Abstract
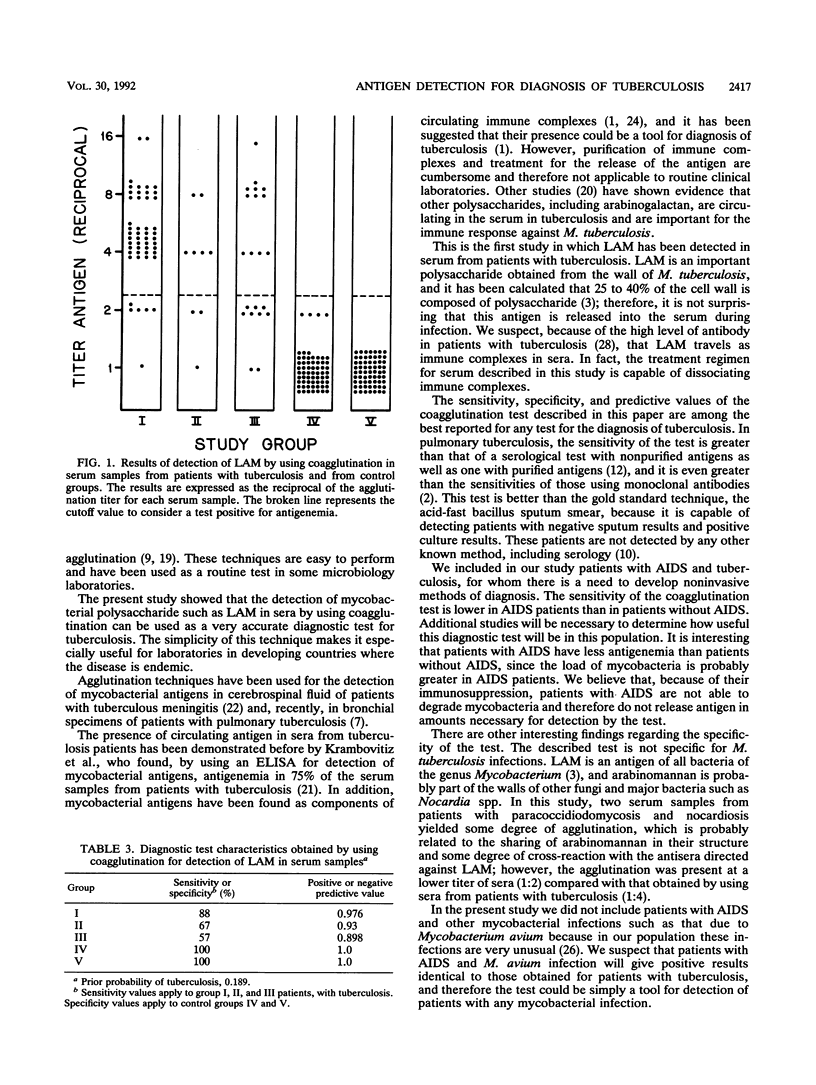
A coagglutination technique was established for the detection of lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human serum samples and evaluated for its utility in the diagnosis of tuberculosis at the Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias in Mexico City. The test had a sensitivity of 88% in patients with sputum-smear-positive active pulmonary tuberculosis. The sensitivity in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis negative for acid-fast bacilli in sputum was 67%. Less favorable results were obtained for patients with AIDS and tuberculosis, with a sensitivity of 57%. The specificity in control patients with lung diseases different from tuberculosis and in healthy subjects was 100%. The positive predictive value was 100%, and the negative predictive value for patients with sputum-positive active pulmonary tuberculosis was 97%. The results of this study suggest that the detection of lipoarabinomannan is an accurate test for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya A., Ranadive S. N., Kale M., Bhattacharya S. Antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of immune complexes in clinical tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):205–209. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothamley G., Udani P., Rudd R., Festenstein F., Ivanyi J. Humoral response to defined epitopes of tubercle bacilli in adult pulmonary and child tuberculosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;7(5):639–645. doi: 10.1007/BF01964242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noël A., Gicquel B., Lecossier D., Lévy-Frébault V., Nassif X., Hance A. J. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1069–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdash N. M., Manos J. P., Ross D., Bannister E. R. Evaluation of the acid-fast smear. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):190–191. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.190-191.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambiaso C. L., Van Vooren J. P., Farber C. M. Immunological detection of mycobacterial antigens in infected fluids, cells and tissues by latex agglutination. Animal model and clinical application. J Immunol Methods. 1990 May 8;129(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90414-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerosaletti K. M., Roghmann M. C., Bentley D. W. Comparison of latex agglutination and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for the detection of pneumococcal antigen in elderly pneumonia patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):553–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.553-557.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Reggiardo Z., Daniel T. M., Girling D. J., Mitchison D. A. Serodiagnosis of tuberculosis using an ELISA with antigen 5 and a hemagglutination assay with glycolipid antigens. Results in patients with newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis ranging in extent of disease from minimal to extensive. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):385–389. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. M., Debanne S. M. The serodiagnosis of tuberculosis and other mycobacterial diseases by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1137–1151. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. M. New approaches to the rapid diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):599–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskeland S. O., Berdal B. P. Bacterial antigen detection in body fluids: methods for rapid antigen concentration and reduction of nonspecific reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):380–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.380-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards E. A., Larson G. L. New method of grouping beta-hemolytic streptococci directly on sheep blood agar plates by coagglutination of specifically sensitized protein A-containing staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):972–976. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.972-976.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Cave M. D., Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):977–981. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Gaylord H., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the phosphorylated lipopolysaccharide antigens from the leprosy and tubercle bacilli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12345–12351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. L., Pearson A. W., Occhiuti A. R. Detection of bacterial antigens in body fluids with the Wellcogen Haemophilus influenzae b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis (ACYW135) latex agglutination tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1119–1121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1119-1121.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaldor J., Asznowicz R., Buist D. G. Latex agglutination in diagnosis of bacterial infections, with special reference to patients with meningitis and septicemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Aug;68(2):284–289. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhenz M. E., Ellner J. J., Spagnuolo P. J., Daniel T. M. Suppression of lymphocyte responses by tuberculous plasma and mycobacterial arabinogalactan. Monocyte dependence and indomethacin reversibility. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):153–162. doi: 10.1172/JCI110231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krambovitis E., Harris M., Hughes D. T. Improved serodiagnosis of tuberculosis using two assay test. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jul;39(7):779–785. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.7.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krambovitis E., McIllmurray M. B., Lock P. E., Hendrickse W., Holzel H. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by latex particle agglutination. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1229–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92792-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky B. A., Gates J., Tenover F. C., Plorde J. J. Factors affecting the clinical value of microscopy for acid-fast bacilli. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6(2):214–222. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. J., Katilus J., Henson P. M., Dreisin R. B. The purification and identification of circulating immune complexes in tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Nov;128(5):920–925. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.5.920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Ponce de León S., Cruz López A., Tinoco J. C., Schnieders B., Macías A., Ortiz E., Valpuesta V., Nares F. Características del síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida en 93 pacientes del Instituto Nacional de la Nutrición "Salvador Zubirán". Rev Invest Clin. 1987;39 (Suppl):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sada E., Brennan P. J., Herrera T., Torres M. Evaluation of lipoarabinomannan for the serological diagnosis of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2587–2590. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2587-2590.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sada E., Ferguson L. E., Daniel T. M. An ELISA for the serodiagnosis of tuberculosis using a 30,000-Da native antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):928–931. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sada E., Ruiz-Palacios G. M., López-Vidal Y., Ponce de León S. Detection of mycobacterial antigens in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tuberculous meningitis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Lancet. 1983 Sep 17;2(8351):651–652. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirumoorthi M. C., Dajani A. S. Comparison of staphylococcal coagglutination, latex agglutination, and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for bacterial antigen detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.28-32.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


