Abstract
The subunit c stoichiometry of Escherichia coli ATP synthase was studied by intermolecular cross-linking via oxidation of bi-cysteine-substituted subunit c (cA21C/cM65C). Independent of the carbon source used for growth and independent of the presence of other FoF1 subunits, an equal pattern of cross-link formation stopping at the formation of decamers was obtained.
ATP synthases (FoF1) catalyze the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate by utilizing the energy of an electrochemical gradient of protons or sodium ions. In Escherichia coli, the ATP synthase is built up of the membrane-embedded Fo complex (ab2c10), which couples ion translocation to ATP synthesis/hydrolysis within the peripheral catalytic F1 part (α3β3γδɛ) via a rotary mechanism. This rotary movement is energized by the successive protonation/deprotonation of the essential carboxylate cD61 in the middle of the C-terminal transmembrane helix of each c subunit, resulting in a rotation of the oligomeric ring relative to the ab2 stator interface. The energy of the rotation is transferred to the three catalytic sites located in the β subunits within the stator element via a centrally located γɛ subcomplex, which is fixed to a set of c subunits within the ring. Therefore, the number of c monomers per ring determines the number of ions transported per revolution, which, in turn, directly defines the ion-to-ATP ratio, as well as the P/O ratio, of oxidative phosphorylation (4, 14, 32).
Structural data on subunit c oligomers demonstrate that the stoichiometry varies between 10 and 15 among different organisms (4, 18, 19, 24, 29). As a consequence, due to the three catalytic sites present in F1 and a synthesis rate of three molecules of ATP per revolution, a variation in the number of c subunits and, therefore, ion binding sites in the c ring of different species automatically leads to different ion-to-ATP ratios, ranging from 3.3 to 5 per ATP synthesized. ATP synthases with small c rings are present in organisms that maintain a high ion motive force mainly in the form of a membrane potential, whereas ATP synthases with large c rings were mostly found in species with a high ion motive force existing predominantly in the form of a pH gradient rather than a membrane potential, as in chloroplasts or cyanobacteria (4, 32). The experimental determination of the thermodynamic H+/ATP ratios revealed values of 4 for the chloroplast enzyme (reference 28 and references therein) and the prokaryotic dodecameric V-type ATP synthase from Thermus thermophilus (29) and 3 for the mitochondrial enzyme (reviewed in reference 9), which is in agreement with the calculated subunit stoichiometric ratios of 4.7, 4.0, and 3.3 (4, 29, 32). In the case of the E. coli enzyme, the H+/ATP ratio varied between 2 and 4 when determined by various methods (28; reviewed in reference 30). The recently determined value of 4.0 ± 0.3 (mean ± standard deviation) for reconstituted E. coli FoF1 (28) implies that the thermodynamic H+/ATP ratio might be different from the subunit stoichiometric ratio (3.3) and needs further clarification.
Several lines of evidence argue for a fixed subunit c stoichiometry within one organism. First, for an atp mutant strain which showed a reduced expression of the atpE gene (coding for subunit c) due to a point mutation within the ribosome binding site, a variable stoichiometry of subunit c was suggested (25). However, a detailed analysis revealed that the Fo preparation from the mutant comprised a heterogeneous population consisting of assembled Fo complexes with a subunit c stoichiometry comparable to that of the wild type together with free ab2 subcomplexes (17). Second, the finding of open c rings, which exhibit structural gaps of one or more c subunits observed for Ilyobacter tartaricus, Propionigenium modestum, and spinach chloroplasts by atomic force microscopy, implicated a constrained and fixed stoichiometry for the ring determined by the biochemical properties of the c subunits and their nearest-neighbor interactions (20, 23).
A stable c ring was isolated from several species and analyzed for the number of monomers present per ring by atomic force or electron microscopy (reviewed in reference 4; compare also references 24 and 29). However, until now, the high instability of the c ring in the case of E. coli and even in the thermophilic Bacillus stearothermophilus PS3 did not allow the formation of two-dimensional crystals for analysis, and therefore, the stoichiometry of 10 monomers per ring was determined by intermolecular cross-linking (11, 13) and genetic fusion of the monomers (22), respectively. However, in the case of E. coli ATP synthase, the stoichiometry can be artificially forced to deviate to a certain extent, since genetically fused multimers of subunit c yielded at least partly functional subunit c rings with an artificial stoichiometry ranging from 9 to 12 (11, 12). In addition, it has been discussed that the subunit c stoichiometry is variable within one organism depending on the growth conditions (26). This seems to open the possibility for the ATP synthase to respond to different metabolic states of the cell, thereby changing the H+/ATP ratio via a regulated subunit c stoichiometry (compare reference 30). Moreover, the data suggested that more c subunits were assembled into the ATP synthase in cells grown on glucose than in cells grown on succinate (26), which would be opposite to the generally accepted considerations described above.
