Abstract
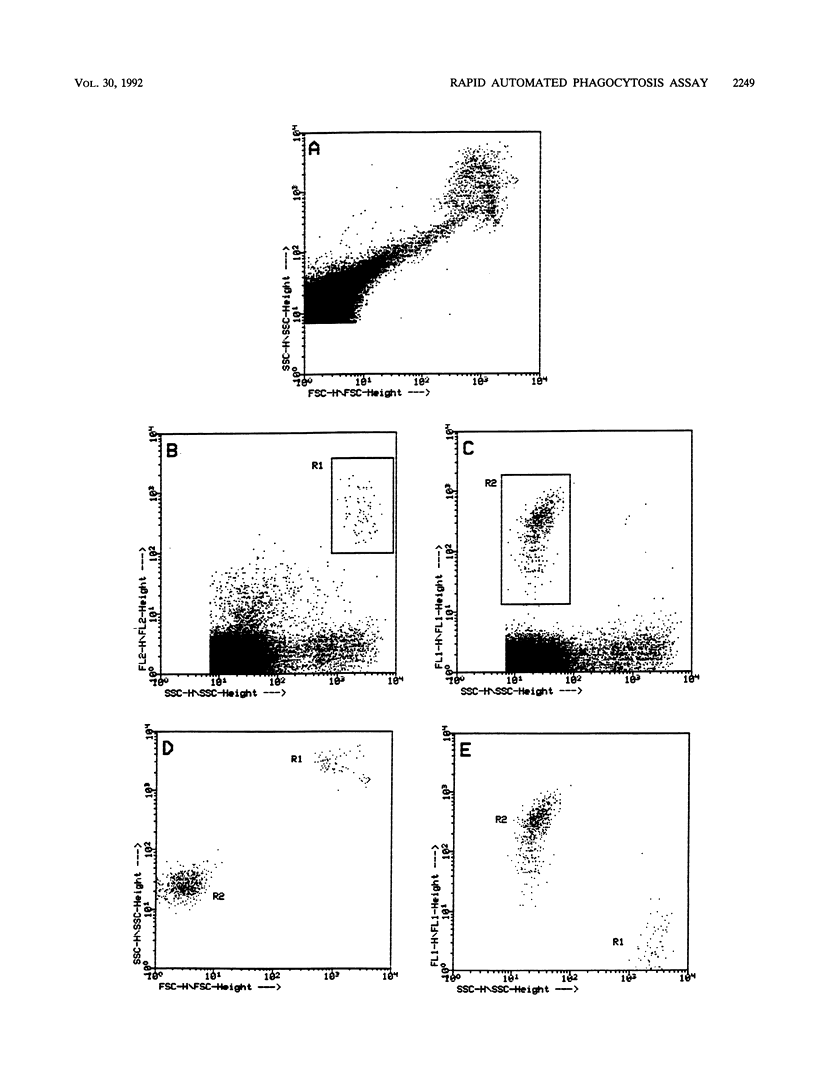
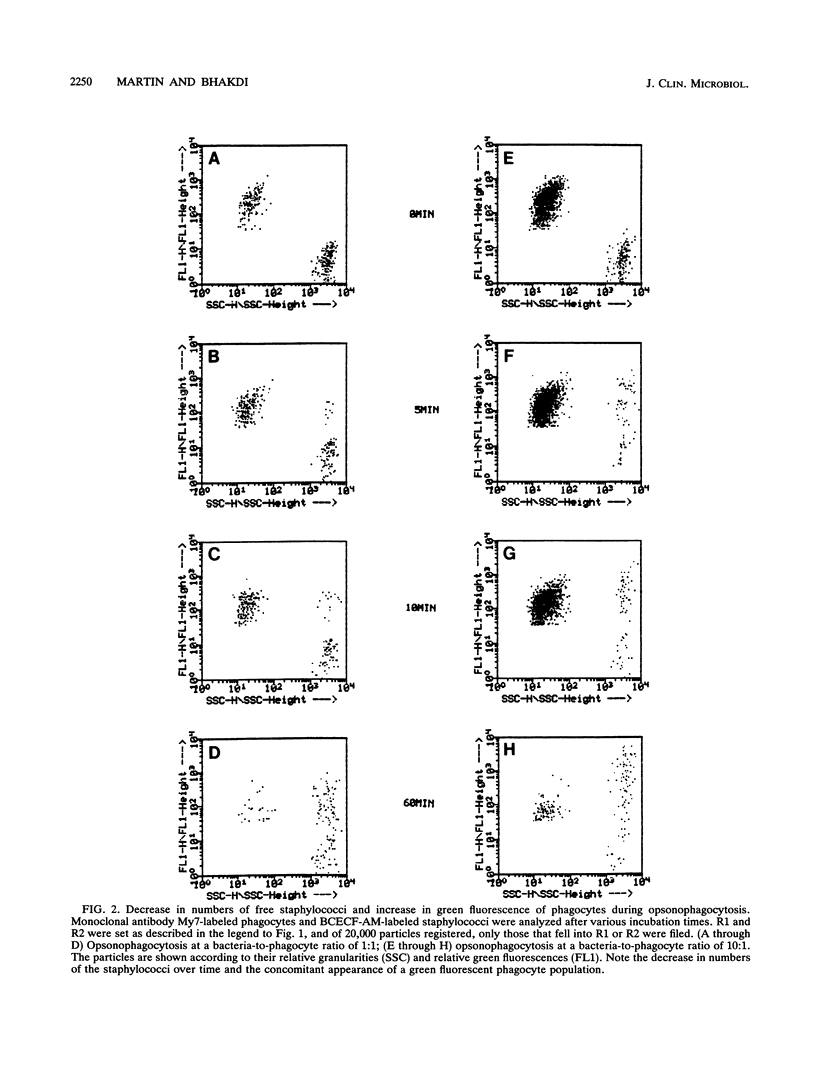
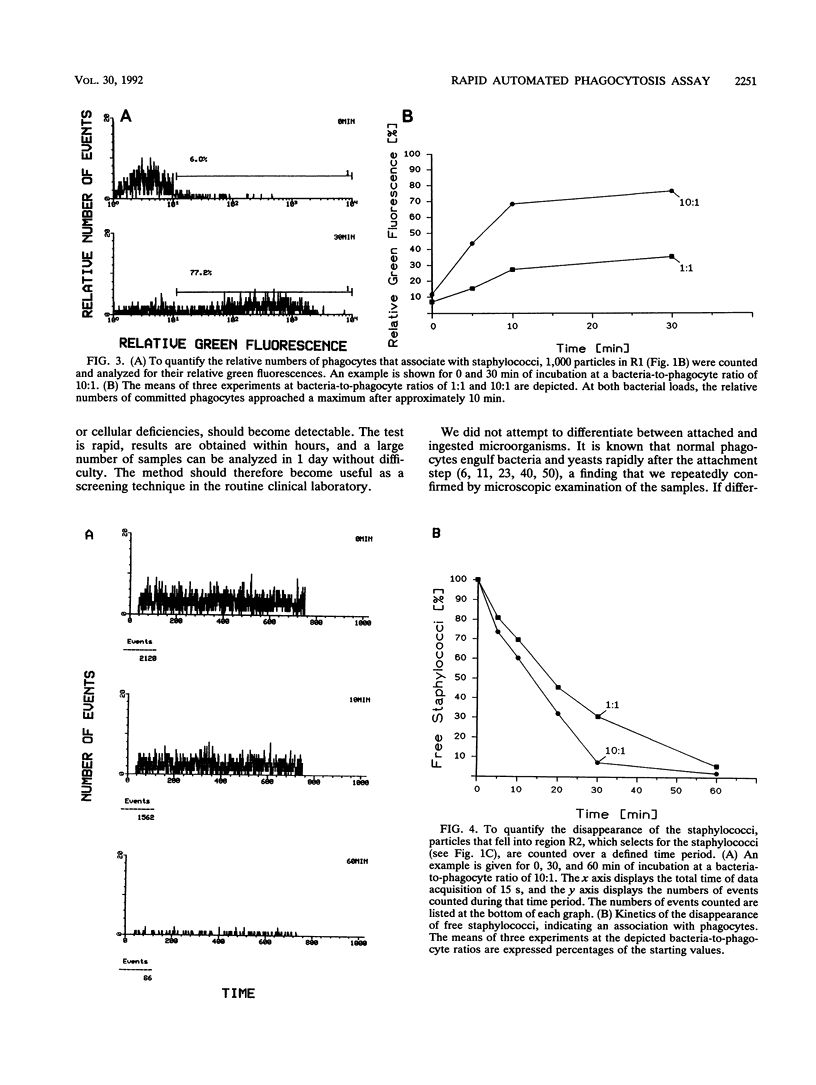
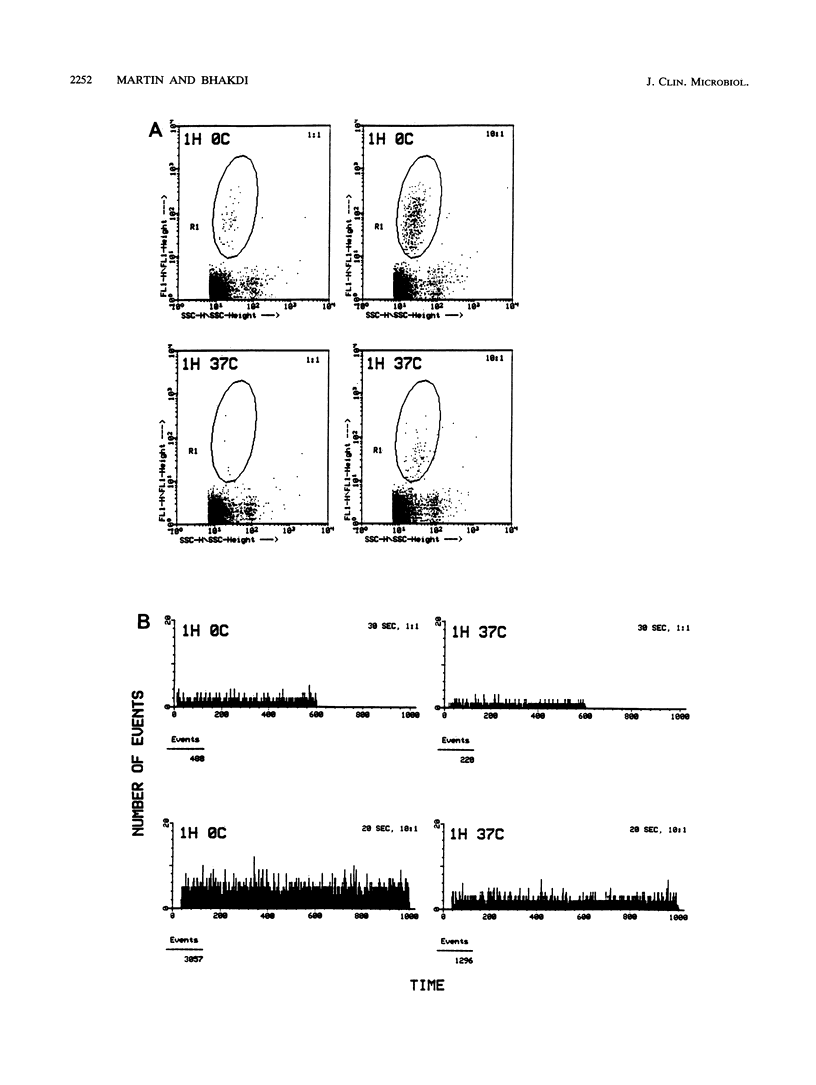
We describe a novel flow cytometric method for quantifying opsonophagocytosis and killing of Staphylococcus aureus in cell-rich plasma obtained after dextran sedimentation of erythrocytes. To analyze opsonophagocytosis, phagocytes were labeled with a phycoerythrin-conjugated monoclonal antibody and were incubated with viable staphylococci containing carboxyfluorescein as a vital fluorescent dye. Phagocytosing cells assumed a dual, orange-green fluorescence. The relative numbers of bacteria associating with phagocytes could be determined by quantifying the decrease of free green fluorescent particles. A parallel incubation of fluorescent bacteria with unlabeled cell-rich plasma was performed to assess phagocytic killing. Blood cells were lysed with 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)-dimethyl-ammonio]-1-propanesulfonate. This detergent spared viable bacteria, and residual green fluorescent particles were counted. The decrease in the number of these particles relative to the controls yielded the degree of killing. At bacteria-to-phagocyte ratios of 1:1 and 10:1, approximately 36 and 75% of the phagocytes participated in opsonophagocytosis, respectively. Over 90% of the staphylococci were phagocyte associated after 30 to 60 min. Killing rates were on the order of 66% +/- 12% and 80% +/- 7% after 1 and 2 h of incubation, respectively. These numbers, which were confirmed by colony countings, were significantly lower than those reported in the majority of past reports.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andoh A., Fujiyama Y., Kitoh K., Hodohara K., Bamba T., Hosoda S. Flow cytometric assay for phagocytosis of human monocytes mediated via Fc gamma-receptors and complement receptor CR1 (CD35). Cytometry. 1991;12(7):677–686. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassøe C. F., Solberg C. O. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus by human leukocytes: quantitation by a flow cytometric and a microbiological method. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Feb;92(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J., Carter S. W., 3rd, Grasso R. J. A rapid radiometric assay for measuring phagocytosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in macrophage cultures. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jul 11;91(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinati-Pires R., Melki S. E., Colletto G. M., Carneiro-Sampaio M. M. Evaluation of a fluorochrome assay for assessing the bactericidal activity of neutrophils in human phagocyte dysfunctions. J Immunol Methods. 