Abstract
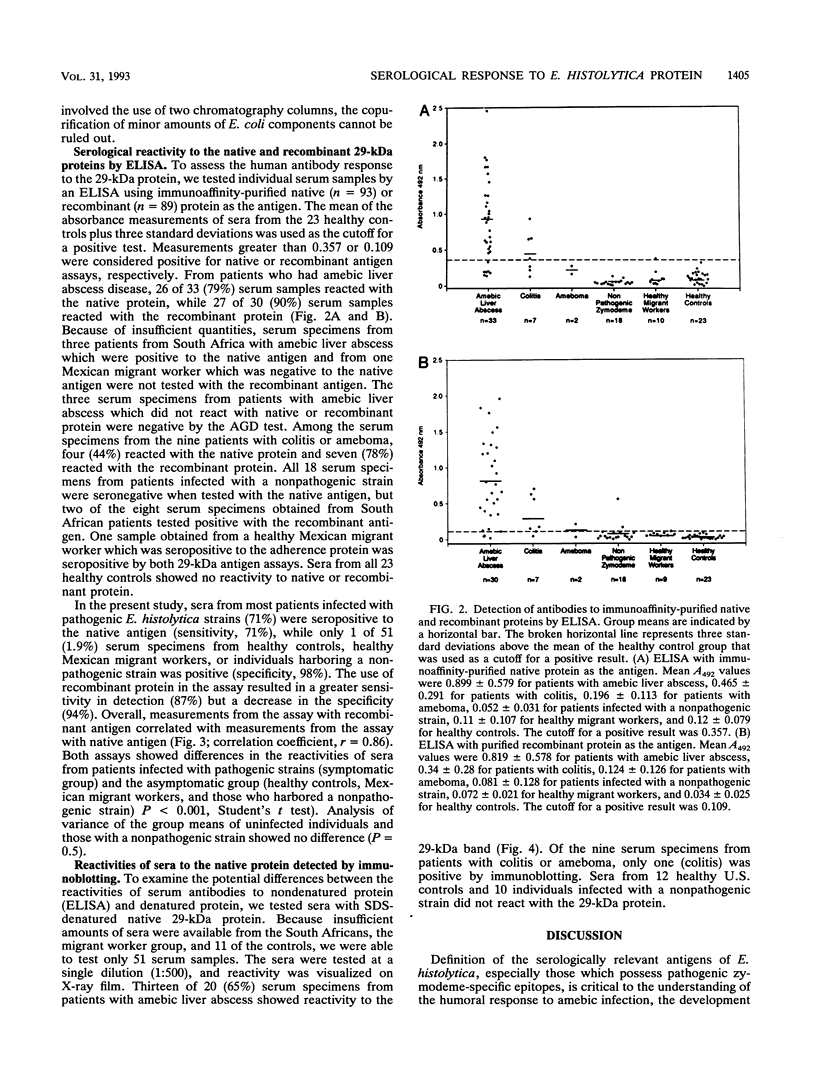
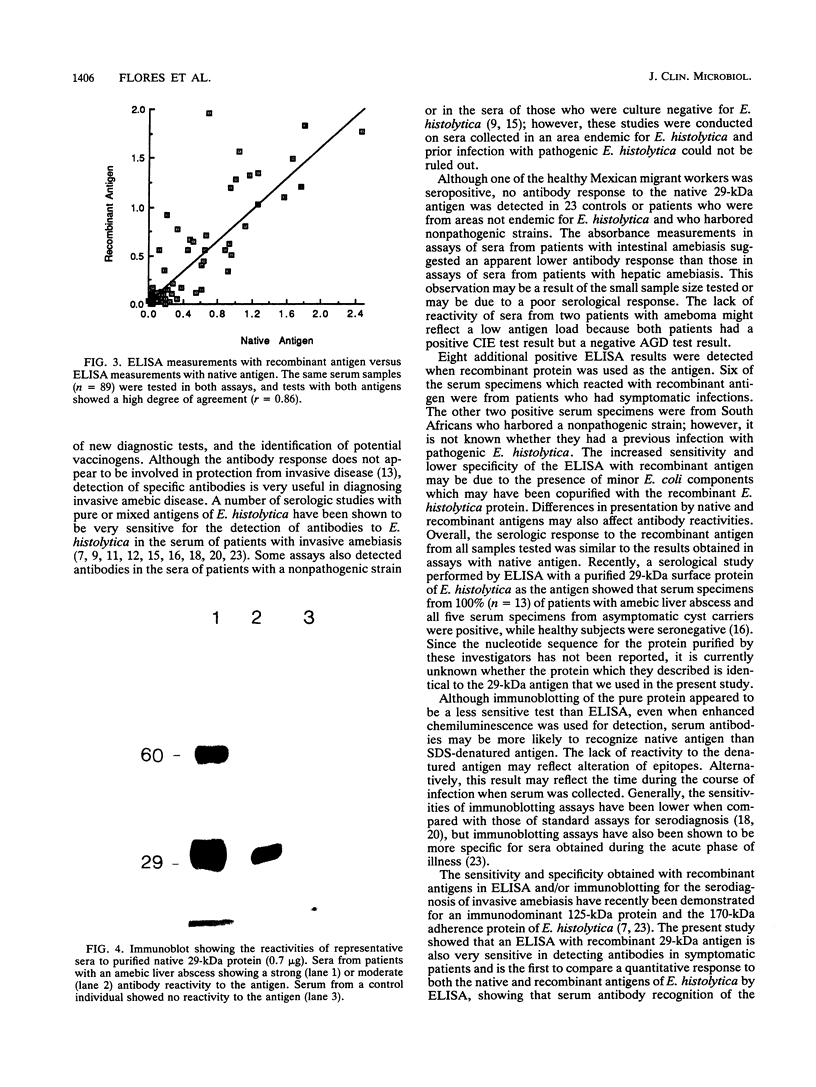
The 29-kDa peripheral membrane protein of Entamoeba histolytica has recently been demonstrated to have epitopes on pathogenic clinical isolates which were not detected by monoclonal antibodies on nonpathogenic isolates. To analyze the serological response to this protein, we tested 93 serum specimens (from 33 patients with amebic liver abscess, 7 patients with colitis, 2 patients with ameboma, 18 individuals harboring a nonpathogenic zymodeme strain, 10 healthy Mexican migrant workers, and 23 healthy controls) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using immunoaffinity-purified native or recombinant protein. When tested by ELISA with the native antigen, 79% (26 of 33) of the serum specimens from patients with amebic liver abscess, 4 of 9 serum specimens from symptomatic patients with colitis or ameboma, and serum from one migrant worker were positive. None of the 18 subjects harboring a nonpathogenic strain or 23 control individuals were seropositive to the native antigen (sensitivity, 71%; specificity, 98%). Of 30 serum specimens from patients with amebic liver abscess tested with recombinant antigen, 27 were seropositive (90%). In addition, six patients with colitis or ameboma and two individuals who harbored a nonpathogenic strain were seropositive to the recombinant antigen. One healthy Mexican migrant worker tested positive by both ELISAs (sensitivity, 87%; specificity, 94%). Immunoblotting of 51 serum specimens to sodium dodecyl sulfate-denatured native 29-kDa protein was less sensitive (65%) than ELISA in detecting serum antibodies to the antigen. These results suggest a similar antibody response to native and recombinant antigens (r = 0.86) and support the potential utility of a quantitative assay with defined recombinant antigen for the serodiagnosis of invasive amebiasis in nonendemic areas in conjunction with other diagnostic tools.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores B. M., Batzer M. A., Stein M. A., Petersen C., Diedrich D. L., Torian B. E. Structural analysis and demonstration of the 29 kDa antigen of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica as the major accessible free thiol-containing surface protein. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):755–763. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Giladi M., Huber M., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. DNA probes specific for Entamoeba histolytica possessing pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):926–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.926-931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R. Immunologic tools in the diagnosis of amebiasis: epidemiology in the United States. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):239–246. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotter H., Mannweiler E., Schreiber M., Tannich E. Sensitive and specific serodiagnosis of invasive amebiasis by using a recombinant surface protein of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3163–3167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3163-3167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino E., Glender W., del Muro R., Ortiz-Ortiz L. Evaluation of the ELISA test for detection of Entamoeba histolytica in feces. J Clin Lab Anal. 1990;4(1):39–42. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860040108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Jackson T. F., Petri W. A., Jr, Murphy C. F., Ungar B. L., Gathiram V., Skilogiannis J., Simjee A. E. Association of serum antibodies to adherence lectin with invasive amebiasis and asymptomatic infection with pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):768–772. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Flores B. M., Batzer M. A., Stein M. A., Stroeher V. L., Carlton J. E., Diedrich D. L., Torian B. E. Molecular and cellular characterization of the 29-kilodalton peripheral membrane protein of Entamoeba histolytica: differentiation between pathogenic and nonpathogenic isolates. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):542–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.542-549.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Keene W. E., McKerrow J. H. Thiol proteinase expression and pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2772–2777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2772-2777.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert R., Mahaza C., Bernard C., Buffard C., Senet J. M. Evaluation of a new bicolored latex agglutination test for immunological diagnosis of hepatic amoebiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1422–1424. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1422-1424.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. Review of the human immune mechanisms directed against Entamoeba histolytica. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):261–272. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathar M. A., Bredenkamp B. L., Gathiram V., Simjee A. E., Jackson T. F. Detection of Entamoeba histolytica immunoglobulins G and M to plasma membrane antigen by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):332–335. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.332-335.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shandil R. K., Vinayak V. K. Immunochemical characterisation of a 29-Kda surface-associated molecule of Entamoeba histolytica and its recognition by serum from patients with amoebiasis. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jan;36(1):41–45. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. L., Jr, Jackson T. F., Reed S. L., Calderon J., Kunz-Jenkins C., Gathiram V., Li E. Serodiagnosis of invasive amebiasis using a recombinant Entamoeba histolytica protein. JAMA. 1991 Oct 9;266(14):1984–1986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian B. E., Flores B. M., Stroeher V. L., Hagen F. S., Stamm W. E. cDNA sequence analysis of a 29-kDa cysteine-rich surface antigen of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6358–6362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian B. E., Reed S. L., Flores B. M., Plorde J., Stamm W. E. Serologic response to the 96,000-Da surface antigen of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):794–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Li E., Jackson T. F., Zhang T., Gathiram V., Stanley S. L., Jr Use of a recombinant 170-kilodalton surface antigen of Entamoeba histolytica for serodiagnosis of amebiasis and identification of immunodominant domains of the native molecule. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2788–2792. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2788-2792.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]