In this study, intermolecular cross-linking of bi-cysteine-substituted c subunits on the membrane level was used as a direct approach to visualize under in vivo conditions that the number of c subunits within the rotary ring of the E. coli ATP synthase is constant independent of the carbon source used for growth and, in addition, independent of the presence of the other subunits of the FoF1 complex.
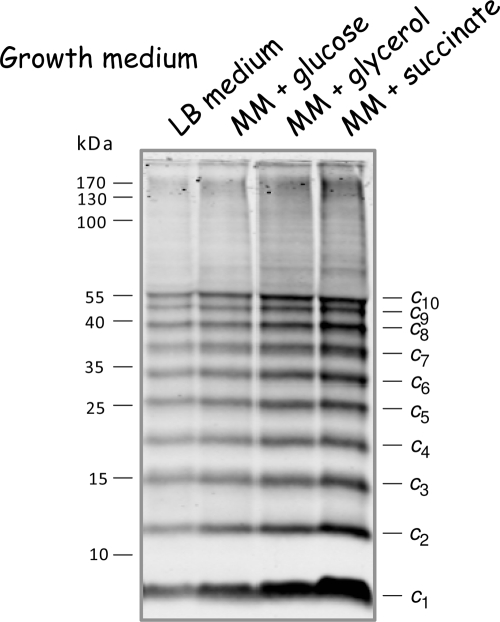
To investigate the stoichiometry of subunit c for dependence on the metabolic status, cells of the E. coli atp deletion strain DK8 (Table 1) transformed with plasmid pBWU13.NOC, which synthesizes an ATP synthase with the bi-cysteine-substituted subunit c (cA21C/cM65C), were grown on fermentable and nonfermentable carbon sources. The use of the bi-cysteine-substituted subunit c mutant was based on the data of R. H. Fillingame's group (11, 13) and fits very well with the structural considerations on the subunit c ring of E. coli (5, 6). In detail, cells were grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) rich medium, in which the primary source for carbon and energy is amino acids, or in supplemented minimal medium (17) with glucose, glycerol, or succinate as the sole carbon and energy source. Due to the high instability of the oligomeric subunit c ring of E. coli in the absence of a membrane environment, in contrast to other organisms from which a stable c ring can be isolated, it was important to perform an analysis at the membrane level without further manipulation. Therefore, after the preparation of membrane vesicles, intermolecular cross-links were generated by oxidation of cysteine residues with copper-1,10-phenanthroline, according to the method of Jones et al. (13), and directly analyzed by immunoblotting (Fig. 1). The formation of an identical cross-linking pattern for subunit c independent of the carbon source used for growth could be observed, which strongly argues in favor of a comparable subunit c stoichiometry with 10 c monomers per ring. However, due to an incomplete cross-linking of the subunit c ring (10 cross-link events per ring can occur at most), all other intermediates of subunit c oligomerization are also visible in appreciable amounts, stopping at the level of decamer formation, thereby generating a ladder-like appearance (Fig. 1; compare also results in references 11 to 13 and 17), whereas the faint background observed is negligible compared to the distinct pattern of the intensively labeled bands. Our data, obtained by the method previously used to determine that the preferred stoichiometry of subunit c is 10 (11), revealed that comparable subunit c oligomers were formed in each case, irrespective of whether ATP is exclusively produced by oxidative phosphorylation or by substrate-level/oxidative phosphorylation and, furthermore, independent of its functioning as an ATP synthase or as an ATP-hydrolyzing proton pump to maintain an electrochemical proton gradient across the cytoplasmic membrane.
TABLE 1.
