Abstract
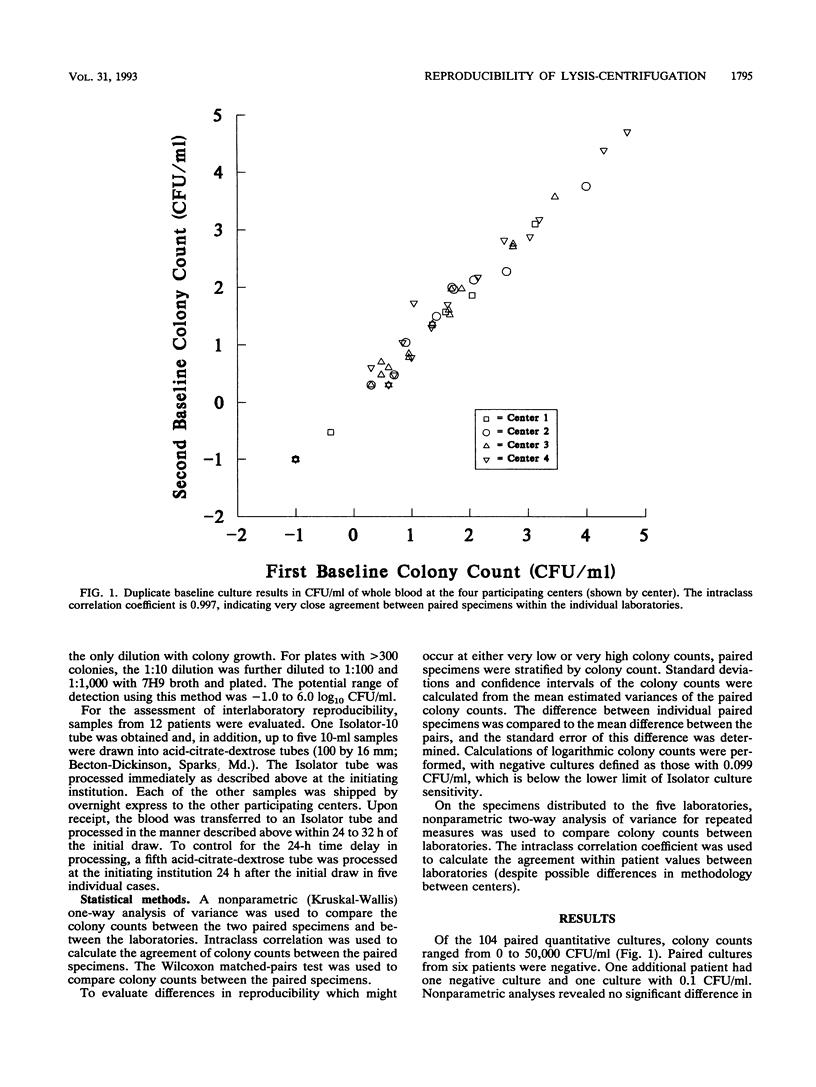
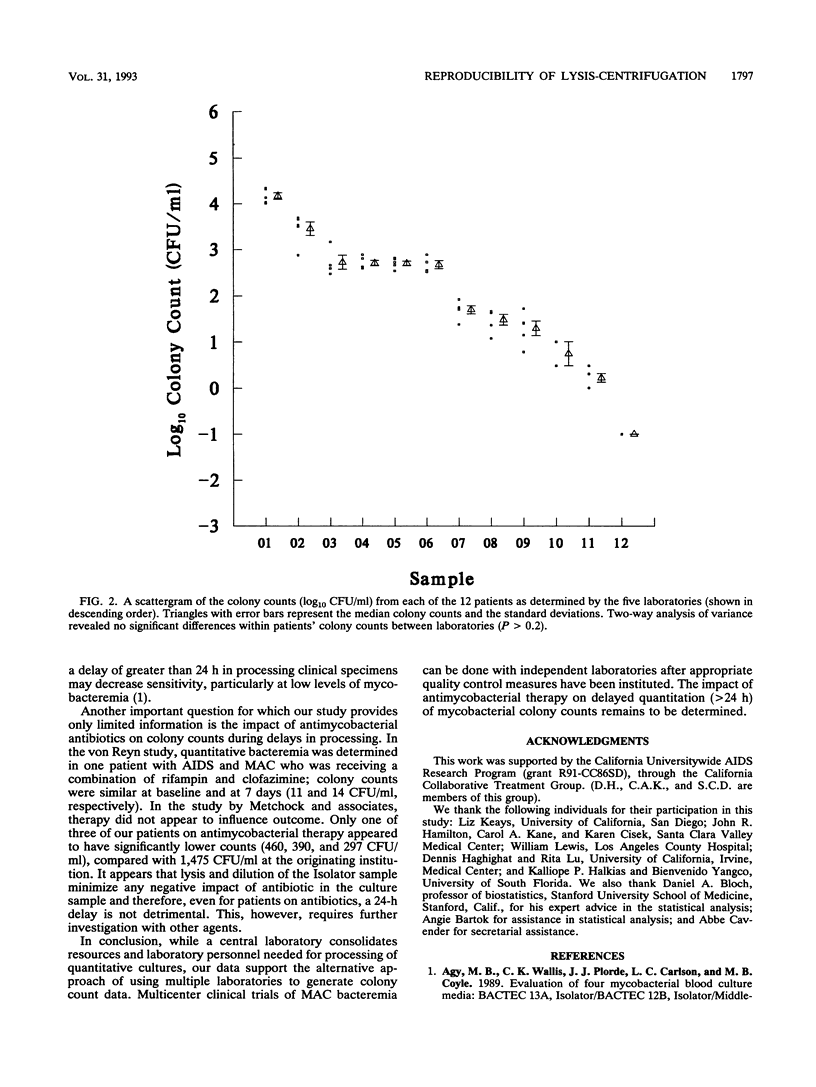
While quantitative mycobacterial blood cultures have been accepted as the standard for evaluating response to various Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) treatment regimens, variability in this methodology has not been evaluated in a rigorous fashion. We thus studied the reproducibility of quantitative MAC cultures by a lysis-centrifugation culture system within and among five institutions. To measure the intralaboratory variation in mycobacterial colony counts, colony counts from duplicate blood specimens collected from 52 AIDS patients with MAC bacteremia were determined. Colony counts ranged from 0 to 50,000 CFU/ml. Nonparametric analyses revealed there was no significant difference in colony counts between the 52 duplicate specimens. The agreement between the intralaboratory paired specimens, as measured by the intraclass correlation coefficient, was 0.997. To measure the interlaboratory variation, multiple 10-ml aliquots from 12 patients were distributed to five institutions and processed within 24 to 32 h by lysis-centrifugation. For the 12 specimens distributed to the five laboratories, two-way analysis of variance for repeated measures revealed no significant difference in an individual patient's colony counts between laboratories (P > 0.2). We conclude that quantitation of mycobacterial colony counts by the lysis-centrifugation system is reproducible within and between institutions. Clinical trials evaluating response to therapeutic interventions for MAC can use multiple laboratories for quantitation of mycobacteremia. Furthermore, a 24- to 32-h delay in processing appeared to have no impact on reproducibility.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiu J., Nussbaum J., Bozzette S., Tilles J. G., Young L. S., Leedom J., Heseltine P. N., McCutchan J. A. Treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in AIDS with amikacin, ethambutol, rifampin, and ciprofloxacin. California Collaborative Treatment Group. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 1;113(5):358–361. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-5-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. B., Sidhu G. S., Lewin S., Levine J. F., Masur H., Simberkoff M. S., Nicholas P., Good R. C., Zolla-Pazner S. B., Pollock A. A. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare: a cause of disseminated life-threatening infection in homosexuals and drug abusers. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):539–546. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr Mycobacterium avium complex infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 9;324(19):1332–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105093241906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper C. A., Meng T. C., Nussbaum J., Chiu J., Feigal D. F., Bartok A. E., Leedom J. M., Tilles J. G., Deresinski S. C., McCutchan J. A. Treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex bacteremia in AIDS with a four-drug oral regimen. Rifampin, ethambutol, clofazimine, and ciprofloxacin. The California Collaborative Treatment Group. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Mar 15;116(6):466–472. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-6-466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Kovacs J. A., Gill V., Roberts G. D., Ames J., Park C. H., Straus S., Lane H. C., Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Bacteremia due to Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):782–785. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B., Edwards F. F., Kiehn T. E., Whimbey E., Donnelly H., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Armstrong D. Continuous high-grade mycobacterium avium-intracellulare bacteremia in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1985 Jan;78(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90458-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Reyn C. F., Hennigan S., Niemczyk S., Jacobs N. J. Effect of delays in processing on the survival of Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare in the isolator blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1211–1214. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1211-1214.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


