Abstract
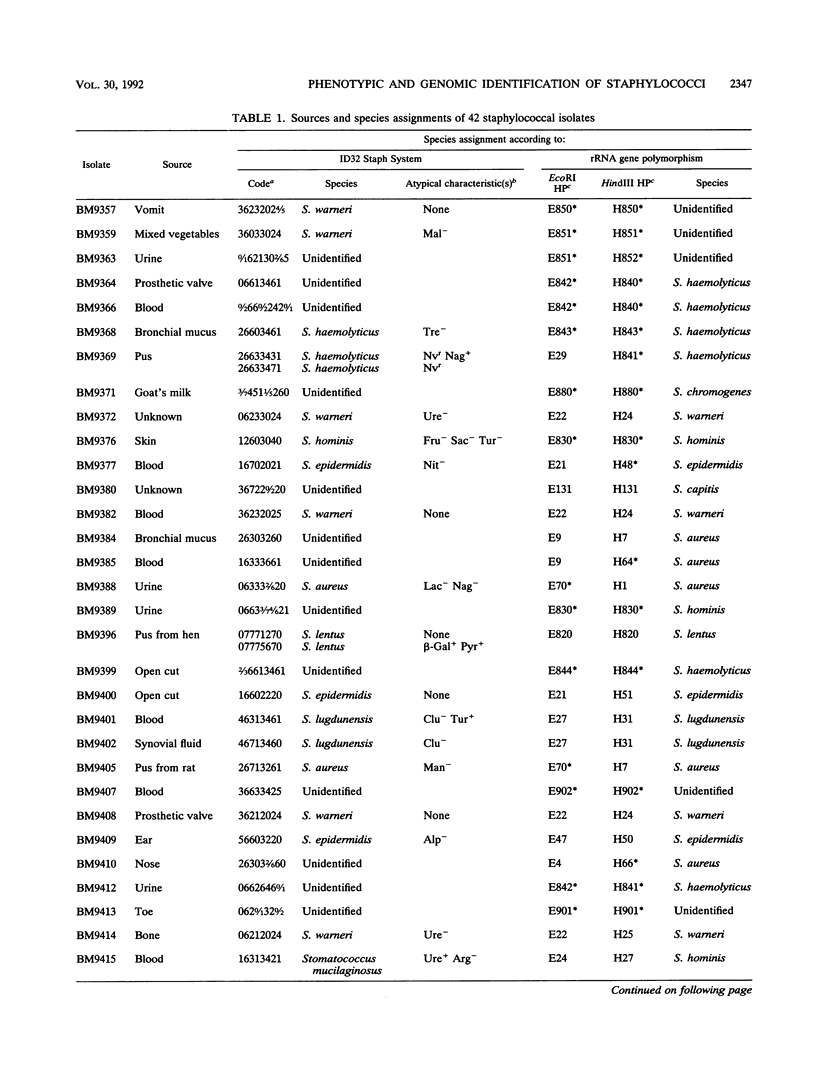
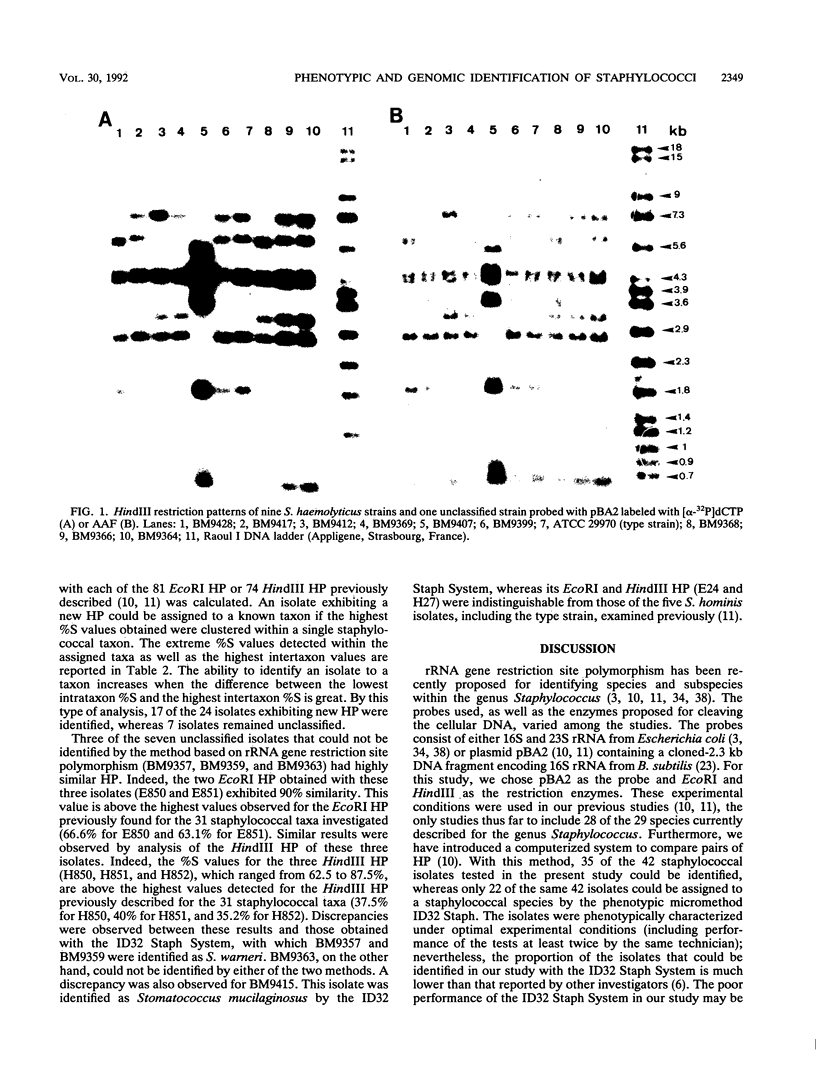
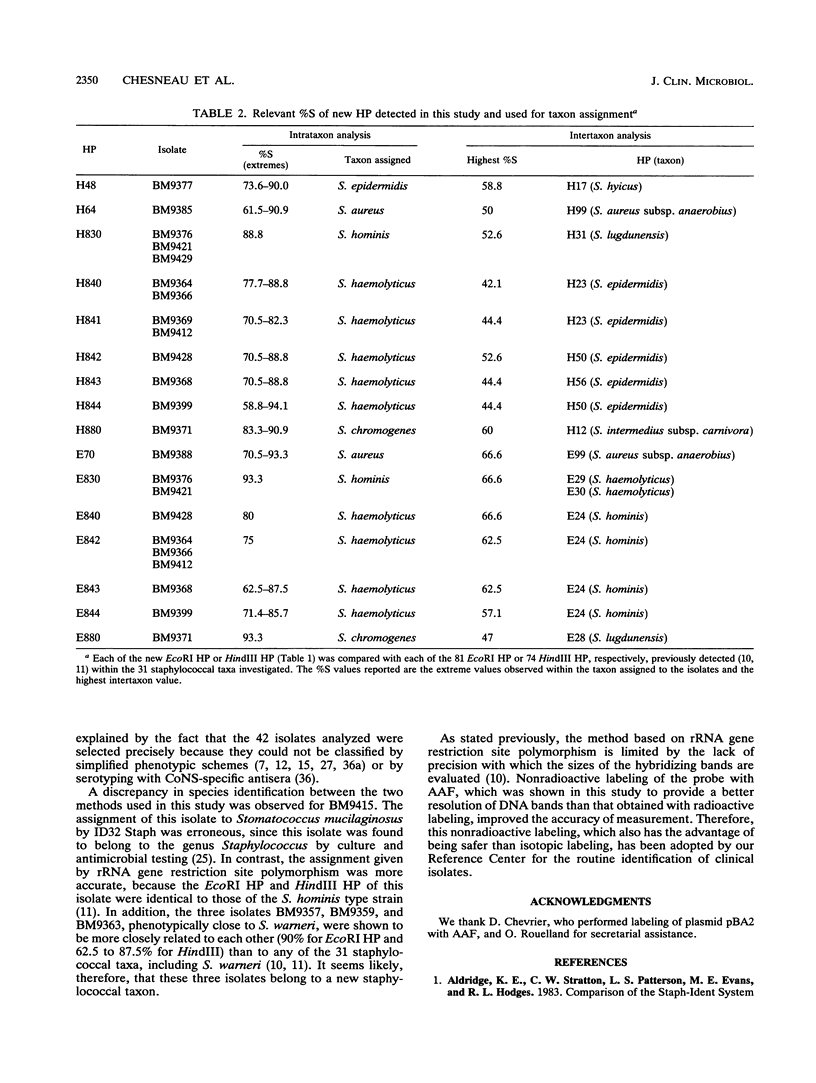
The usefulness of the ID32 Staph System and a method based on rRNA gene restriction site polymorphism was evaluated by the study of 42 staphylococcal clinical isolates phenotypically difficult to identify. The ID32 Staph micromethod and the genomic method are adapted for recognition of 27 and 31 staphylococcal taxa, respectively. The genomic method is based on a Dice analysis of the hybridization patterns obtained by cutting the cellular DNA either with EcoRI or with HindIII and by probing with pBA2, containing the Bacillus subtilis gene encoding 16S rRNA, labeled either with [alpha-32P]dCTP or with acetylaminofluorene. This study showed that the nonradioactive labeling provided a better resolution of the hybridizing bands than radioactive labeling. Of the 42 isolates selected, only 22 could be assigned to a staphylococcal species by the ID32 Staph System, whereas 35 could be identified by the genomic method. This latter method also enabled the screening of three unclassified isolates having hybridization patterns more closely related to each other than to any of the 31 staphylococcal taxa investigated. These three isolates could belong to a staphylococcal taxon not yet described.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Stratton C. W., Patterson L. S., Evans M. E., Hodges R. L. Comparison of the Staph-Ident system with a conventional method for species identification of urine and blood isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):516–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.516-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida R. J., Jorgensen J. H. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci with the API STAPH-IDENT system. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):254–257. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.254-257.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Harry V., Jaskot D., Hammerberg O. Typing of coagulase-negative staphylococci by Southern hybridization of chromosomal DNA fingerprints using a ribosomal RNA probe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;9(8):588–594. doi: 10.1007/BF01967213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P., Chatelain R., Riou J. Y. Intérêt du composé vibriostatique O/129 pour différencier les genres Staphylococcus et Micrococcus. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Nov-Dec;133(3):449–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y., Bes M., Boeufgras J. M., Monget D., Fleurette J., Auckenthaler R., Devriese L. A., Kocur M., Marples R. R., Piemont Y. International collaborative evaluation of the ATB 32 staph gallery for identification of the Staphylococcus species. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Aug;273(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y., Fleurette J., Forey F. Micromethod for biochemical identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):503–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.503-508.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carret G., Flandrois J. P., Bismuth R., Saulnier M. Relative value of staphylocoagulase and fibrinogen affinity for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;53(3):351–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clink J., Pennington T. H. Staphylococcal whole-cell polypeptide analysis: evaluation as a taxonomic and typing tool. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Feb;23(1):41–44. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser M. L., Morvan A., Aubert S., Dilasser F., el Solh N. Evaluation of a ribosomal RNA gene probe for the identification of species and subspecies within the genus Staphylococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 May;138(5):889–899. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-5-889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser M. L., Morvan A., Grimont F., el Solh N. Characterization of Staphylococcus species by ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):989–999. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Schleifer K. H., Adegoke G. O. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci from farm animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;58(1):45–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Earls J. E., Jeznach P. A., Parker D. S. Species identification and biotyping of staphylococci by the API staph-ident system. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):260–263. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.260-263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger O., Charilaou C. C., Cundy K. R. Comparison of the API Staph-Ident and DMS Staph-Trac systems with conventional methods used for the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):68–72. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.68-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Chevrier D., Grimont P. A., Lefevre M., Guesdon J. L. Acetylaminofluorene-labelled ribosomal RNA for use in molecular epidemiology and taxonomy. Res Microbiol. 1989 Sep;140(7):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudding R. Differentiation of staphylococci on the basis of nuclease properties. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1098–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1098-1101.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm D., Labischinski H., Schallehn G., Naumann D. Classification and identification of bacteria by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jan;137(1):69–79. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hájek V., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H., Springer N., Zitzelsberger W., Kroppenstedt R. M., Kocur M. Staphylococcus muscae, a new species isolated from flies. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):97–101. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias A., Ceglowski P., Trautner T. A. Plasmid transformation in Bacillus subtilis. Effects of the insertion of Bacillus subtilis rRNA genes into plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):149–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00327660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., George C. G. Identification of Staphylococcus species and subspecies with the MicroScan Pos ID and Rapid Pos ID panel systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):738–744. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.738-744.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Wolfshohl J. F. Identification of Staphylococcus species with the API STAPH-IDENT system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.509-516.