Abstract
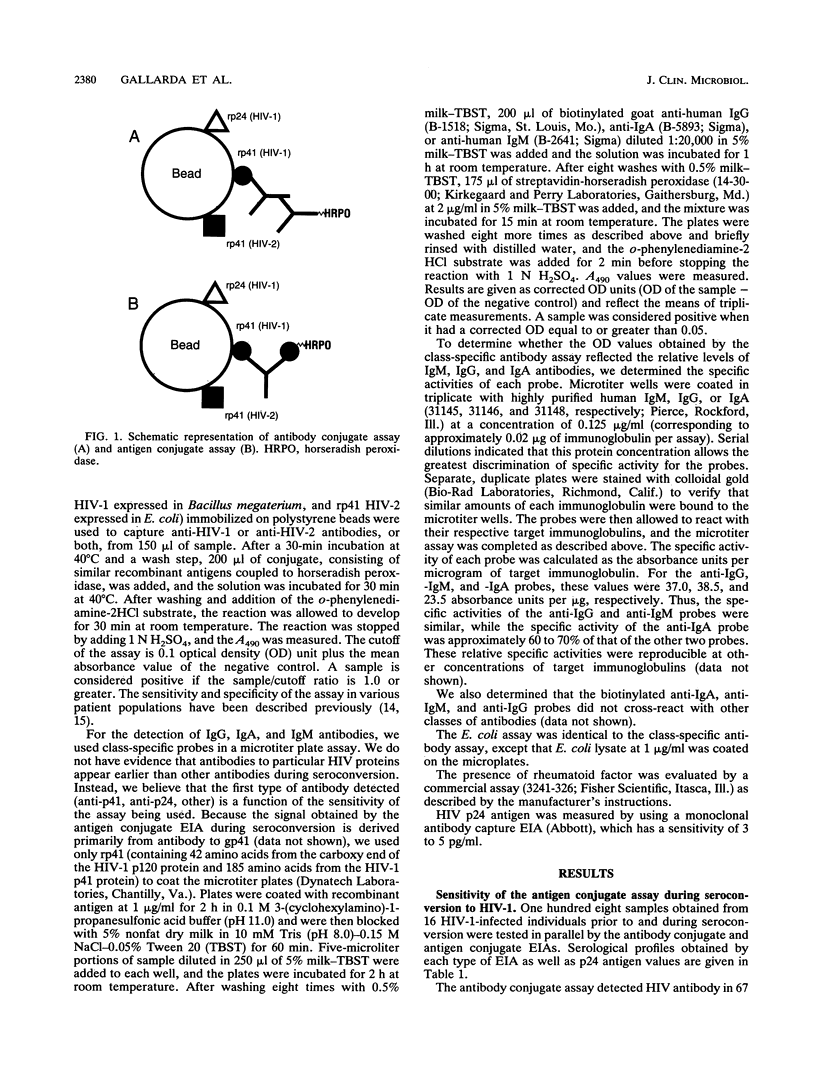
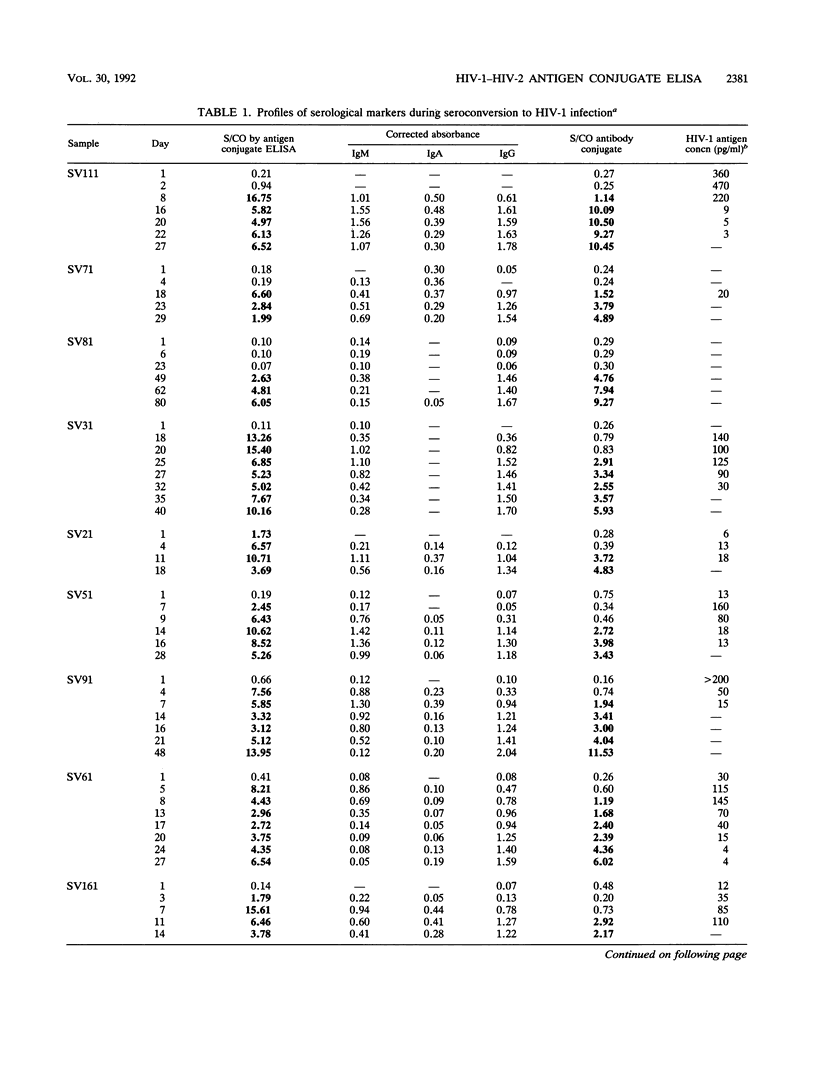
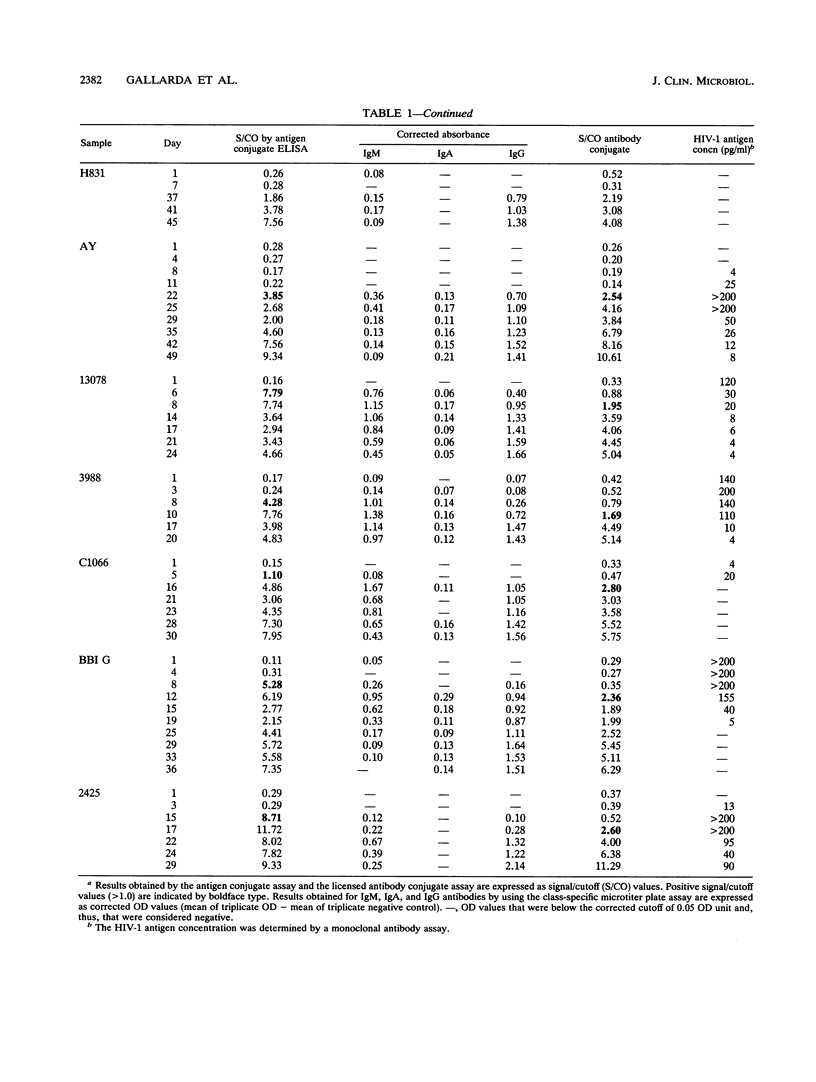
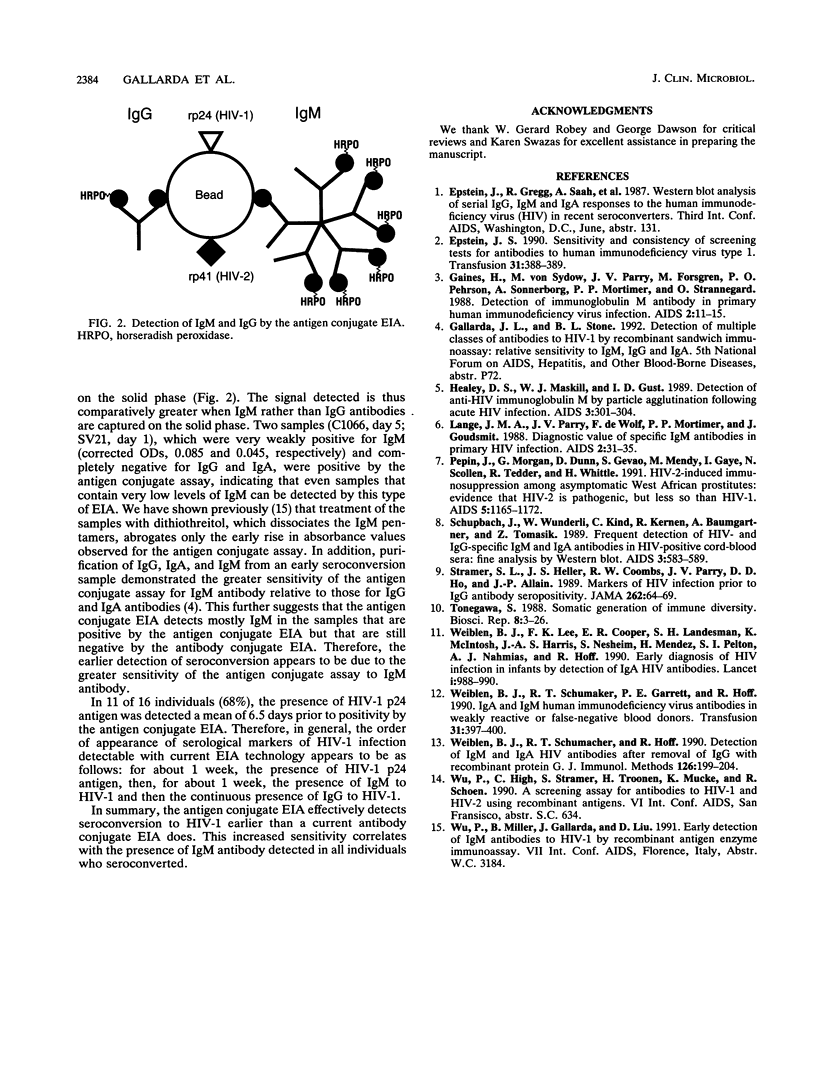
Sequential plasma samples obtained from 16 individuals who seroconverted were tested for the presence of antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) by an antigen conjugate enzyme immunoassay (EIA) and a conventional antibody conjugate assay. In 11 of these individuals, the antigen conjugate assay detected antibody to HIV-1 2 to 11 days (mean, 5.5 days) earlier than the antibody conjugate assay. In 11 individuals, HIV-1 p24 antigen was detected a median of 6.5 days (range, 3 to 14 days) prior to positivity by the antigen conjugate EIA. Using class-specific probes, we determined the profiles of immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG, and IgA antibodies for each individual and correlated these profiles with the EIA signals from both assays. In general, the appearance of IgM exhibited a peak at about 1 week postseroconversion, which was followed by gradually declining levels. Absorbance levels for IgG antibody, however, rose steadily and reached a plateau after 3 to 5 weeks. The levels of IgA were generally low and