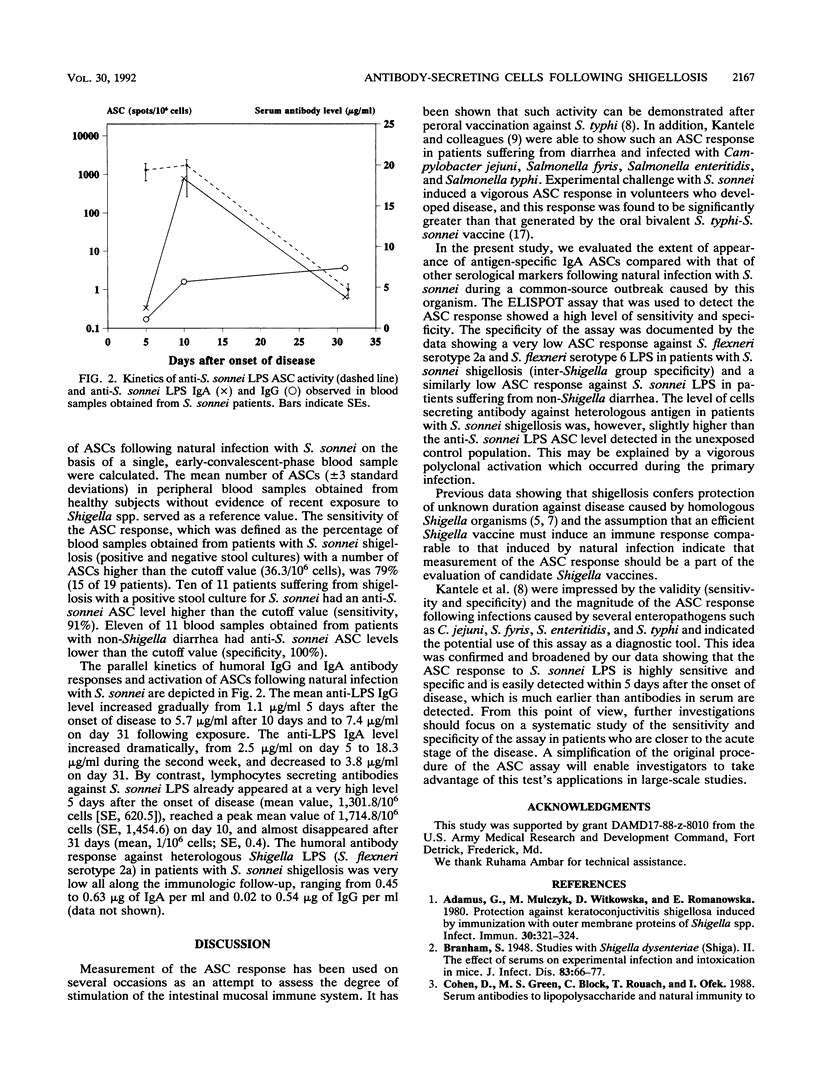
The appearance of antigen-specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody-secreting cells (ASCs) following natural infection with Shigella sonnei during a common-source outbreak caused by this organism was evaluated in a modified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISPOT). A mean IgA ASC value of 2,131.6/10(6) cells against homologous S. sonnei lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was detected in blood samples obtained from patients with bacteriologically proven S. sonnei shigellosis 5 and 10 days after the onset of disease. In the same blood samples, the level of ASC measured against heterologous antigen (Shigella flexneri serotype 2a LPS) was significantly lower than that of the homologous antigen (mean value, 33.12/10(6) cells). Furthermore, the mean number of activated B cells that secreted anti-S. sonnei LPS antibodies was significantly higher among patients with S. sonnei shigellosis than it was among patients with non-Shigella diarrhea (2.5/10(6) cells; standard error, 1.0) and healthy subjects (5.1/10(6) cells; standard error, 2.3) (P less than 0.05). The anti-LPS IgA ASC activity was easily detected within 5 days of the onset of disease, a point at which the levels of anti-S. sonnei LPS IgG and even IgA antibodies were hardly detectable in serum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamus G., Mulczyk M., Witkowska D., Romanowska E. Protection against keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa induced by immunization with outer membrane proteins of Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):321–324. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.321-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Block C., Green M. S., Lowell G., Ofek I. Immunoglobulin M, A, and G antibody response to lipopolysaccharide O antigen in symptomatic and asymptomatic Shigella infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):162–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.162-167.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Immunity in shigellosis. II. Protection induced by oral live vaccine or primary infection. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):12–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest B. D. Identification of an intestinal immune response using peripheral blood lymphocytes. Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):81–83. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Van de Verg L., Formal S. B., Hale T. L., Tall B. D., Cryz S. J., Tramont E. C., Levine M. M. Studies in volunteers to evaluate candidate Shigella vaccines: further experience with a bivalent Salmonella typhi-Shigella sonnei vaccine and protection conferred by previous Shigella sonnei disease. Vaccine. 1990 Aug;8(4):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantele A. M., Takanen R., Arvilommi H. Immune response to acute diarrhea seen as circulating antibody-secreting cells. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1011–1016. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantele A., Arvilommi H., Jokinen I. Specific immunoglobulin-secreting human blood cells after peroral vaccination against Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1126–1131. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Collins H. H., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Intestinal immunoglobulin A responses in rabbits to a Salmonella typhi strain harboring a Shigella sonnei plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):387–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.387-389.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Kern S. E., Bauer D. H., Scott P. J., Porter P. Direct demonstration in intestinal secretions of an IgA memory response to orally administered Shigella flexneri antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):475–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Summers P. L., Reeder A. A., Bertovich M. J., Formal S. B. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity: K lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes are effective against shigella. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2778–2784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesel D. W., Hess C. B., Cho Y. J., Klimpel K. D., Klimpel G. R. Natural and recombinant interferons inhibit epithelial cell invasion by Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):828–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.828-833.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D., Holt P. G. A solid-phase immunoenzymatic technique for the enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Verg L., Herrington D. A., Murphy J. R., Wasserman S. S., Formal S. B., Levine M. M. Specific immunoglobulin A-secreting cells in peripheral blood of humans following oral immunization with a bivalent Salmonella typhi-Shigella sonnei vaccine or infection by pathogenic S. sonnei. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):2002–2004. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.2002-2004.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwillich S. H., Duby A. D., Lipsky P. E. T-lymphocyte clones responsive to Shigella flexneri. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):417–421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.417-421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



