Abstract
A convergent route to the synthesis of manassantins A and B, potent inhibitors of HIF-1, is described. Central to the synthesis is a stereoselective addition of an organozinc reagent to a 2-benzenesulfonyl cyclic ether to achieve the 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-cis-tetrahydrofuran of the natural products. Preliminary structure—activity relationships suggested that the (R)-configuration at C-7 and C-7″′ is not critical for HIF-1 inhibition. In addition, the hydroxyl group at C-7 and C-7″′ can be replaced with carbonyl group without loss of activity.
Tumor cells function under a condition of low physiological oxygen levels known as hypoxia. To cope with this environment, tumor cells have developed a number of essential mechanisms to promote angiogenesis and cell survival.1 Among these coping mechanisms is a response mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1).2 More than 60 target genes that HIF-1 regulates have been identified, and the products of these genes act at various steps in tumor progression.3 In addition, tumor cells characterized by over-expression of HIF-1 have been shown to be more resistant to traditional cancer treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy.4 Due to the importance of HIF-1 in tumor development and progression, a considerable amount of effort has been made to identify HIF-1 inhibitors for treatment of cancer. Several small molecules have been reported to inhibit the HIF-1 signaling pathway,5 however, these compounds often exhibit biological activities other than HIF-1 inhibition. In addition, most of them lack the desired selectivity for the HIF-1 signaling pathway or toxicity profiles required for a useful therapeutic agent.
Interestingly, the dineolignans manassantins A (1) and B (2) (Figure 1), isolated from the aquatic plant Saururus cernuus L., have been shown to be potent inhibitors of HIF-1.6 However, their molecular mechanisms of action have yet to be established. Hanessian and co-workers recently reported the first total synthesis of 1 and 2 as well as confirmed the absolute configuration of the natural products.7 In broad connection with our interest in the stereoselective synthesis of tetrasubstituted tetrahydrofurans,8 we undertook the synthesis of 1 and 2 to develop a synthetic route to the natural products that would be easily amenable to the development of analogues for biological studies. Herein, we report a synthesis of 1 and 2 through nucleophilic addition of an organozinc reagent to a 2-benzenesulfonyl cyclic ether to achieve the 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-cis-tetrahydrofuran moiety of the natural products and preliminary structure—activity relationships.
Figure 1.
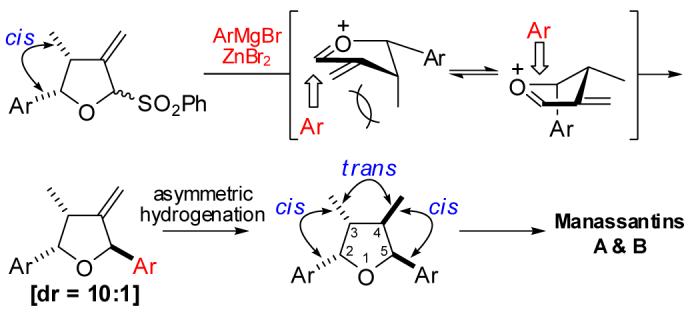
Retrosynthetic plan for manassantins A (1) and B (2).
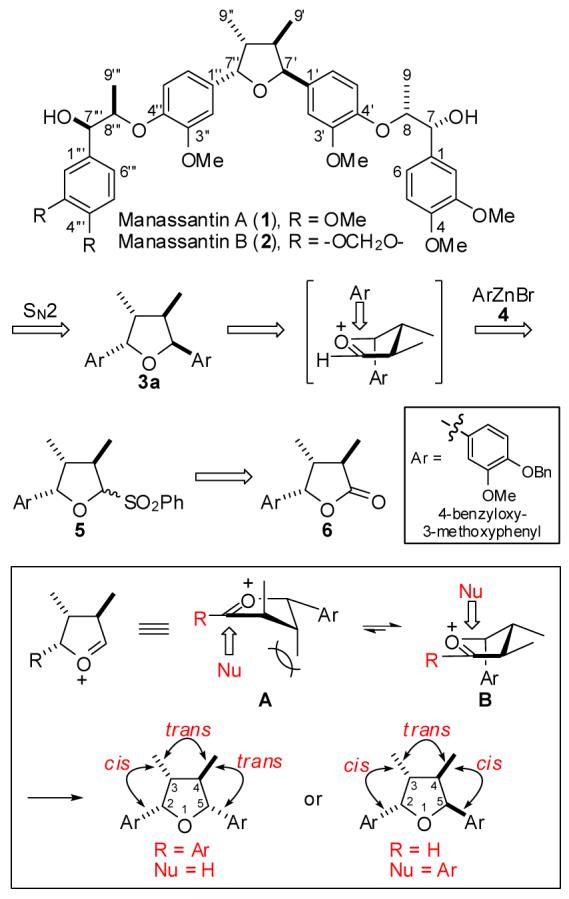
Figure 1 describes our approach to the synthesis of manassantins A (1) and B (2). Previously, we reported a stereoselective synthesis of 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-trans-and 2,3-trans-3,4-trans-4,5-trans-tetrahydrofurans via BF3·OEt2-promoted reductive deoxygenation of cyclic hemiketals.8 The stereochemical outcome was rationalized based on Woerpel’s “inside attack” model.9 Based on the same rationale, we envisioned that the organozinc reagent 4 would be added to the sterically more favorable conformation (B) of the 2-benzenesulfonyl cyclic ether 5 from the inside face of the envelope conformer to stereoselectively provide the 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-cis tetrahydrofuran (3a). This core tetrahydrofuran unit 3a could be coupled to the appropriate side arms via SN2 reactions to complete the synthesis of 1 and 2.