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler C. Characterization of Staphylococcus hyicus with the ATB 32 Staph system and with conventional tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1221–1224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1221-1224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee J. T., Hindmarch J. M., Meechan D. F. Identification of staphylococci by pyrolysis gas-liquid chromatography. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Nov;16(4):483–495. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-4-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masse M. J., Meulien P., Le Guern A., Kourilsky P. Monoclonal antibody detection of 2-acetyl-aminofluorene-modified DNA probes for the specific detection of nucleic acids in hybridization procedures. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1985 Nov-Dec;136D(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(85)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzon-Moreno C., Aubert S., Morvan A., Solh N. E. Usefulness of three probes in typing isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J Med Microbiol. 1991 Aug;35(2):80–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-2-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell A. G., Nahaie M. R., Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E., Hájek V. Numerical analysis of fatty acid profiles in the identification of staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):2023–2033. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-2023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H., Harker C., Thomson-Carter F. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci by using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and rRNA restriction patterns. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):390–392. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.390-392.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierre J., Gutmann L., Bornet M., Bergogne-Berezin E., Williamson R. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci by electrophoretic profile of total proteins and analysis of penicillin-binding proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):443–446. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.443-446.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchen P., Fuchs R. P., Sage E., Leng M. Chemically modified nucleic acids as immunodetectable probes in hybridization experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3466–3470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. L., Washburn P. J. Evaluation of the Staph-Zym system with staphylococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):59–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.59-61.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. J. Comparative zone electrophoresis of catalase of Staphylococcus species isolated from mammalian skin. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Dec;22(12):1691–1698. doi: 10.1139/m76-250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. J., Kloos W. E. Comparative zone electrophoresis of esterases of Staphylococcus species isolated from mammalian skin. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jun;22(6):771–779. doi: 10.1139/m76-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



