Abstract
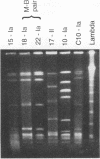
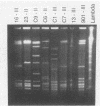
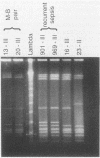
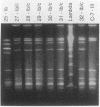
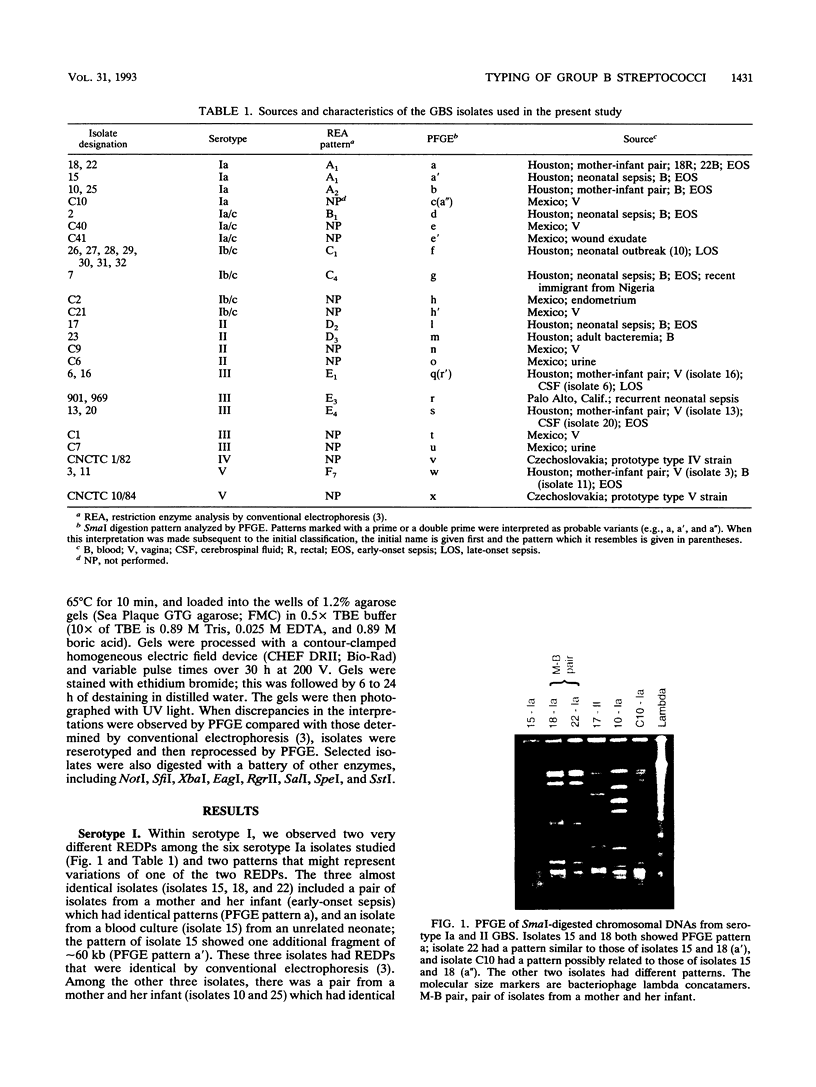
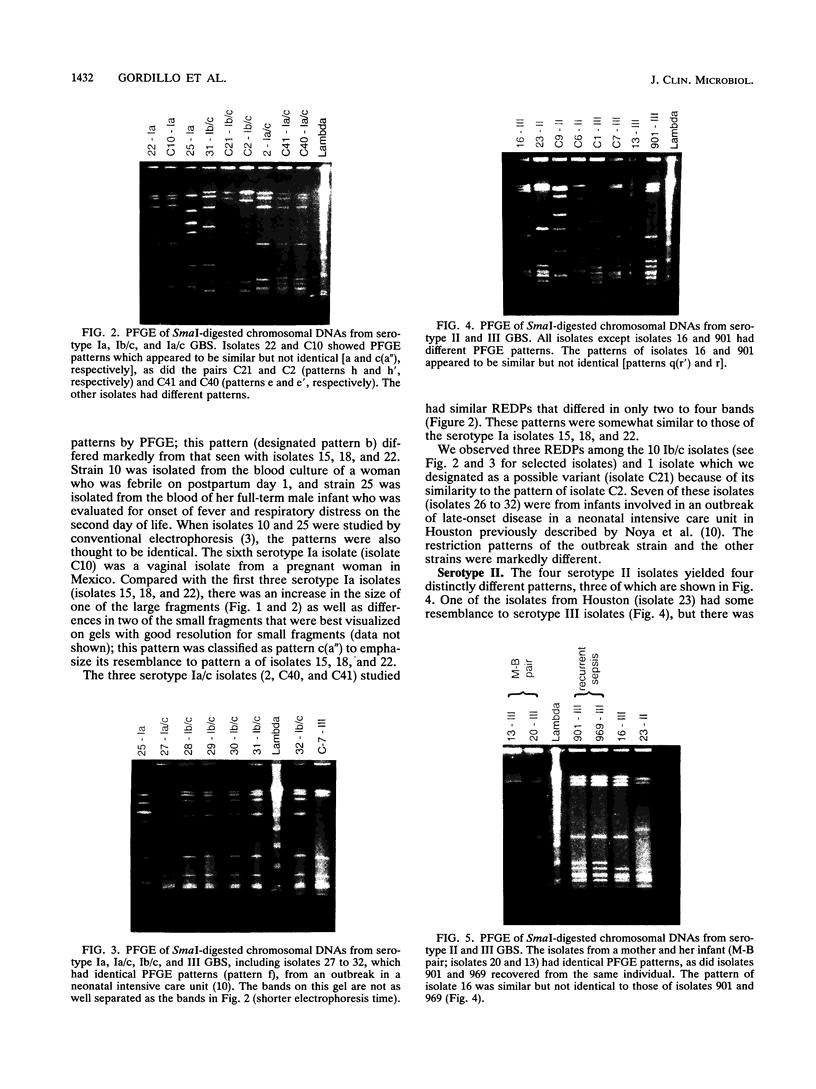
The SmaI restriction endonuclease digestion patterns of chromosomal DNAs from 35 group B streptococci were analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Nineteen different patterns and four possible variants were identified. Twenty-four isolates were previously analyzed by conventional electrophoresis of HindIII-digested and/or BglII plus EcoRI double-digested chromosomal DNA. Although interpretations by both methods were essentially the same, PFGE identified as variants two isolates that were previously classified as the same isolate. More importantly, PFGE of the chromosomal DNA of group B streptococci digested with SmaI generated more easily defined patterns, since fewer and better separated bands were obtained, whereas digestion with HindIII or EcoRI plus BglII typically generated 100 or more bands. SalI digestion also yielded easily evaluable results, although the SalI fragments were somewhat smaller than those generated by SmaI. In our hands, PFGE patterns were more easily discerned and interpreted than were patterns previously generated by conventional electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingen E., Denamur E., Lambert-Zechovsky N., Aujard Y., Brahimi N., Geslin P., Elion J. Analysis of DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism extends the evidence for breast milk transmission in Streptococcus agalactiae late-onset neonatal infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):569–573. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Baker C. J., Troup N. J., Tompkins L. S. Restriction endonuclease analysis of human and bovine group B streptococci for epidemiologic study. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1352–1356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1352-1356.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner P. I., Gopalakrishna K. V., Wolinsky E., McHenry M. C., Tan J. S., Rosenthal M. Group B streptococcus (S. agalactiae) bacteremia in adults: analysis of 32 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Nov;56(6):457–473. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197711000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. G., Singh K. V., Murray B. E. DNA fingerprinting of Enterococcus faecium by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis may be a useful epidemiologic tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2752–2757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2752-2757.