Abstract
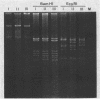
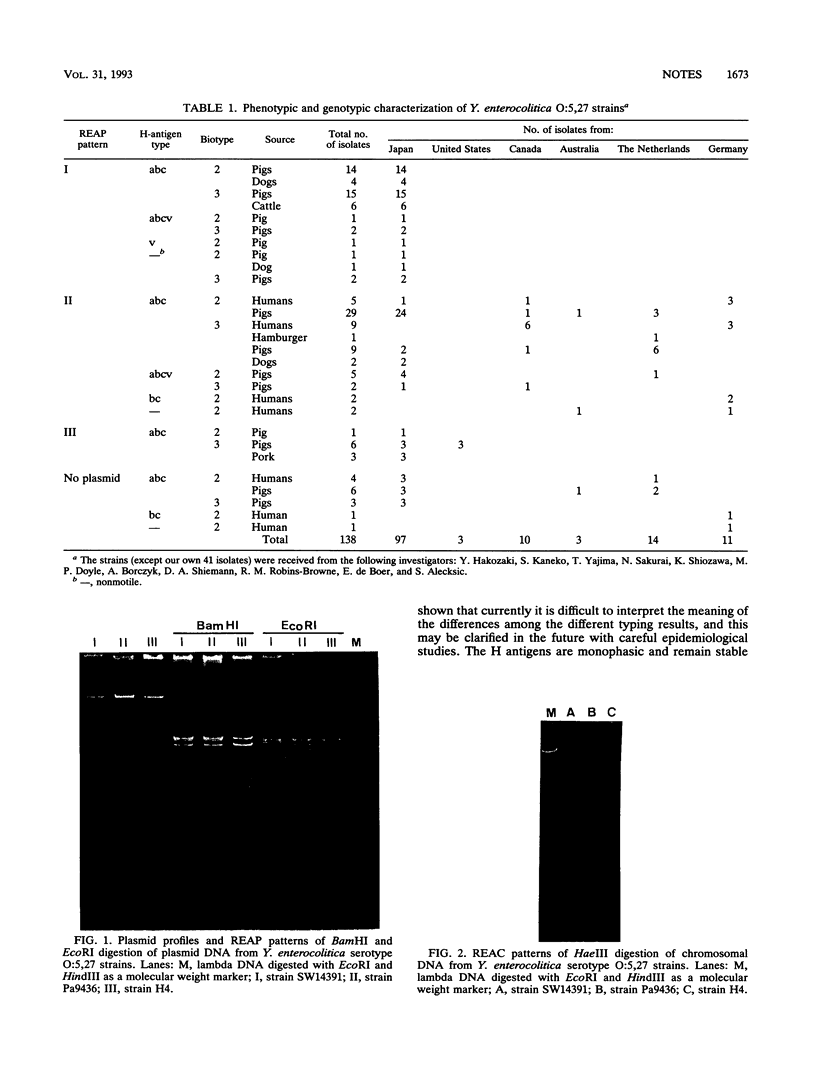
Restriction endonuclease analyses of virulence plasmid DNA (REAP) and chromosomal DNA and other phenotypic characteristics were used to study the differentiation of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:5,27 strains. There was a close correlation between REAP patterns and the geographical distribution of serotype O:5,27. Human isolates produced only one REAP pattern, which was also found with isolates from pigs and dogs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleksić S., Bockemühl J., Wuthe H. H., Aleksić V. Occurrence and clinical importance of the pathogenic serogroup O: 5, 27 of Yersinia enterocolitica in the Federal Republic of Germany and methods for its serological and bacteriological identification. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Aug;269(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa Y., Akahane S., Shiozawa K., Honma T. Investigations of source and route of Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Tsubokura M. Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 3B serotype 03 phage type II infection in pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Dec;47(6):1011–1015. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Nesbakken T., Aleksic S., Mollaret H. H. Comparison of restriction endonuclease analysis and phenotypic typing methods for differentiation of Yersinia enterocolitica isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1125–1131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1125-1131.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbakken T., Kapperud G., Sørum H., Dommarsnes K. Structural variability of 40-50 Mdal virulence plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica. Geographical and ecological distribution of plasmid variants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1987 Jun;95(3):167–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb03107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Borman P. A rapid biochemical method for purifying high molecular weight bacterial chromosomal DNA for restriction enzyme analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3631–3631. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]