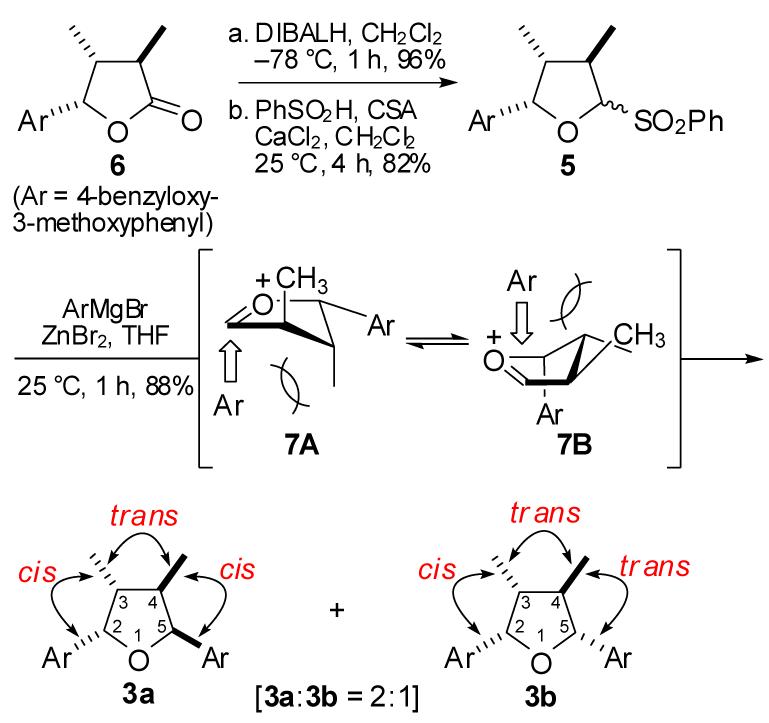
As shown in Scheme 1, reduction of 68 with DIBALH followed by treatment with PhSO2H and camphorsulfonic acid provided the 2-benzenesulfonyl cyclic ether 5.10 Unfortunately, the key nucleophilic substitution reaction of 5 with (4-benzyloxy-3-methoxyphenyl)zinc(II) bromide 4, derived in situ from (4-benzyloxy-3-methoxyphenyl)magnesium bromide and ZnBr2,10 provided a 2:1 diastereomeric mixture of 2,5-diaryl-3,4-dimethyl tetrahydrofurans. Careful analysis of 1H NMR spectral data revealed that the major diastereomer had the desired 2,3-cis3,4-trans-4,5-cis-configuration (3a) and the minor diastereomer had the 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-trans-configuration (3b). We reasoned that the poor diastereoselectivity of the reaction would stem from two competing factors. According to Woerpel’s “inside attack” model, 4 would be delivered to 5 from the inside face of the envelope conformer (7B) to provide the desired tetrahydrofuran (3a). However, the addition of 4 to the oxocarbenium intermediate via 7B also causes an unfavorable repulsive interaction with the C-4 methyl group leading to poor diastereoselectivity. We hypothesized that minimization of the steric repulsion between the incoming nucleophile and the C-4 methyl group would improve the disastereoselectivity.
Scheme 1.
