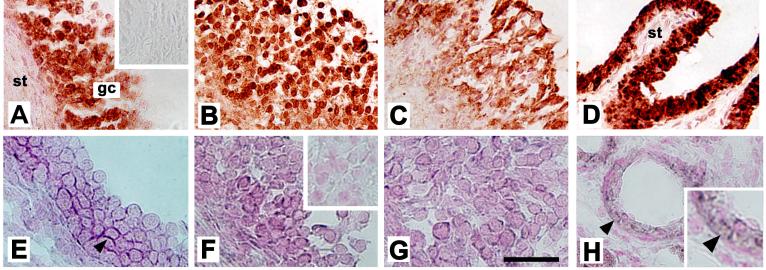
Figure 4.
Localization of AKR1C3 protein as well as PGE-F isomerase (AKR1C1/AKR1C2) mRNA to cells of monkey follicles obtained 0 (A, E), 12 (not shown), 24 (B, F), and 36 (C, G) hours after hCG administration. All follicles are shown with stroma (st) in lower left, granulosa cells (gc) central, and the follicle antrum in the upper right of the image. AKR1C3 was detected by immunocytochemistry (red/brown) in granulosa cells of monkey follicles (A-C); stromal cells were consistently devoid of staining. No staining was observed when the primary antibody was omitted (inset, A). Monkey seminal vesicle showed intense immunostaining in the luminal epithelium, but not stroma (st), which served as a positive control (D). Sections in Panels A-D were not counterstained. AKR1C1/AKR1C2 mRNA was detected by in situ hybridization in granulosa cells of monkey follicles (E-G); staining appears dark purple (arrowhead). Inset in Panel F shows absence of dark purple staining in granulosa cells when sense probe was used; only nuclear counterstain (pink) is visible. Small vessels in the monkey ovarian stroma stained for AKR1C1/AKR1C2 mRNA (Panel H, arrows) and served as a positive control; ovarian stroma located away from follicles did not stain. An enlarged view of image in panel H (inset) shows staining in cells near the vessel lumen. For Panels A-D, bar in Panel G=50 μm. For Panels E-H, bar in Panel G=25 μm. Data shown are representative of n=3-4 animals/group.