Strains, plasmids, and primers used in the study
| Strain, plasmid, or primer | Genotype, description, or sequencea | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli strains | ||
| BL21(DE3) | F−dcm ompT hsdS(rB− mB−) gal λ(DE3) | Novagen, Gibbstown, NJ |
| DK8 | HfrPO1 bglR thi1 relA1 ilv::Tn10 Tetr ΔatpBEFHAGDC | 16 |
| HB1(DE3) | F−dcm ompT hsdS(rB− mB−) gal λ(DE3) ilv::Tn10 TetrΔatpBEFHAGDC [P1 cotransduction of ΔatpBEFHAGDC and ilv::Tn10 from DK8 to BL21(DE3)] | This work |
| Plasmids | ||
| pBWU13.NOC | pBR322 with HindIII-NdeI fragment containing atpBEFHAGDC; cA21C cM65C bC21S Apr | 17 |
| pET-22b | cloning vector; Apr | Novagen, Gibbstown, NJ |
| pET22-atpE-c21/65 | pET-22b with NdeI-EcoRI fragment containing atpE; cA21C cM65C Apr | This work |
| Primersb | ||
| pET22-atpE-NdeI | 5′-GAGATATACATATGGAAAACCTGAATATGGATC-3′ | |
| pET22-atpE-EcoRI | 5′-GGAGCTCGAATTCCTACGCGACAGCGAACATCAC-3′ |
Restriction sites are underlined.
Primers were used for cloning of pET22-atpE-c21/65 by PCR using pBWU13.NOC as template, with the start codon of atpE in the NdeI site and the EcoRI site directly downstream from the stop codon of atpE, and ligating the NdeI/EcoRI-restricted PCR fragment into the correspondingly restricted vector pET-22b.
FIG. 1.
Immunoblot analysis of cross-linked subunit c (cA21C/cM65C) in inverted membrane vesicles of cells grown in the presence of different carbon sources. Membranes (5 mg/ml) prepared from E. coli DK8/pBWU13.NOC containing bi-cysteine-substituted subunit c were cross-linked with 1.5 mM copper-1,10-phenanthroline at pH 8.0, separated by nonreducing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (20 μg/lane), and immunoblotted as described by Krebstakies et al. (17). Blot membranes were incubated with anti-c monoclonal antibody GDH 9-2A2 (2) as the primary and IRDye800DX-labeled goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (Rockland, Gilbertsville, PA) as the secondary antibody and finally detected by using the two-channel Odyssey system (LI-COR). MM, minimal medium.
The results of several other studies also indicate that the c ring size is constant and independent of environmental parameters. Studies of the chloroplast subunit c oligomer of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii revealed a fixed stoichiometry that is not affected by the metabolic status of the cell caused by variations in light intensities, pH value, carbon source, or CO2 concentration (21). The anaerobic acetogenic bacterium Acetobacterium woodii encodes two types of c subunits, an 8-kDa bacterial Fo-like c subunit and an 18-kDa eukaryotic VO-like subunit (with only one proton binding site), present in the ring in a 9:1 stoichiometry. Growth experiments under autotrophic conditions using formate as the carbon source (ATP synthase required), as well as under heterotrophic fermenting conditions on fructose, methanol, or betaine (ion-pumping ATPase function required), excluded the possibility of carbon source-dependent variation of the stoichiometry (7). For the alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus strain OF4 and the thermoalkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain TA2.A1, it has been shown by completely different methods that the stoichiometry of the subunit c ring is independent of the pH of the medium used to grow the cells (10, 18).
Although 20 μg of membrane proteins were separated in each lane by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and a uniform transfer of proteins to the nitrocellulose membrane was controlled by Ponceau S staining (data not shown), the immunoblot analysis revealed different amounts of subunit c depending on the cell growth medium used (Fig. 1), and furthermore, the amounts of the other subunits of the ATP synthase were also increased in a similar range (data not shown), a phenomenon generally observed even for the wild-type strain E. coli K12 (G. Deckers-Hebestreit, personal observation). With a decrease in the possible energy yield provided by the medium applied for growth, the growth rate decreased as expected, while an increase in the amount of the FoF1 subunits shown here for subunit c is observable. The generation times of the cells ranged from 0.7 h in LB medium to 0.9 h in minimal medium with glucose, 1.8 h with glycerol, and about 6 h with succinate. The unusually long generation time for cells grown in minimal medium with succinate, which is not observed for wild-type cells (data not shown), is possibly due to dense protein packing within the membrane, producing a significant membrane proton permeability generated by the simultaneous overproduction of the plasmid-encoded ATP synthase and the increased synthesis of the C4-dicarboxylate transporter DctA that is necessary to obtain a sufficient transport capacity for the uptake of succinate (compare references 3, 33, and 17).