Nucleophilic addition of (4-benzyloxy-3-methoxyphenyl)zinc(II) bromide to 2-benzenesulfonyl cyclic ether
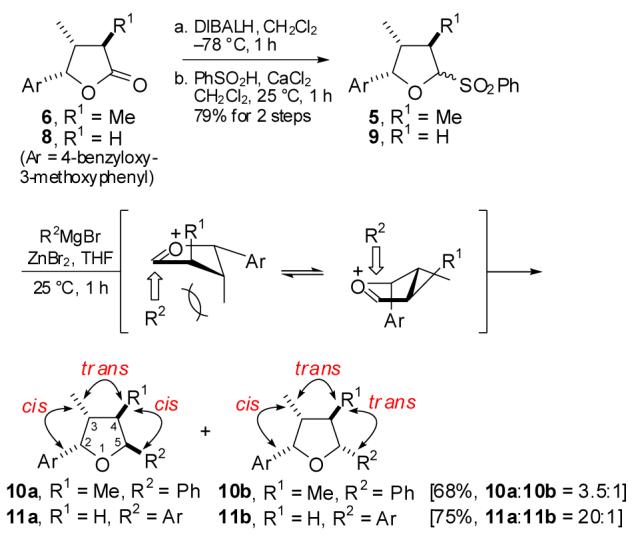
To prove this hypothesis, we tested two model systems where the repulsive interaction was reduced by addition of a smaller nucleophile or removal of the C-4 methyl group (Scheme 2). As expected, addition of a sterically less demanding PhZnBr to 5 gave a 3.5:1 diastereomeric mixture of 10a and 10b. In addition, when 4 was added to the cyclic ether 9, the reaction proceeded with excellent distereoselectivity (dr = 20:1). Based on the observations, we envisioned that the installation of a sterically less demanding exo-methylene group as a precursor to the C-4 methyl group and stereoselective reduction of the double bond would provide 3a in good stereoselectivity.
Scheme 2.
Model studies for nucleophilic addition reaction
As shown in Scheme 3, alkylation of 8 with Eschenmoser’s salt and m-CPBA oxidation smoothly proceeded to afford 12 (80% for 2 steps).11 Reduction of 12 with DIBALH followed by treatment with PhSO2H provided 13 in 64% yield. As expected, the exo-methylene group in 13 directed the addition of 4 via “inside attack” model to provide the desired 2,3-cis-2,5-trans-tetrahydrofuran 14 as a major diastereomer (dr = 10:1, 41%). However, catalytic hydrogenation under conventional conditions (e.g. Pd/C, PtO2) or diimide reduction of 14 only gave the desired 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-cis-tetrahydrofuran as a minor diastereomer (dr = 1:1–1:4). After extensive search of reaction conditions, we were delighted to find that asymmetric hydrogenation of 14 in the presence of Ir and (4S,5S)-ThrePHOX12 provided 3a in 99% yield (dr = 4:1).13
Scheme 3.
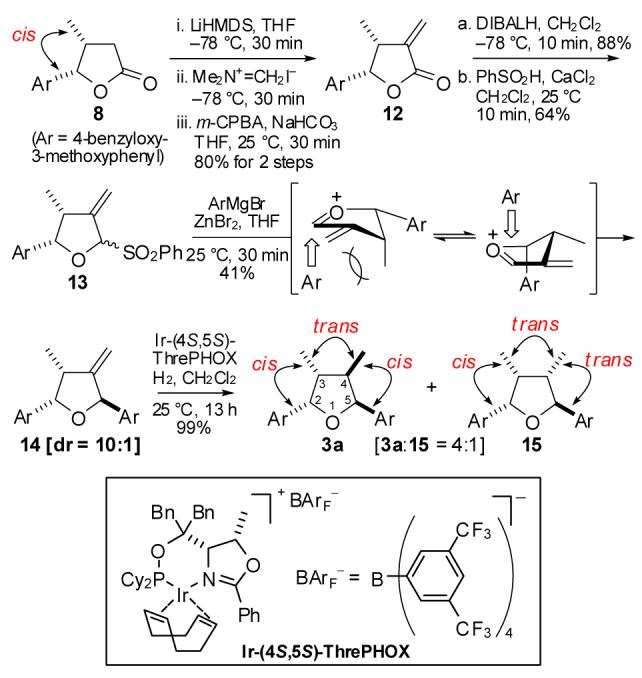
Stereoselective synthesis of 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-cis-tetrahydrofuran
With the desired tetrahydrofuran 3a in hand, we turned our attention to the installation of the side arms (Scheme 4). We anticipated that coupling of 16 and 17 by Mitsunobu coupling or oxidation—reduction condensation via alkoxydiphenylphosphines14 would proceed to afford 18. However, our efforts for coupling reactions were unsuccessful in all attempts and led us to adopt the procedures reported by Ley15 and Hanessian.7 A BEMP-mediated SN2 reaction of 16 and 1716 followed by stereocontrolled-reduction using polymer-supported BH4 completed the synthesis of manassnatins A (1). In order to accomplish the synthesis of 2, 16 was subjected to the BEMP-mediated SN2 reaction with 1 equivalent of 17 to form the mono-alkylation product 19 (29%) in addition to 18 (21%). Compound 19 was then subjected to a second BEMP-mediated SN2 reaction with 2016 to give 21 (77%). Reduction of 21 with polymer-supported BH4 then afforded manassantin B (2).
