Abstract
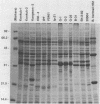
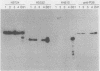
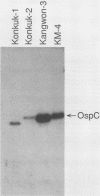
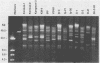
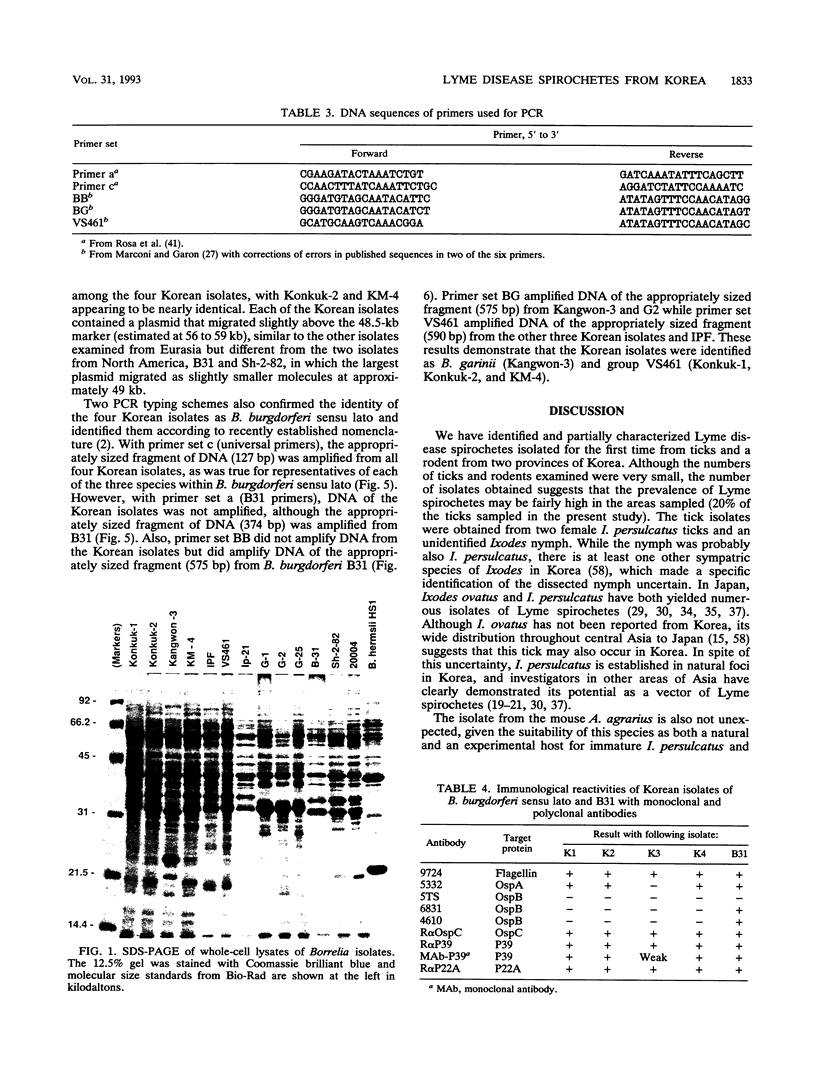
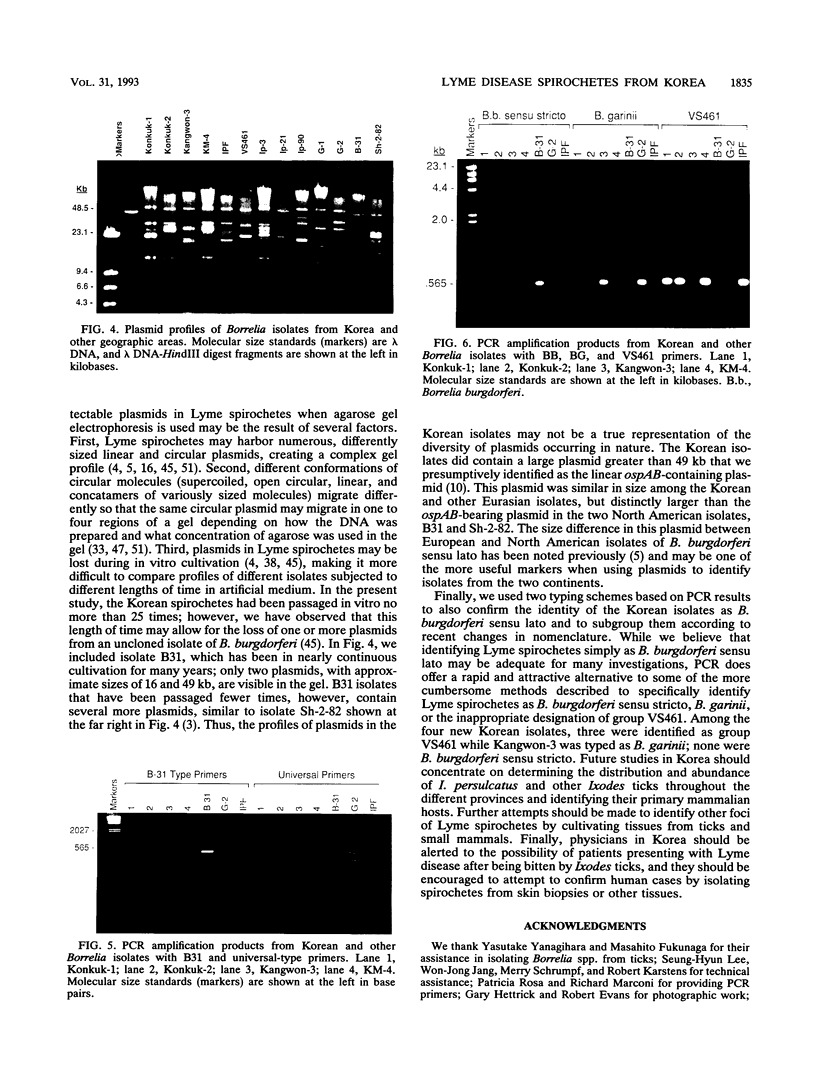
Lyme disease spirochetes, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, were identified and characterized for the first time in Korea. Four isolates, designated Konkuk-1, Konkuk-2, Kangwon-3, and KM-4, were made from midgut suspensions of three Ixodes ticks and heart tissue from one mouse, Apodemus agrarius, collected from Chungbuk and Kangwon provinces. The four Korean isolates and B. burgdorferi sensu lato from other geographic areas and biological sources were compared by using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for protein profiles, Western blot (immunoblot) analysis for reactivities with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, and agarose gel electrophoresis for plasmid profiles. Two typing schemes using polymerase chain reaction identified three of the isolates as members of group VS461 and one, Kangwon-3, as Borrelia garinii. These results demonstrate the potential for human Lyme disease to occur in some provinces of Korea.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam T., Gassmann G. S., Rasiah C., Göbel U. B. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from various sources. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2579–2585. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2579-2585.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranton G., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C., Assous M., Grimont P. A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Schrumpf M. E. Polymorphisms of major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Hill W. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from Ixodes pacificus ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2296–2301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2296-2301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Clonal polymorphisms of outer membrane protein OspB of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2733–2741. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2733-2741.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Jauris S., Lottspeich F., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Soutschek E. Molecular analysis and expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi gene encoding a 22 kDa protein (pC) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogstraal H., Clifford C. M., Saito Y., Keirans J. E. Ixodes (Partipalpiger) ovatus Neumann, subgen. nov.: identity, hosts, ecology, and distribution (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1973 Apr 25;10(2):157–164. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/10.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. A., Kodner C. B., Johnson R. C. DNA analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi NCH-1, the first northcentral U.S. human Lyme disease isolate. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):698–703. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.698-703.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata M., Baba S., Iguchi K., Yamaguti N., Russell H. Lyme disease in Japan and its possible incriminated tick vector, Ixodes persulcatus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):854–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriuchechnikov V. N., Korenberg E. I., Shcherbakov S. V., Kovalevskii Iu V., Levin M. L. Identifikatsiia borrelii, izolirovannykh v SSSR ot kleshchei Ixodes persulcatus Schulze. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1988 Dec;(12):41–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurashige S., Bissett M., Oshiro L. Characterization of a tick isolate of Borrelia burgdorferi that possesses a major low-molecular-weight surface protein. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1362–1366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1362-1366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Pascocello J. A. Antigenic characteristics of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from ixodid ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2344–2349. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2344-2349.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Piesman J., Burgdorfer W. Lyme borreliosis: relation of its causative agent to its vectors and hosts in North America and Europe. Annu Rev Entomol. 1991;36:587–609. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.36.010191.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Lane R. S., Perng G. C., Brown J. A., Johnson R. C. DNA and protein analyses of tick-derived isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi from California. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.700-707.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Development of polymerase chain reaction primer sets for diagnosis of Lyme disease and for species-specific identification of Lyme disease isolates by 16S rRNA signature nucleotide analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2830–2834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2830-2834.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Lubke L., Hauglum W., Garon C. F. Species-specific identification of and distinction between Borrelia burgdorferi genomic groups by using 16S rRNA-directed oligonucleotide probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.628-632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa T., Okada Y., Beppu Y., Oku T., Kawamori F., Yanagihara Y. Immunological properties of Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from the Ixodes ovatus in Shizuoka, Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(10):913–919. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa T., Okada Y., Yanagihara Y., Sato N. Antigenic properties of Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from Ixodes ovatus and Ixodes persulcatus in Hokkaido, Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1568–1573. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1568-1573.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuschka F. R., Fischer P., Musgrave K., Richter D., Spielman A. Hosts on which nymphal Ixodes ricinus most abundantly feed. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jan;44(1):100–107. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.44.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuschka F. R., Lange R., Spielman A., Richter D., Fischer P. Subadult Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae) on rodents in Berlin, West Germany. J Med Entomol. 1990 May;27(3):385–390. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/27.