For quantitation of the increase observed for the ATP synthase, namely subunit c shown in Fig. 1, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD)-sensitive ATPase activities of the different membrane vesicles were determined as described by Krebstakies et al. (17). The activities varied by a factor of approximately 3.4, ranging from 0.8 μmol Pi·min−1·mg−1 for cells grown in LB medium to 1.8 and 2.3 μmol Pi·min−1·mg−1 for cells grown in minimal medium with glucose and glycerol, respectively, and 2.7 μmol Pi·min−1·mg−1 for cells grown in minimal medium with succinate. The results suggest that under different growth conditions, the amount of ATP synthase present in the cell changes, but not the subunit c stoichiometry, as previously discussed (26). Furthermore, the data are in good accord with studies of the transcriptional regulation of the atp operon by lacZ fusions that revealed a variation of the expression within a relatively narrow range of about a factor of three (15). However, these studies arrive at the conclusion that the cell growth rate rather than the type of carbon compound used for growth is the major variable in controlling atp gene expression (15), a result that is also observed by Schemidt et al. (26) for the transcriptional lacZ fusion to the atp promoter, as well as the two translational fusions to atpB. In this context it is worthwhile mentioning that in our studies, only the weak promoter P3 is present for transcription of the atp operon from the plasmid derived from pBWU13, while the main promoter, P1 (Patp), and a second weak promoter, P2, were missing, leading to an approximately fivefold increase of FoF1 synthesis compared to the level in the corresponding wild-type E. coli strain 1100 as determined by DCCD-sensitive ATPase activities (G. Deckers-Hebestreit, personal observation). Taking into account that the amount of enzyme complexes in the membrane increases within the range of about a factor of 3 due to a change in the growth medium minimized the possibility that the stoichiometry of subunit c may be biased by the overexpression system.
Our data are in contrast to the conclusions of Schemidt et al. (26), which may be explained by the following differences: we used a direct approach on the membrane level, without any further manipulation but with special emphasis on the high instability of the c ring, and visualized the number of c subunits present per ring, instead of determining the amount of subunit c synthesized in comparison to Fo subunits a or b in an indirect way. Schemidt et al. (26) based their conclusions on translational lacZ fusions to genes atpE and atpB (the latter coding for subunit a of Fo) inserted ectopically into the chromosome. However, regarding two different proteins, one has to keep in mind that the stability of the mRNA, as well as the stability of both proteins, might be different, which is the case at least for subunits a and c (8, 27). In addition, the amounts of subunits b and c present in FoF1 complexes isolated from solubilized membranes by anti-F1 immunoprecipitation were quantitated by immunoblotting, which is, however, only possible within the range of linear transfer rates for the individual protein studied.