Scheme 4.
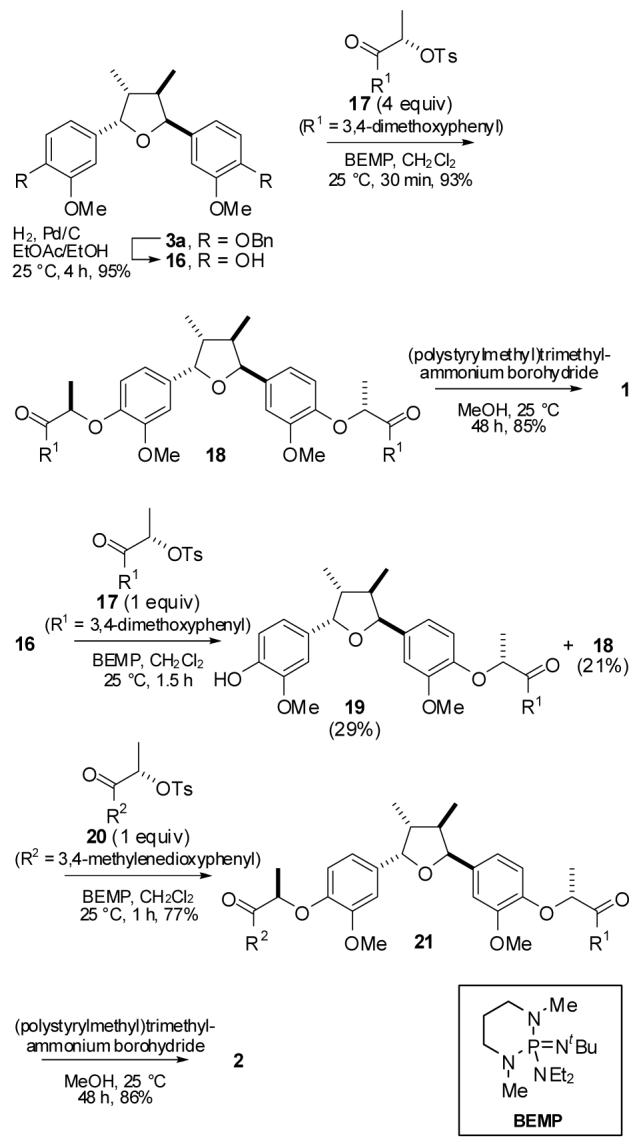
Completion of synthesis of manassantins A (1) and B (2)
ODD-Luc assay17 to assess HIF-1 inhibitory activity of 1, 18, and anti-diol diastereomer 22 ((7S,7″′S)-epimer) revealed that 1, 18, and 22 exhibited similar levels of HIF-1 inhibitory activity (IC50 = 1–10 nM). The data suggested that the (R)-configuration at C-7 and C-7″′ is not critical for HIF-1 inhibition. In addition, the hydroxyl group at C-7 and C-7″′can be replaced with carbonyl group without significant loss of activity.
In summary, we applied a direct nucleophilic addition of the organozinc reagent 4 to the 2-benzenesulfonyl cyclic ether 5 followed by an asymmetric hydrogenation to synthesize the 2,3-cis-3,4-trans-4,5-cis-tetrahydrofuran moiety of 1 and 2, potent inhibitors of HIF-1. The stereoselectivity of the nucleophilic addition reaction was improved by introduction of the sterically less demanding exo-methylene group as a surrogate for the C-9′ methyl group in 1 and 2. The synthetic strategy would allow access to more potent and selective analogues of 1 and 2 for biological studies to identify their molecular mechanism of action.
Supplementary Material
Figure 2.