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Heath J. D., Sharma B. R., Weinstock G. M. Comparison of genomic DNAs of different enterococcal isolates using restriction endonucleases with infrequent recognition sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2059–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2059-2063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Markowitz S. M., Lopardo H. A., Patterson J. E., Zervos M. J., Rubeglio E., Eliopoulos G. M., Rice L. B., Goldstein F. W. Evidence for clonal spread of a single strain of beta-lactamase-producing Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis to six hospitals in five states. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):780–785. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Mattingly S. J., Quentin R., Goudeau A., Selander R. K. Identification of a high-virulence clone of type III Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) causing invasive neonatal disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4731–4735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noya F. J., Rench M. A., Metzger T. G., Colman G., Naidoo J., Baker C. J. Unusual occurrence of an epidemic of type Ib/c group B streptococcal sepsis in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1135–1144. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opal S. M., Cross A., Palmer M., Almazan R. Group B streptococcal sepsis in adults and infants. Contrasts and comparisons. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Mar;148(3):641–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pischel K. D., Weisman M. H., Cone R. O. Unique features of group B streptococcal arthritis in adults. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Jan;145(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riefler J., 3rd, Molavi A., Schwartz D., DiNubile M. Necrotizing fasciitis in adults due to group B streptococcus. Report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Mar;148(3):727–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small C. B., Slater L. N., Lowy F. D., Small R. D., Salvati E. A., Casey J. I. Group B streptococcal arthritis in adults. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. The development of a phage-typing system for group-B streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):133–143. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese A., Mireault K., Arbeit R. D. Group B streptococcal bacteremia in men. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):912–917. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Eagon R. G. Type-specific antigens of group B type Ic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.596-604.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yow M. D., Leeds L. J., Thompson P. K., Mason E. O., Jr, Clark D. J., Beachler C. W. The natural history of group B streptococcal colonization in the pregnant woman and her offspring. I. Colonization studies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 May 1;137(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]