Abstract
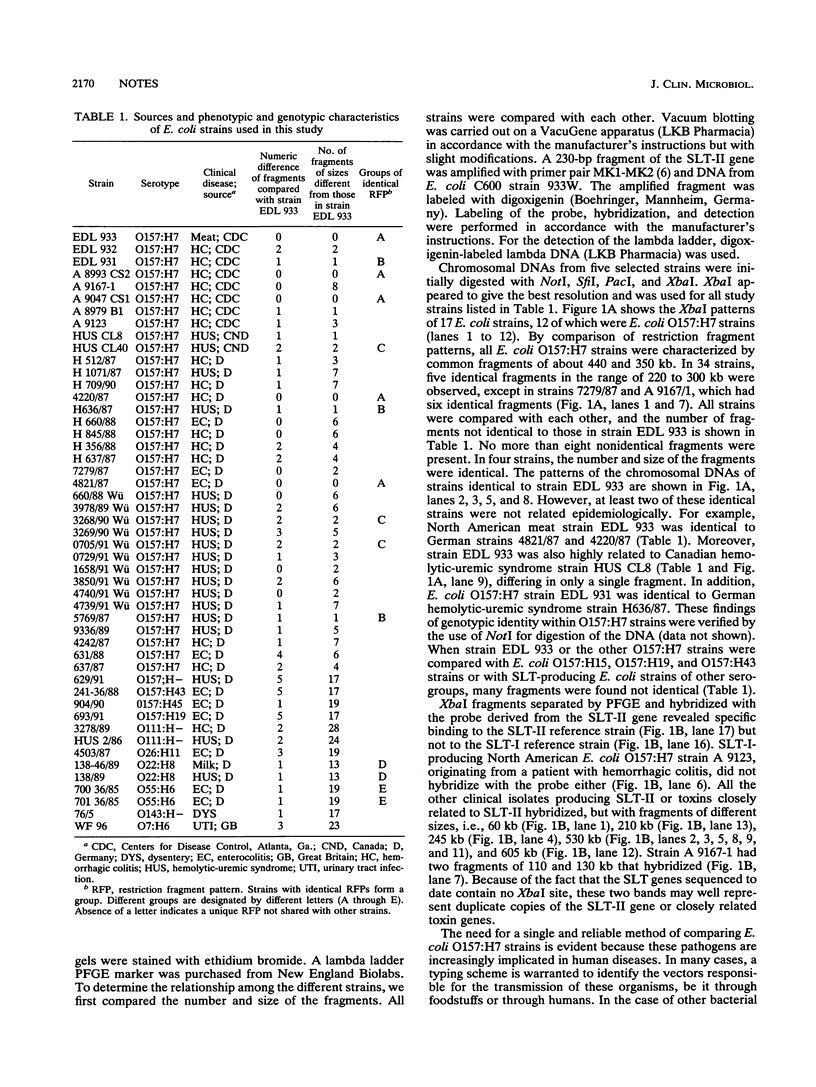
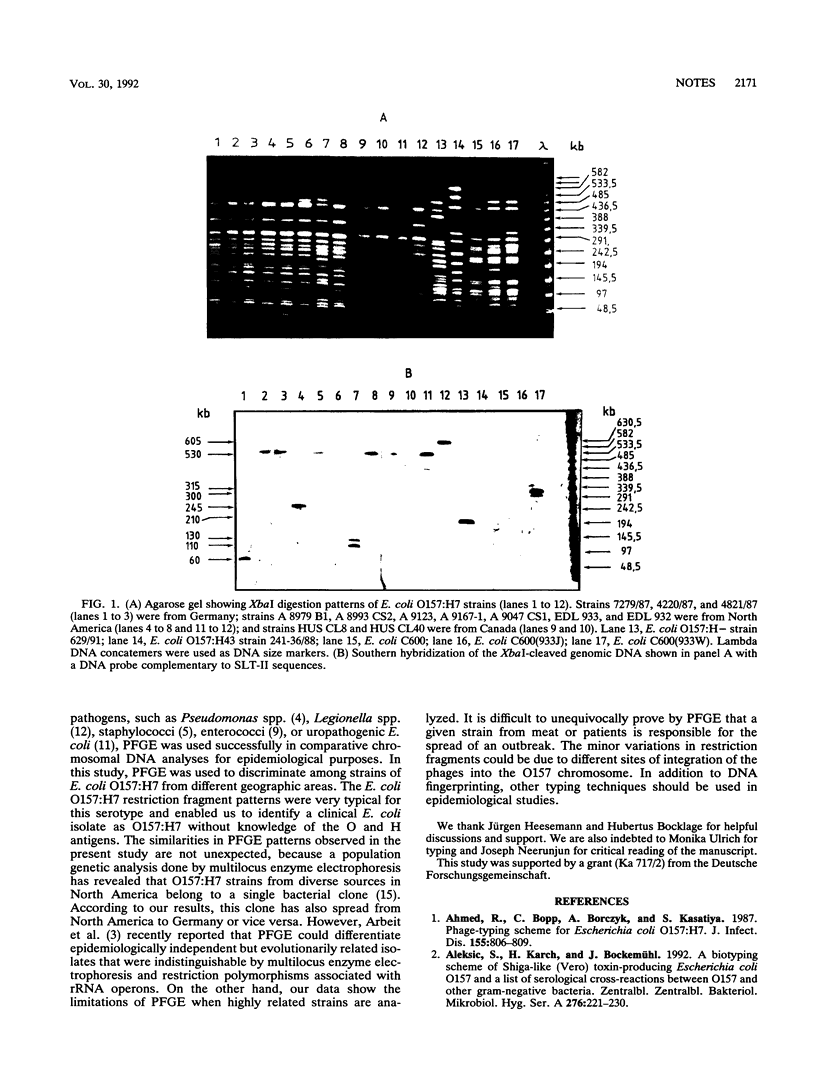
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of genomic DNA was carried out on Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains from different geographic locations to determine its value in an epidemiological survey of O157 infections. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of XbaI-digested DNA fragments clearly separated E. coli O157:H7 strains from nontoxigenic E. coli O157:H19, O157:H43, and O157:H45 strains and from Shiga-like-toxin-producing E. coli strains of other serogroups. However, among the E. coli O157:H7 strains, the restriction patterns either were identical or differed only by a few fragment bands. In some cases, it was therefore impossible to distinguish among epidemiologically unrelated strains. Hybridization experiments with a DNA probe complementary to Shiga-like toxin II sequences revealed that the Shiga-like toxin II genes were located on DNA fragments of different lengths. Our data show that for a single highly conserved clone, such as E. coli O157:H7, other typing techniques may need to be performed in addition to DNA fingerprinting in epidemiological surveys.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Bopp C., Borczyk A., Kasatiya S. Phage-typing scheme for Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):806–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleksić S., Karch H., Bockemühl J. A biotyping scheme for Shiga-like (Vero) toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 and a list of serological cross-reactions between O157 and other gram-negative bacteria. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jan;276(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyama S., Ohta M., Shimokata K., Kato N., Takeuchi J. Genomic DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiological marker for study of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2690–2695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2690-2695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T. Single primer pair for amplifying segments of distinct Shiga-like-toxin genes by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2751–2757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2751-2757.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. G., Singh K. V., Murray B. E. DNA fingerprinting of Enterococcus faecium by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis may be a useful epidemiologic tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2752–2757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2752-2757.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff S. M., Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Lewis J. H., Hargrett-Bean N., Kobayashi J. M. Toxin genotypes and plasmid profiles as determinants of systemic sequelae in Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):994–998. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M., Bender L., Blum G., Schmittroth M., Achtman M., Tschäpe H., Hacker J. Virulence patterns and long-range genetic mapping of extraintestinal Escherichia coli K1, K5, and K100 isolates: use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2664–2672. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2664-2672.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M., Bender L., Marre R., Hacker J. Pulsed field electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments for the detection of nosocomial Legionella pneumophila in hospital water supplies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):813–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.813-815.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Clausen C. R., Newland J. W., Neill R. J., Moseley S. L. Genotypic variation in pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolated from patients in Washington, 1984-1987. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):344–347. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wachsmuth I. K., Wilson R. A. Genetic evidence of clonal descent of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1124–1133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]