1989 May 12;119(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes R., Bassøe C. F. Human leukocyte phagocytosis of zymosan particles measured by flow cytometry. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1983 Oct;91(5):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes R. Flow cytometric assay for combined measurement of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruning J. W., Kardol M. J., Arentzen R. Carboxyfluorescein fluorochromasia assays. I. Non-radioactively labeled cell mediated lympholysis. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschmann H., Winter M. Assessment of phagocytic activity of granulocytes using laser flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Nov 30;124(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90358-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantinieaux B., Hariga C., Courtoy P., Hupin J., Fondu P. Staphylococcus aureus phagocytosis. A new cytofluorometric method using FITC and paraformaldehyde. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jul 26;121(2):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech P., Lehrer R. I. Heterogeneity of human neutrophil phagolysosomes: functional consequences for candidacidal activity. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. A., Tyrer H. W. Quantitation of neutrophil phagocytosis, using fluorescent latex beads. Correlation of microscopy and flow cytometry. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Sep;98(3):374–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérer M., Walker C., Kristensen F., Reinhardt M. C. A simple and rapid flow cytometric method for routine assessment of baker's yeast uptake by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattorossi A., Nisini R., Pizzolo J. G., D'Amelio R. New, simple flow cytometry technique to discriminate between internalized and membrane-bound particles in phagocytosis. Cytometry. 1989 May;10(3):320–325. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foroozanfar N., Aghai Z., Ala F., Hobbs J. R. Inhibition of thymidine uptake by staphylococci, a new method for the investigation of phagocytosis. J Immunol Methods. 1976;11(3-4):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargan R. A., Brumfitt W., Hamilton-Miller J. M. Failure of water to lyse polymorphonuclear neutrophils completely. Role of pH and implications for assessment of bacterial killing. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Nov 30;124(2):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey D. M., Sheppard K. J., Fletcher J. A method for measuring rate of neutrophil phagocytosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis or Candida guilliermondii using uptake of tritiated uridine. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasui M., Hirabayashi Y., Kobayashi Y. Simultaneous measurement by flow cytometry of phagocytosis and hydrogen peroxide production of neutrophils in whole blood. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 8;117(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes A. P., Fletcher J., Garnett M., Robins A. A novel flow cytometric method for measuring protein digestion within the phagocytic vacuole of polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 31;135(1-2):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90268-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hed J., Hallden G., Johansson S. G., Larsson P. The use of fluorescence quenching in flow cytofluorometry to measure the attachment and ingestion phases in phagocytosis in peripheral blood without prior cell separation. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jul 16;101(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst J. K., Albrich J. M., Green T. R., Rosen H., Klebanoff S. Myeloperoxidase-dependent fluorescein chlorination by stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4812–4821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husseini R. H., Hoadley M. E., Hutchinson J. J., Penn C. W., Smith H. Intracellular killing of Candida albicans by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes: comparison of three methods of assessment. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Aug 2;81(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Karpas A., Vann W. F. Capsular antibodies induce type-specific phagocytosis of capsulated Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1090–1095. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1090-1095.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers T. W., Eckmann C. M., Weening R. S., Roos D. A rapid turbidimetric assay of phagocytosis and serum opsonizing capacity. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Nov 13;124(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Warner N. L. Paraformaldehyde fixation of hematopoietic cells for quantitative flow cytometry (FACS) analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.996-1004.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. Measurement of candidacidal activity of specific leukocyte types in mixed cell populations I. Normal, myeloperoxidase-deficient, and chronic granulomatous disease neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.42-47.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Participation of immunoglobulins and complement components in the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):714–724. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.714-724.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):313–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.313-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J., Diamond R. D. A rapid fluorescent assay to distinguish attached from phagocytized yeast particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jul 16;101(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E., Bhakdi S. Quantitative analysis of opsonophagocytosis and of killing of Candida albicans by human peripheral blood leukocytes by using flow cytometry. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2013–2023. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2013-2023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maródi L., Leijh P. C., Van Furth R. A micromethod for the separate evaluation of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human monocytes and granulocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oben J. A., Foreman J. C. A simple quantitative fluorimetric assay of in vitro phagocytosis in human neutrophils. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Aug 9;112(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda T., Maeda H. A new simple fluorometric assay for phagocytosis. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 17;88(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. D., Noel J. G., Sramkoski R. M., Ogle C. K., Alexander J. W. Phagocytosis of opsonized fluorescent microspheres by human neutrophils. A two-color flow cytometric method for the determination of attachment and ingestion. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 25;115(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Brain J. D. Uptake of latex particles by macrophages: characterization using flow cytometry. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):C220–C226. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.3.C220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perticarari S., Presani G., Mangiarotti M. A., Banfi E. Simultaneous flow cytometric method to measure phagocytosis and oxidative products by neutrophils. Cytometry. 1991;12(7):687–693. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Effect of protein A on staphylococcal opsonization. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.760-764.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Extracellular and bacterial factors influencing staphylococcal phagocytosis and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):496–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.496-501.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Kinetics of phagocytosis and bacterial killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):502–509. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolland A., Merdrignac G., Gouranton J., Bourel D., Le Verge R., Genetet B. Flow cytometric quantitative evaluation of phagocytosis by human mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cells using fluorescent nanoparticles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Feb 11;96(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid L., Brune K. Assessment of phagocytic and antimicrobial activity of human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1120–1126. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1120-1126.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit K. E. Phagocytosis and intracellular killing of pathogenic yeasts by human monocytes and neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):932–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.932-938.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Rommel F. A rapid micro method for the simultaneous determination of phagocytic-microbiocidal activity of human peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp J. A., Wilson J. S., Saunders G. C., Stewart C. C. Phagocytosis: flow cytometric quantitation with fluorescent microspheres. Science. 1982 Jan 1;215(4528):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.7053559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveum R. J., Chused T. M., Frank M. M., Brown E. J. A quantitative fluorescent method for measurement of bacterial adherence and phagocytosis. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jun 24;90(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szejda P., Parce J. W., Seeds M. S., Bass D. A. Flow cytometric quantitation of oxidative product formation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3303–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vel W. A., Namavar F., Verweij A. M., Pubben A. N., MacLaren D. M. Killing capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Oct;18(2):173–180. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-2-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Nguyen B. Y., Sisson S. P., Kim Y. Opsonization of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus: the role of specific antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1681–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. M., Galvin A. M., Robins R. A., Reeves W. G. A flow cytometric method for the measurement of phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90301-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura M., Boler J., Valdimarsson H. Phagocytosis measured as inhibition of uridine uptake by Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



