Abstract
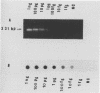
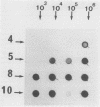
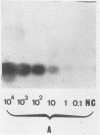
A sensitive assay for Leptospira spp., the causative agent of leptospirosis, was developed on the basis of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A 331-bp sequence from the Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola rrs (16S) gene was amplified, and the PCR products were analyzed by DNA-DNA hybridization by using a 289-bp fragment internal to the amplified DNA. Specific PCR products also were obtained with DNA from the closely related nonpathogenic Leptospira biflexa but not with DNA from other spirochetes, such as Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia hermsii, Treponema denticola, Treponema pallidum, Spirochaeta aurantia, or more distant organisms such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Proteus mirabilis. The assay was able to detect as few as 10 bacteria. Leptospira DNA was detected in urine from experimentally infected mice. In addition, the test was found to be suitable for diagnosing leptospirosis in humans. Cerebrospinal fluid and urine from patients with leptospirosis were positive, whereas samples from control uninfected patients were negative.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler B., Faine S. Host immunological mechanisms in the resistance of mice to leptospiral infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.67-72.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit D., Steyn L., Shoemaker S., Sogin M. Direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical specimens by DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2437-2441.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLINGHAUSEN H. C., Jr, MCCULLOUGH W. G. NUTRITION OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA AND GROWTH OF 13 OTHER SEROTYPES: FRACTIONATION OF OLEIC ALBUMIN COMPLEX AND A MEDIUM OF BOVINE ALBUMIN AND POLYSORBATE 80. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Horie I., Okuzako N., Mifuchi I. Nucleotide sequence of a 16S rRNA gene for Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):366–366. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. J., Olyhoek T., Smits M. A., Bokhout B. A. Sample preparation method for polymerase chain reaction-based semiquantitative detection of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo subtype hardjobovis in bovine urine. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2805–2808. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2805-2808.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay P. E., Clarke J. R., Strugnell R. A., Taylor-Robinson D., Goldmeier D. Use of the polymerase chain reaction to detect DNA sequences specific to pathogenic treponemes in cerebrospinal fluid. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 15;56(3):233–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Baril C., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Genome conservation in isolates of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7582–7588. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7582-7588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivic A., MacDougall J., Russell R. R., Penn C. W. Isolation and characterization of a plasmid from Treponema denticola. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Mar 1;62(2-3):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T. G. A specific and sensitive assay for the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DER HOEDEN J. The pathogenicity of leptospiras to field rodents in Israel; a new test animal for use in Leptospira research. J Infect Dis. 1954 Nov-Dec;95(3):213–219. doi: 10.1093/infdis/95.3.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Gravekamp C., Gerritsen M. J., Quint W., Cornelissen M. T., Schegget J. T., Terpstra W. J. Detection of leptospires in urine by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2258–2262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2258-2262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Macke T. J., Fox G. E. A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:143–151. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(85)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. A., Cole S. T. A rapid method for the detection of potentially viable Mycobacterium leprae in human biopsies: a novel application of PCR. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Dec;53(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]