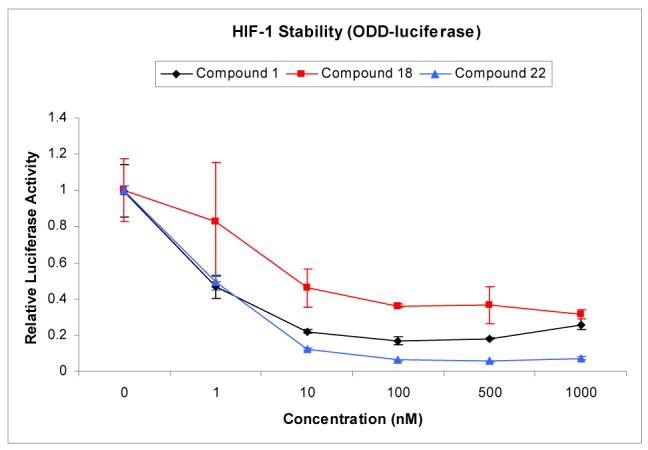
Inhibition of HIF-1 by 1, 18, and 22.
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Chuan-Yuan Li (Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center) for the 4T1-ODD-Luc. This work was supported by Duke University, Duke Chemistry Undergraduate Summer Research Program, and NIH/NCI CA40355. H.K. gratefully acknowledges the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD) (KRF-2006-352-E00028) for a postdoctoral fellowship.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available General experimental procedures including spectroscopic and analytical data for 1, 2, 3a, 3b, 5, 9, 10a, 10b, 11a, and 12–21 along with copies of 1H and 13C NMR spectra; detailed assay procedure. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Harris AL. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:38–47. doi: 10.1038/nrc704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Semenza GL. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999;15:551–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.15.1.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Semenza GL. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:721–732. doi: 10.1038/nrc1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4 (a).Moon EJ, Brizel DM, Chi JT, Dewhirst MW. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2007;9:1237–1294. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Dewhirst MW, Cao Y, Moeller B. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2008;8:425–437. doi: 10.1038/nrc2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5 (a).Giaccia A, Siim BG, Johnson RS. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003;2:803–811. doi: 10.1038/nrd1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Semenza GL. Drug Discovery Today. 2007;12:853–859. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6 (a).Rao KV, Alvarez FM. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983;24:4947–4950. [Google Scholar]; (b) Hodges TW, Hossain CF, Kim YP, Zhou YD, Nagle DG. J. Nat. Prod. 2004;67:767–771. doi: 10.1021/np030514m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Hossain CF, Kim Y-P, Baerson SR, Zhang L, Bruick RK, Mohammed KA, Agarwal AK, Nagle DG, Zhou Y-D. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005;333:1026–1033. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hanessian S, Reddy GJ, Chahal N. Org. Lett. 2006;8:5477–5480. doi: 10.1021/ol0621710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim H, Wooten CM, Park Y, Hong J. Org. Lett. 2007;9:3965–3968. doi: 10.1021/ol7016388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9 (a).Shaw JT, Woerpel KA. J. Org. Chem. 1997;62:6706–6707. doi: 10.1021/jo962186j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Larsen CH, Riggway BH, Shaw JT, Woerpel KA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:12208–12209. [Google Scholar]; (c) Shaw JT, Woerpel KA. Tetrahedron. 1999;55:8747–8756. [Google Scholar]; (d) Bear TJ, Shaw JT, Woerpel KA. J. Org. Chem. 2002;67:2056–2064. doi: 10.1021/jo010823m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Smith DM, Woerpel KA. Org. Lett. 2004;6:2063–2066. doi: 10.1021/ol0492647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10 (a).Brown DS, Ley SV. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988;29:4869–4872. [Google Scholar]; (b) Brown DS, Bruno M, Davenport RJ, Ley SV. Tetrahedron. 1989;45:4293–4308. [Google Scholar]
- 11 (a).Schreiber J, Maag H, Hashimoto N, Eschenmoser A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1971;10:330–331. [Google Scholar]; (b) Mandal M, Yun H, Dudley GB, Lin S, Tan DS, Danishefsky SJ. J. Org. Chem. 2005;70:10619–10637. doi: 10.1021/jo051470k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McIntyre S, Hoermann E, Menges F, Smidt P, Pfaltz A. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005;347:282–288. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Asymmetric hydrogenation of 14 in the presence of Ir and (4R,5R)-ThrePHOX provided 3a as a minor diastereomer (dr = 1:2).
- 14.Shintou T, Mukaiyama T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:7359–7367. doi: 10.1021/ja0487877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee AL, Ley SV. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003;1:3957–3966. doi: 10.1039/b308761a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Following the procedures reported in ref 15, 17 and 20 were prepared from 1,2-dimethyl-4-(2-propen-1-yl)benzene and 5-(2-propen-1-yl)-1,3-benzodioxole, respectively.
- 17.Li F, Sonveaux P, Rabbani ZN, Liu S, Yan B, Huang Q, Vujaskovic Z, Dewhirst MW, Li CY. Mol. Cell. 2007;26:63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.02.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