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickel S., Arena V., Jr, Bauer W. Physical properties and gel electrophoresis behavior of R12-derived plasmid DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1465–1482. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Nakao M., Sato N., Mori M. Isolation of Lyme disease spirochetes from an ixodid tick in Hokkaido, Japan. Acta Trop. 1991 Apr;49(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(91)90031-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Nakao M., Uchikawa K., Fujita H. Prevalence of Lyme borreliosis spirochetes in ixodid ticks of Japan, with special reference to a new potential vector, Ixodes ovatus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1992 Mar;29(2):216–220. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/29.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Miyamoto K., Uchikawa K., Fujita H. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from Ixodes persulcatus and Ixodes ovatus ticks in Japan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Oct;47(4):505–511. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Bretz A. G. Polymorphism of outer surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi as a tool for classification. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jun;277(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80867-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T. G. A specific and sensitive assay for the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T., Hogan D. Recombination between genes encoding major outer surface proteins A and B of Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):3031–3040. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Kime K. K., Schrumpf M. E., Coe J. E., Simpson W. J. Antibody response in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) experimentally infected with the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3445–3451. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3445-3451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H., Schwan T. G. Antibody to a 39-kilodalton Borrelia burgdorferi antigen (P39) as a marker for infection in experimentally and naturally inoculated animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.236-243.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Garon C. F., Schwan T. G. Analysis of supercoiled circular plasmids in infectious and non-infectious Borrelia burgdorferi. Microb Pathog. 1990 Feb;8(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Hayes S. F., Schwan T. G. Molecular and immunological analysis of a polymorphic periplasmic protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1940–1948. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1940-1948.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Schwan T. G. Reactivity of human Lyme borreliosis sera with a 39-kilodalton antigen specific to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1329–1337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1329-1337.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Göbel U. B., Graf B., Jauris S., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Zumstein G. An OspA serotyping system for Borrelia burgdorferi based on reactivity with monoclonal antibodies and OspA sequence analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):340–350. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.340-350.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]