The insertion of in vitro-synthesized E. coli subunit c into liposomes is catalyzed by the membrane protein insertase YidC, whereupon subunit c assembles into oligomers with a molecular mass of approximately 80 to 100 kDa (31). In addition, purified E. coli subunit c dissolved in detergent solution showed self-assembly into a ringlike structure (1). However, in both cases the number of c subunits present per oligomer has not been resolved. To determine whether the individual synthesis of subunit c independent of the presence of other FoF1 subunits leads to the formation of a comparable oligomeric ring structure with a preferred stoichiometry of 10 c subunits, we used the same approach as described above. For that purpose, the atp deletion strain HB1(DE3) (Table 1), obtained by P1 transduction using DK8 as the donor and BL21(DE3) as the recipient strain, was transformed with plasmid pET22-atpE-c21/65, which carries the atpE gene under the control of the isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG)-inducible T7 promoter coding for bi-cysteine-substituted subunit c (cA21C/cM65C). After cell growth in ampicillin-containing LB medium and induction of the atpE gene with IPTG, cross-linking of subunit c on the membrane vesicle level was performed as described above. The corresponding immunoblot analysis (Fig. 2) showed again that an identical cross-linking pattern for subunit c, stopping sharply with a c10 oligomer, was obtained irrespective of the presence or absence of the other subunits of the FoF1 complex and even in the presence of large amounts of subunit c in the membrane. For comparison, cross-linked membrane vesicles of cells grown in minimal medium with succinate showing the highest synthesis of FoF1 and, therefore, of subunit c were analyzed in parallel (Fig. 2). Again, all other intermediates of subunit c oligomerization are visible in appreciable amounts, stopping again at the level of decamer formation, demonstrating that subunit c is assembled into a ringlike structure, although the amount of individual c oligomer intermediates observed varied from experiment to experiment (compare also Fig. 1 and results in reference 17). The results revealed that in the case of E. coli, the unique biochemical properties of subunit c that are based on its primary structure obviously determine the shape of the subunits and their nearest-neighbor interactions and, therefore, the diameter of the ring, altogether resulting in an invariability of the subunit c stoichiometry, as has been discussed previously for several other organisms (20, 23). In addition, the assembly of subunit c into a ringlike structure is completely independent of a simultaneous synthesis of the other components of the ATP synthase, as has been also observed by the characterization of single-subunit knockout mutants (G. Deckers-Hebestreit, personal observation), suggesting that the subunit c oligomer is possibly the starter subcomplex for the assembly process of this multisubunit enzyme complex consisting of 22 individual polypeptides.
FIG. 2.
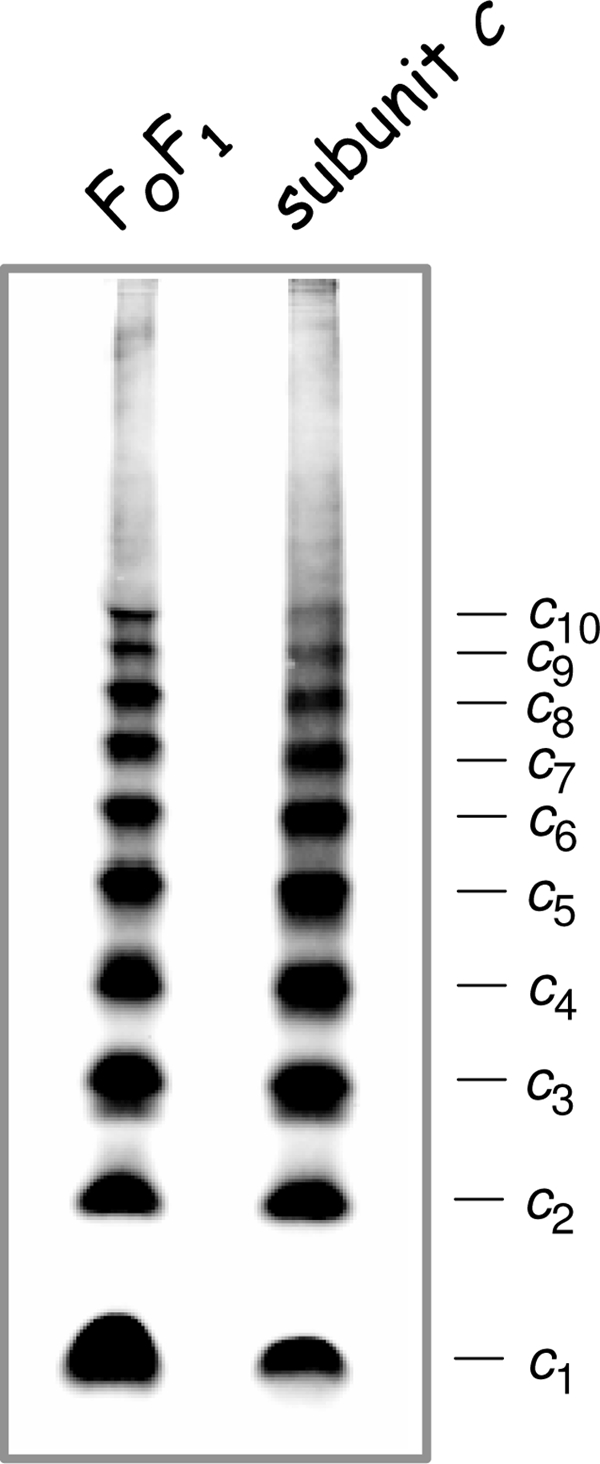
Comparison of cross-linked subunit c (cA21C/cM65C) in membrane vesicles of cells expressing the atp operon (FoF1) and cells exclusively expressing the atpE gene (subunit c). Lanes: FoF1, cells of E. coli DK8/pBWU13.NOC were grown in minimal medium with succinate and harvested at an optical density at 578 nm of 0.8 to 1.0; subunit c, cells of E. coli HB1(DE3)/pET22-atpE-c21/65 were grown in ampicillin-containing LB medium to an optical density of 1.0 prior to induction of atpE gene expression with 1 mM IPTG for 1 h. Membranes (20 μg/lane) containing bi-cysteine-substituted subunit c were examined as described in the legend of Fig. 1.