variable. In contrast to the progressive increase in EIA absorbance observed by the antibody conjugate assay, the antigen conjugate assay displayed a rapid early rise in absorbance which generally coincided with the transient expression of IgM antibody. The subsequent gradual increase coincided with rising levels of IgG. Because the configuration of the antigen conjugate EIA allows for an increased sensitivity for IgM compared with that for other classes of immunoglobulins, these results suggest that earlier detection of antibody to HIV-1 is due to the detection of IgM antibody during the early phase of seroconversion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Epstein J. S. Sensitivity and consistency of screening tests for antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Transfusion. 1991 Jun;31(5):388–389. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1991.31591263189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines H., von Sydow M., Parry J. V., Forsgren M., Pehrson P. O., Sönnerborg A., Mortimer P. P., Strannegård O. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibody in primary human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):11–15. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healey D. S., Maskill W. J., Gust I. D. Detection of anti-HIV immunoglobulin M by particle agglutination following acute HIV infection. AIDS. 1989 May;3(5):301–304. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198905000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Parry J. V., de Wolf F., Mortimer P. P., Goudsmit J. Diagnostic value of specific IgM antibodies in primary HIV infection. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):31–35. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepin J., Morgan G., Dunn D., Gevao S., Mendy M., Gaye I., Scollen N., Tedder R., Whittle H. HIV-2-induced immunosuppression among asymptomatic West African prostitutes: evidence that HIV-2 is pathogenic, but less so than HIV-1. AIDS. 1991 Oct;5(10):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach J., Wunderli W., Kind C., Kernen R., Baumgartner A., Tomasik Z. Frequent detection of HIV- and IgG-specific IgM and IgA antibodies in HIV-positive cord-blood sera: fine analysis by western blot. AIDS. 1989 Sep;3(9):583–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stramer S. L., Heller J. S., Coombs R. W., Parry J. V., Ho D. D., Allain J. P. Markers of HIV infection prior to IgG antibody seropositivity. JAMA. 1989 Jul 7;262(1):64–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of immune diversity. Biosci Rep. 1988 Feb;8(1):3–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01128968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiblen B. J., Lee F. K., Cooper E. R., Landesman S. H., McIntosh K., Harris J. A., Nesheim S., Mendez H., Pelton S. I., Nahmias A. J. Early diagnosis of HIV infection in infants by detection of IgA HIV antibodies. Lancet. 1990 Apr 28;335(8696):988–990. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91061-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiblen B. J., Schumacher R. T., Garrett P. E., Hoff R. IgA and IgM human immunodeficiency virus antibodies in weakly reactive or false-negative blood donors. Transfusion. 1991 Jun;31(5):397–400. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1991.31591263192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiblen B. J., Schumacher R. T., Hoff R. Detection of IgM and IgA HIV antibodies after removal of IgG with recombinant protein G. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Feb 9;126(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90151-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


