Abstract
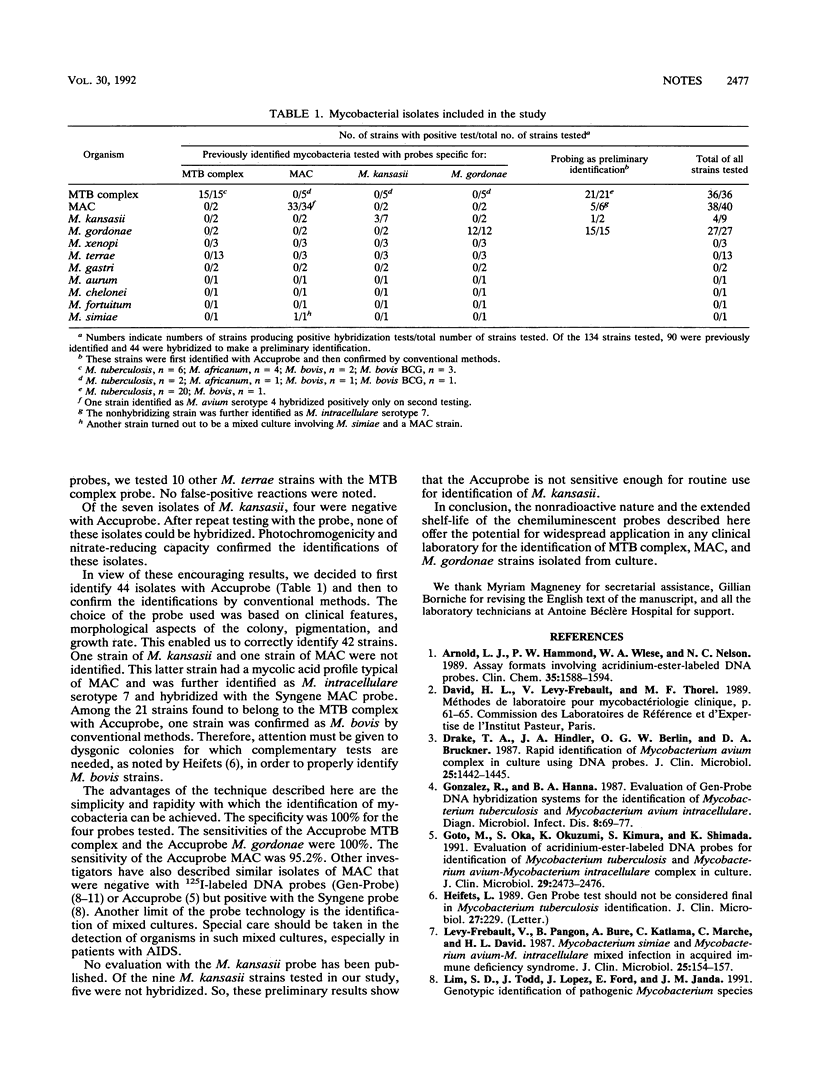
Commercial chemiluminescent DNA probes (Accuprobe; Gen-Probe, San Diego, Calif.) for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) complex, M. avium complex (MAC), M. gordonae, and M. kansasii were evaluated with 134 clinical isolates. These included 36 MTB complex, 40 MAC, 27 M. gordonae, 9 M. kansasii, and 22 Mycobacterium spp. The specificity was 100% for the four probes. The sensitivity was 100% for the MTB complex and M. gordonae probes and 95.2% for the MAC probe. Five of the nine M. kansasii isolates tested were not detected with the probe.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold L. J., Jr, Hammond P. W., Wiese W. A., Nelson N. C. Assay formats involving acridinium-ester-labeled DNA probes. Clin Chem. 1989 Aug;35(8):1588–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Hindler J. A., Berlin O. G., Bruckner D. A. Rapid identification of Mycobacterium avium complex in culture using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1442–1445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1442-1445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez R., Hanna B. A. Evaluation of Gen-Probe DNA hybridization systems for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;8(2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Oka S., Okuzumi K., Kimura S., Shimada K. Evaluation of acridinium-ester-labeled DNA probes for identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare complex in culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2473–2476. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2473-2476.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. Gen-probe test should not be considered final in Mycobacterium tuberculosis identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):229–229. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.229-.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V., Pangon B., Buré A., Katlama C., Marche C., David H. L. Mycobacterium simiae and Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare mixed infection in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):154–157. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.154-157.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musial C. E., Tice L. S., Stockman L., Roberts G. D. Identification of mycobacteria from culture by using the Gen-Probe Rapid Diagnostic System for Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2120–2123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2120-2123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Lu R., Floyd C., Nakasone A., Friedly G., de la Maza L. M. Direct identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium, and Mycobacterium intracellulare from amplified primary cultures in BACTEC media using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1543–1547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1543-1547.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Tasaka H., Dawson D. J. Identification of various serovar strains of Mycobacterium avium complex by using DNA probes specific for Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1694–1697. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1694-1697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi S. H., Hwangbo C. C., Silcox V., Good R. C., Snider D. E., Jr, Middlebrook G. Rapid radiometric methods to detect and differentiate Mycobacterium tuberculosis/M. bovis from other mycobacterial species. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):634–640. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres R. A., Nord J., Feldman R., LaBombardi V., Barr M. Disseminated mixed Mycobacterium simiae-Mycobacterium avium complex infection in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):432–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton D. T., Valesco M. Identification of Mycobacterium gordonae from culture by the Gen-Probe Rapid Diagnostic System: evaluation of 218 isolates and potential sources of false-negative results. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1850–1854. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1850-1854.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