Acknowledgments
We thank Brigitte Herkenhoff-Hesselmann for familiarizing Britta Ballhausen with the technical details necessary to perform these experiments, Heiner Brookman for generating E. coli strain HB1(DE3), and Jörg-Christian Greie for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 431/P2).
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 30 January 2009.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arechaga, I., P. J. G. Butler, and J. E. Walker. 2002. Self-assembly of ATP synthase subunit c rings. FEBS Lett. 515189-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Birkenhäger, R., J.- C. Greie, K. Altendorf, and G. Deckers-Hebestreit. 1999. Fo complex of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Not all monomers of the subunit c oligomer are involved in F1 interaction. Eur. J. Biochem. 264385-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boogerd, F. C., L. Boe, O. Michelsen, and P. R. Jensen. 1998. atp mutants of Escherichia coli fail to grow on succinate due to a transport deficiency. J. Bacteriol. 1805855-5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dimroth, P., C. von Ballmoos, and T. Meier. 2006. Catalytic and mechanical cycles in F-ATP synthases. EMBO Rep. 7276-282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dmitriev, O. Y., P. C. Jones, and R. H. Fillingame. 1999. Structure of the subunit c oligomer of the F1Fo ATP synthase: model derived from solution structure of the monomer and cross-linking in the native enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 967785-7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fillingame, R. H., and O. Y. Dmitriev. 2002. Structural model of the transmembrane Fo rotary sector of H+-transporting ATP synthase derived by solution NMR and intersubunit cross-linking in situ. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1565232-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fritz, M., A. L. Klyszejko, N. Morgner, J. Vonck, B. Brutschy, D. J. Müller, T. Meier, and V. Müller. 2008. An intermediate step in the evolution of ATPases: a hybrid Fo-VO rotor in a bacterial Na+ F1Fo ATP synthase. FEBS J. 2751999-2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hermolin, J., and R. H. Fillingame. 1995. Assembly of Fo sector of Escherichia coli H+ ATP synthase. Interdependence of subunit insertion into the membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2702815-2817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hinkle, P. C. 2005. P/O ratios of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 17061-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ivey, D. M., M. G. Sturr, T. A. Krulwich, and D. B. Hicks. 1994. The abundance of atp gene transcript and of the membrane F1Fo-ATPase as a function of the growth pH of alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus OF4. J. Bacteriol. 1765167-5170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jiang, W., J. Hermolin, and R. H. Fillingame. 2001. The preferred stoichiometry of c subunits in the rotary motor sector of Escherichia coli ATP synthase is 10. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 984966-4971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jones, P. C., and R. H. Fillingame. 1998. Genetic fusions of subunit c in the Fo sector of H+-transporting ATP synthase. Functional dimers and trimers and determination of stoichiometry by cross-linking analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 27329701-29705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jones, P. C., W. Jiang, and R. H. Fillingame. 1998. Arrangement of the multicopy H+-translocating subunit c in the membrane sector of the Escherichia coli F1Fo ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 27317178-17185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Junge, W., and N. Nelson. 2005. Nature's rotary electromotors. Science 308642-644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kasimoglu, E., S.-J. Park, J. Malek, C. P. Tseng, and R. P. Gunsalus. 1996. Transcriptional regulation of the proton-translocating ATPase (atpIBEFHAGDC) operon of Escherichia coli: control by cell growth rate. J. Bacteriol. 1785563-5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Klionsky, D. J., W. S. A. Brusilow, and R. D. Simoni. 1984. In vivo evidence for the role of the ɛ subunit as an inhibitor of the proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1601055-1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Krebstakies, T., I. Aldag, K. Altendorf, J.- C. Greie, and G. Deckers-Hebestreit. 2008. The stoichiometry of subunit c of Escherichia coli ATP synthase is independent of its rate of synthesis. Biochemistry 476907-6916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Meier, T., N. Morgner, D. Matthies, D. Pogoryelov, S. Keis, G. M. Cook, P. Dimroth, and B. Brutschy. 2007. A tridecameric c ring of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase from the thermoalkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain TA2.A1 facilitates ATP synthesis at low electrochemical proton potential. Mol. Microbiol. 651181-1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meier, T., S. A. Ferguson, G. M. Cook, P. Dimroth, and J. Vonck. 2006. Structural investigations of the membrane-embedded rotor ring of the F-ATPase from Clostridium paradoxum. J. Bacteriol. 1887759-7764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Meier, T., J. Yu, T. Raschle, F. Henzen, P. Dimroth, and D. J. Müller. 2005. Structural evidence for a constant c11 ring stoichiometry in the sodium F-ATP synthase. FEBS J. 2725474-5483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Meyer zu Tittingdorf, J. M. W., S. Rexroth, E. Schäfer, R. Schlichting, C. Giersch, N. A. Dencher, and H. Seelert. 2004. The stoichiometry of the chloroplast ATP synthase oligomer III in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is not affected by the metabolic state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 165992-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mitome, N., T. Suzuki, S. Hayashi, and M. Yoshida. 2004. Thermophilic ATP synthase has a decamer c-ring: indication of noninteger 10:3 H+/ATP ratio and permissive elastic coupling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10112159-12164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Müller, D. J., N. A. Dencher, T. Meier, P. Dimroth, K. Suda, H. Stahlberg, A. Engel, H. Seelert, and U. Matthey. 2001. ATP synthase: constrained stoichiometry of the transmembrane rotor. FEBS Lett. 504219-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pogoryelov, D., C. Reichen, A. L. Klyszejko, R. Brunisholz, D. J. Müller, P. Dimroth, and T. Meier. 2007. The oligomeric state of c rings from cyanobacterial F-ATP synthases varies from 13 to 15. J. Bacteriol. 1895895-5902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schemidt, R. A., D. K. W. Hsu, G. Deckers-Hebestreit, K. Altendorf, and W. S. A. Brusilow. 1995. The effects of an atpE ribosome-binding site mutation on the stoichiometry of the c subunit in the F1Fo ATPase of Escherichia coli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 323423-428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schemidt, R. A., J. Qu, J. R. Williams, and W. S. A. Brusilow. 1998. Effects of carbon source on expression of Fo genes and on the stoichiometry of the c subunit in the F1Fo ATPase of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1803205-3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schramm, H.-C., B. Schneppe, R. Birkenhäger, and J. E. G. McCarthy. 1996. The promoter-proximal, unstable IB region of the atp mRNA of Escherichia coli: an independently degraded region that can act as a destabilizing element. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1307162-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Steigmiller, S., P. Turina, and P. Gräber. 2008. The thermodynamic H+/ATP ratios of the H+-ATP synthases from chloroplasts and Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1053745-3750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Toei, M., C. Gerle, M. Nakano, K. Tani, N. Gyobu, M. Tamakoshi, N. Sone, M. Yoshida, Y. Fujiyoshi, K. Mitsuoka, and K. Yokoyama. 2007. Dodecamer rotor ring defines H+/ATP ratio for ATP synthesis of prokaryotic V-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10420256-20261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tomashek, J. J., and W. S. A. Brusilow. 2000. Stoichiometry of energy coupling by proton-translocating ATPases: a history of variability. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 32493-500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.van der Laan, M., P. Bechtluft, S. Kol, N. Nouwen, and A. J. M. Driessen. 2004. F1Fo ATP synthase subunit c is a substrate of the novel YidC pathway for membrane protein biogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 165213-222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.von Ballmoos, C., G. M. Cook, and P. Dimroth. 2008. Unique rotary ATP synthase and its biological diversity. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 3743-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zientz, E., J. Bongaerts, and G. Unden. 1998. Fumarate regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli by the DcuSR (dcuSR genes) two-component regulatory system. J. Bacteriol. 1805421-5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]